Friday☕️

Trending:
- Yesterday, March 20, 2025, a fire broke out at the North Hyde electrical substation in Hayes, West London, near Heathrow Airport. The London Fire Brigade deployed ten fire engines and about 70 firefighters from stations such as Hayes, Heathrow, Hillingdon, and Southall to manage the situation. A 200-meter cordon was set up, leading to the evacuation of 150 people from nearby properties, and residents were advised to keep windows and doors closed due to smoke. The incident caused a power outage affecting over 16,000 homes and businesses in Hayes, Hounslow, and nearby areas, with Scottish and Southern Electricity Networks working to restore power.
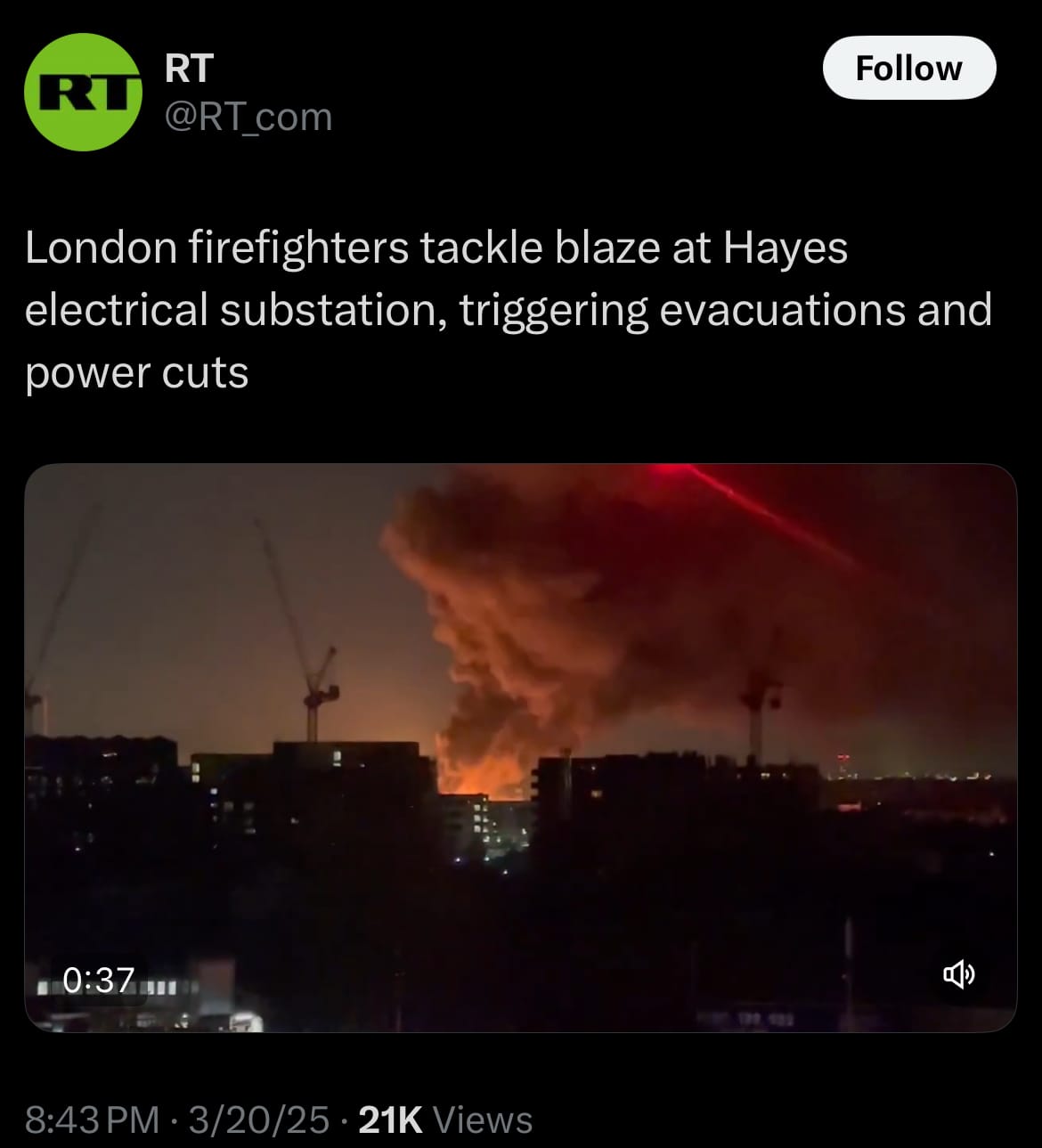
- The fire’s impact extended to Heathrow Airport, located roughly 1.5 to 2 miles south of the substation, resulting in a shutdown of operations until at least 11:59 PM GMT on March 21, 2025. This disruption affected around 1,351 scheduled flights, with at least 120 incoming flights diverted. The exact cause of the fire has not been confirmed, and investigations are ongoing as of March 21. Emergency services, including firefighters, continued their efforts overnight to control the situation, with authorities providing updates as the incident unfolded. The event has drawn attention to the role of the substation in powering critical infrastructure, though no conclusions have been reached about the underlying factors or long-term implications.
Economics & Markets:
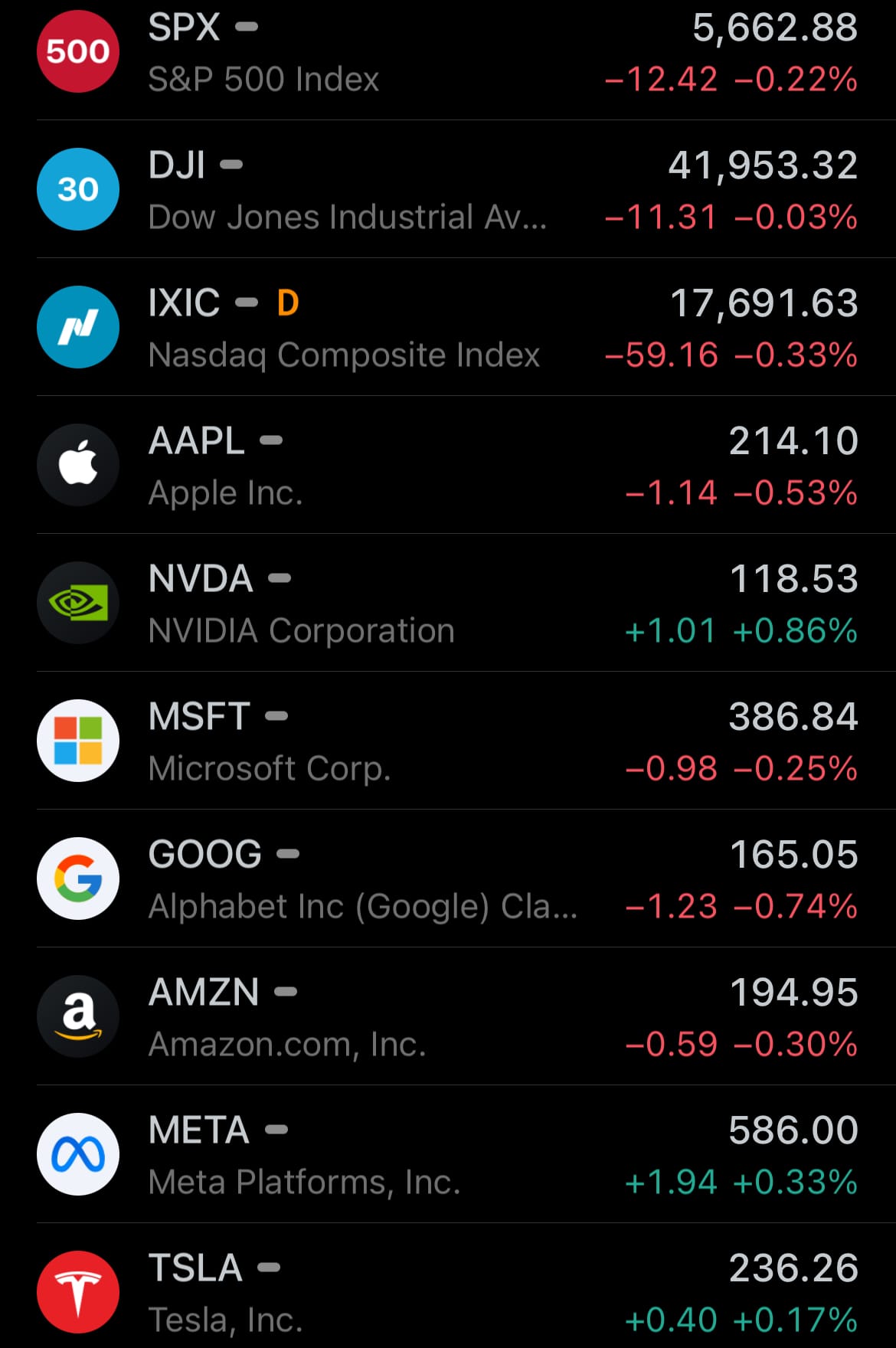
- Yesterday’s U.S. stock market:
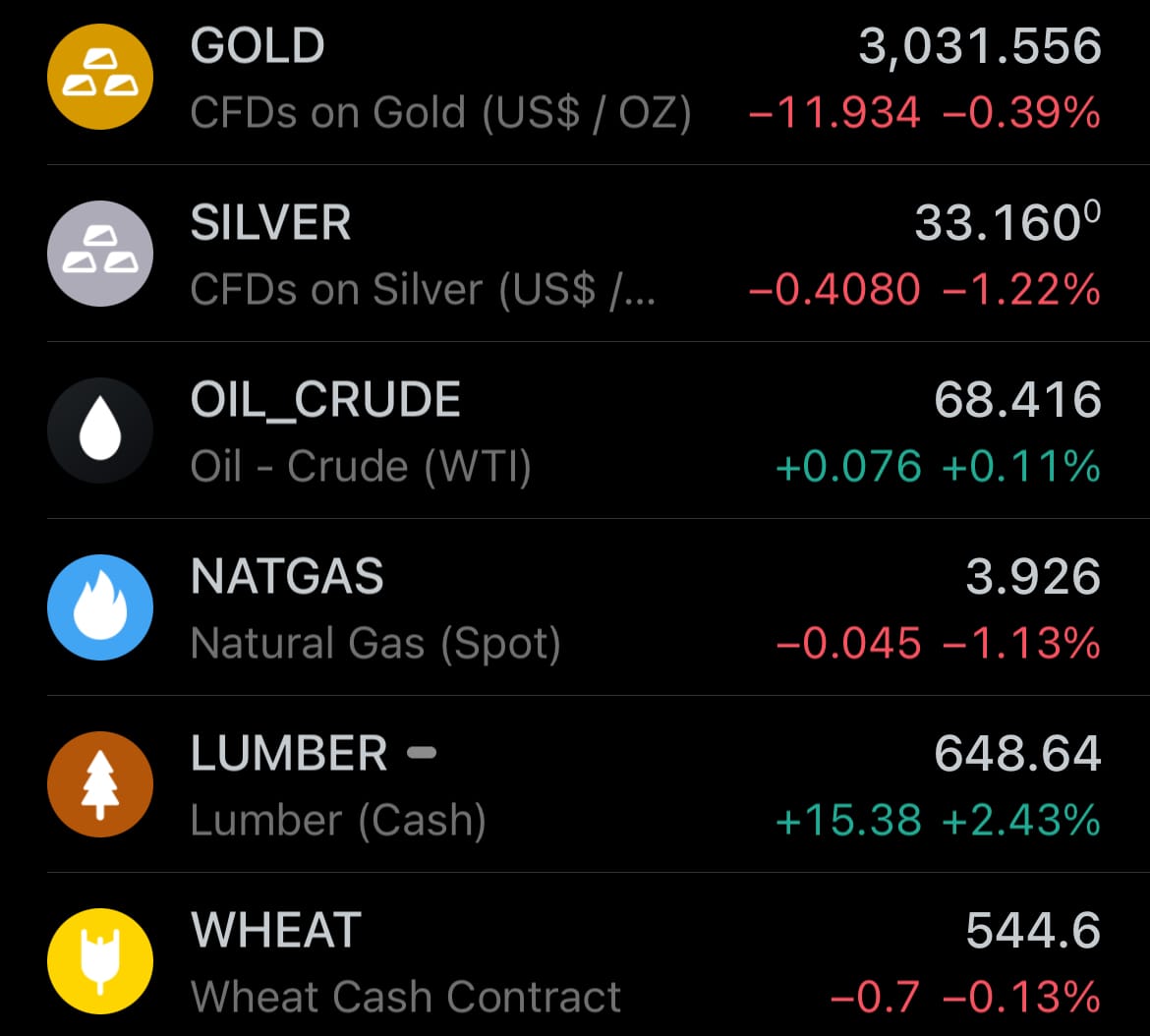
- Yesterday’s commodity market:
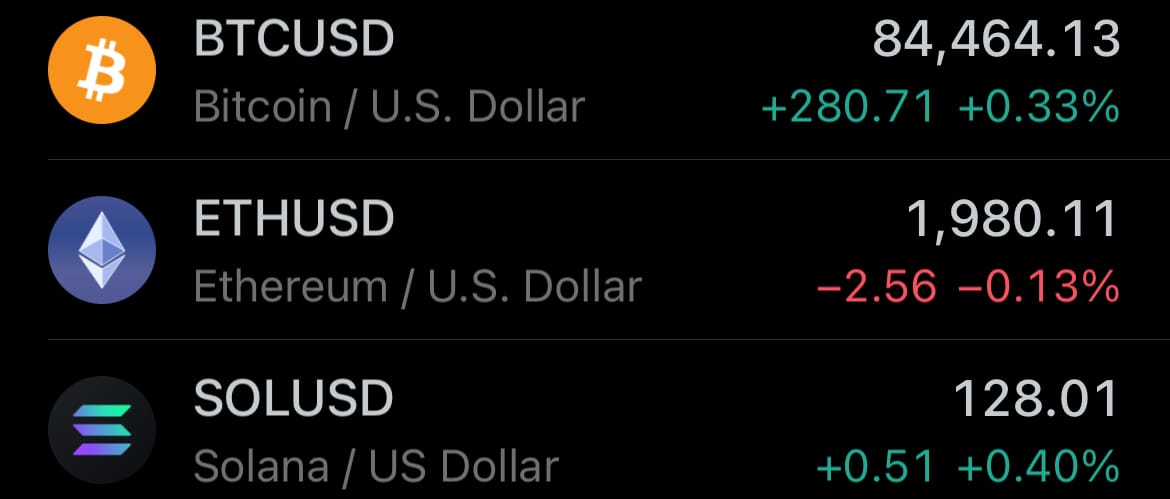
- Yesterday’s crypto market:
Geopolitics & Military Activity:
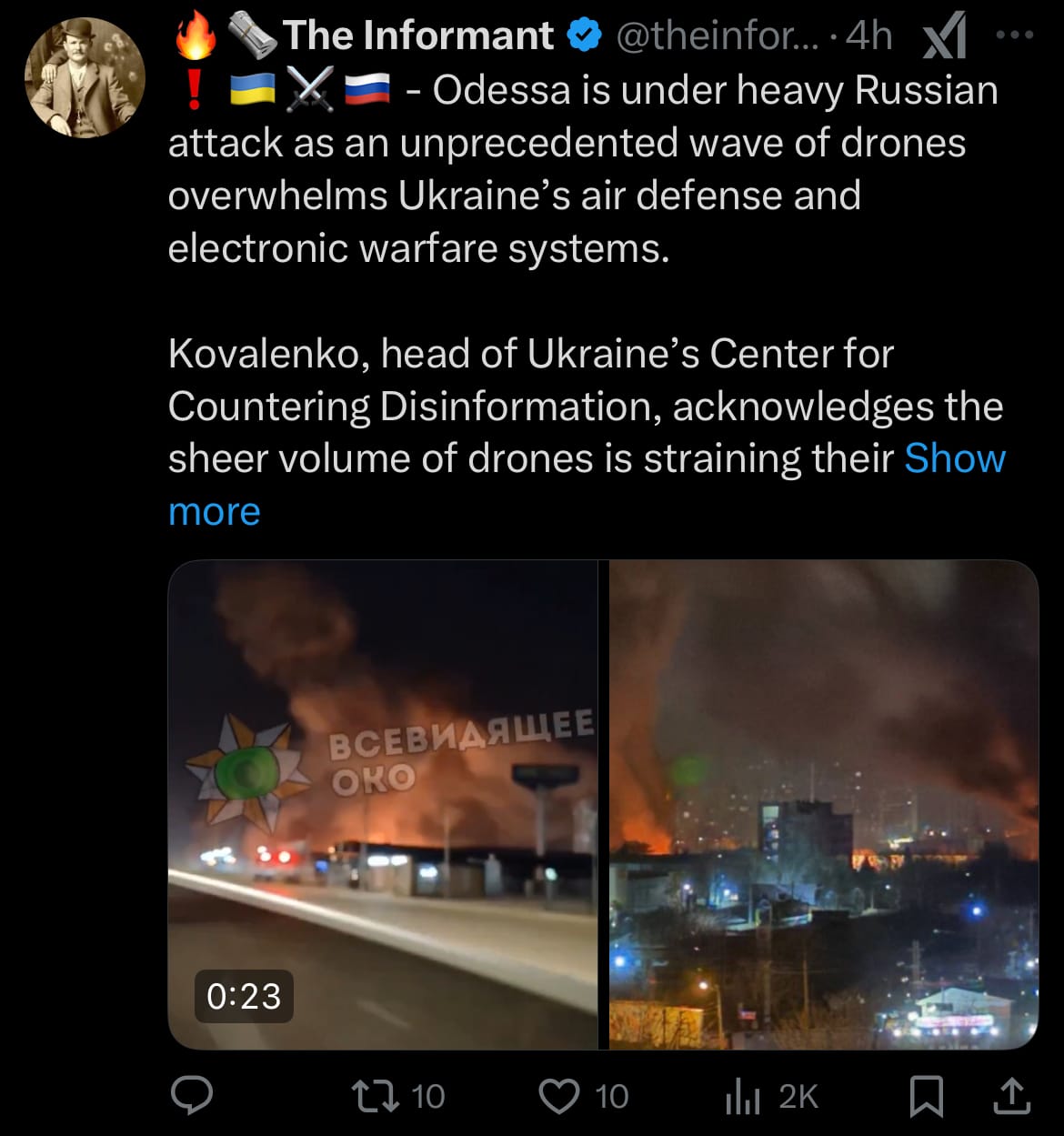
- Over the past 24 hours, spanning March 20 to March 21, 2025, the Russia-Ukraine conflict saw intensified military actions on both sides. In Ukraine, the port city of Odesa faced a significant Russian drone attack starting on March 20. Regional reports indicate that at least 14 drones were launched in two waves between 11 PM and 2 AM local time. Ukrainian air defenses downed 10 drones over Odesa and one over Mykolaiyv. Three districts of Odesa lost power, though the exact extent of infrastructure damage remains unclear. Russian officials have not commented on the specifics of this operation, but the attack aligns with a pattern of targeting Odesa’s port facilities, critical for Ukraine’s maritime trade.
- Concurrently, Ukraine executed a drone strike on Russia’s Engels-2 airbase in Saratov Oblast, roughly 700 kilometers (435 miles) from the front lines, on March 20. The attack, reported around sunrise, triggered a large explosion and fire, with Russian authorities acknowledging damage to an ammunition depot and possibly affecting strategic bombers like the Tu-95 and Tu-160 stationed there. Russia’s Defense Ministry stated that 132 Ukrainian drones were downed across multiple regions, including 54 over Saratov, though local accounts and footage suggest significant impact at Engels, with evacuations ordered and a state of emergency declared in the district.
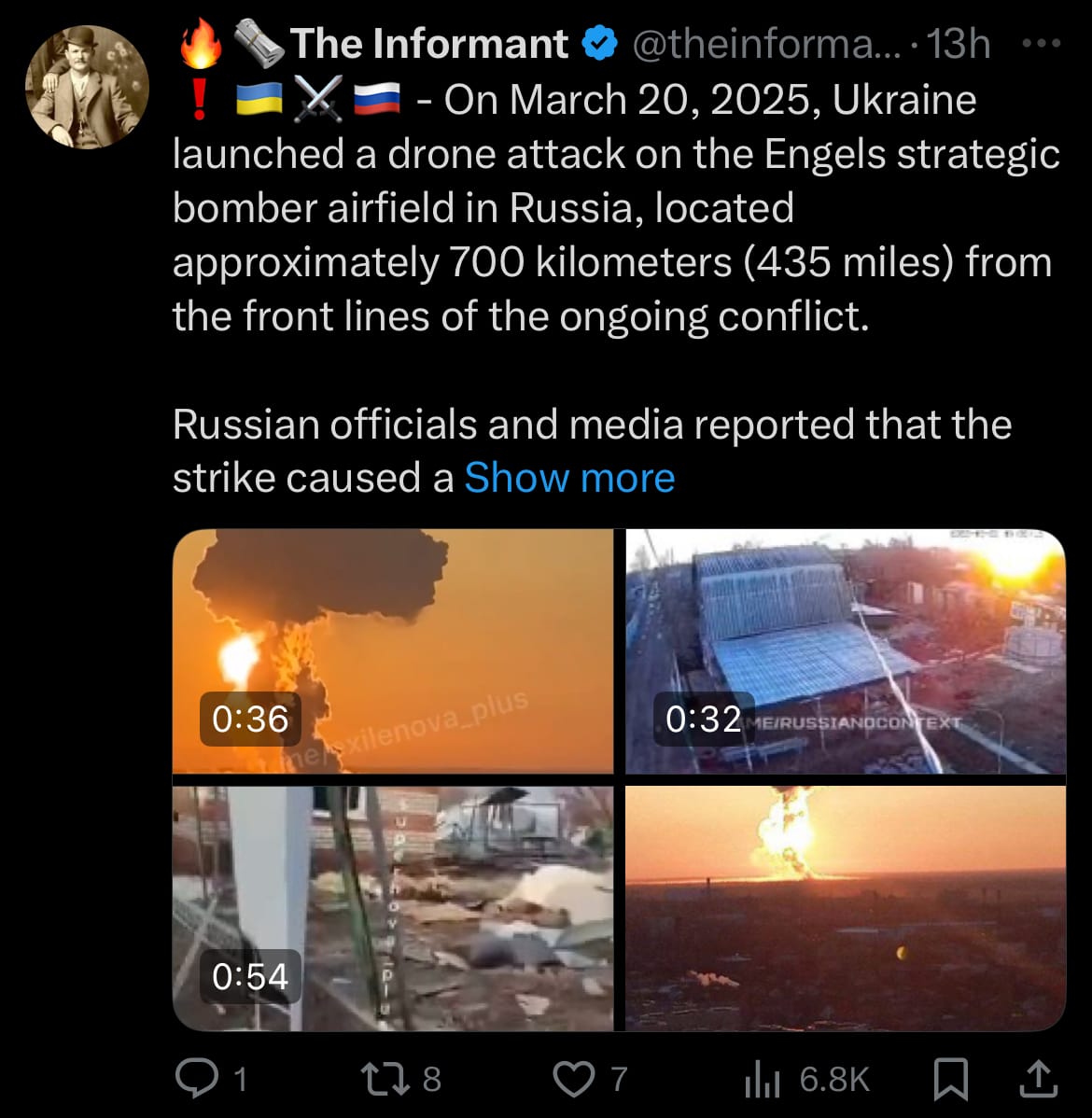
- Ukrainian sources have not detailed the operation’s full scope, but the strike reflects an intent to disrupt Russian air capabilities. Both incidents mark a sharp uptick in the scale and reach of retaliatory strikes within the last day, with each side targeting strategic assets deep in the other’s territory.
Environment & Weather:
Science & Technology:
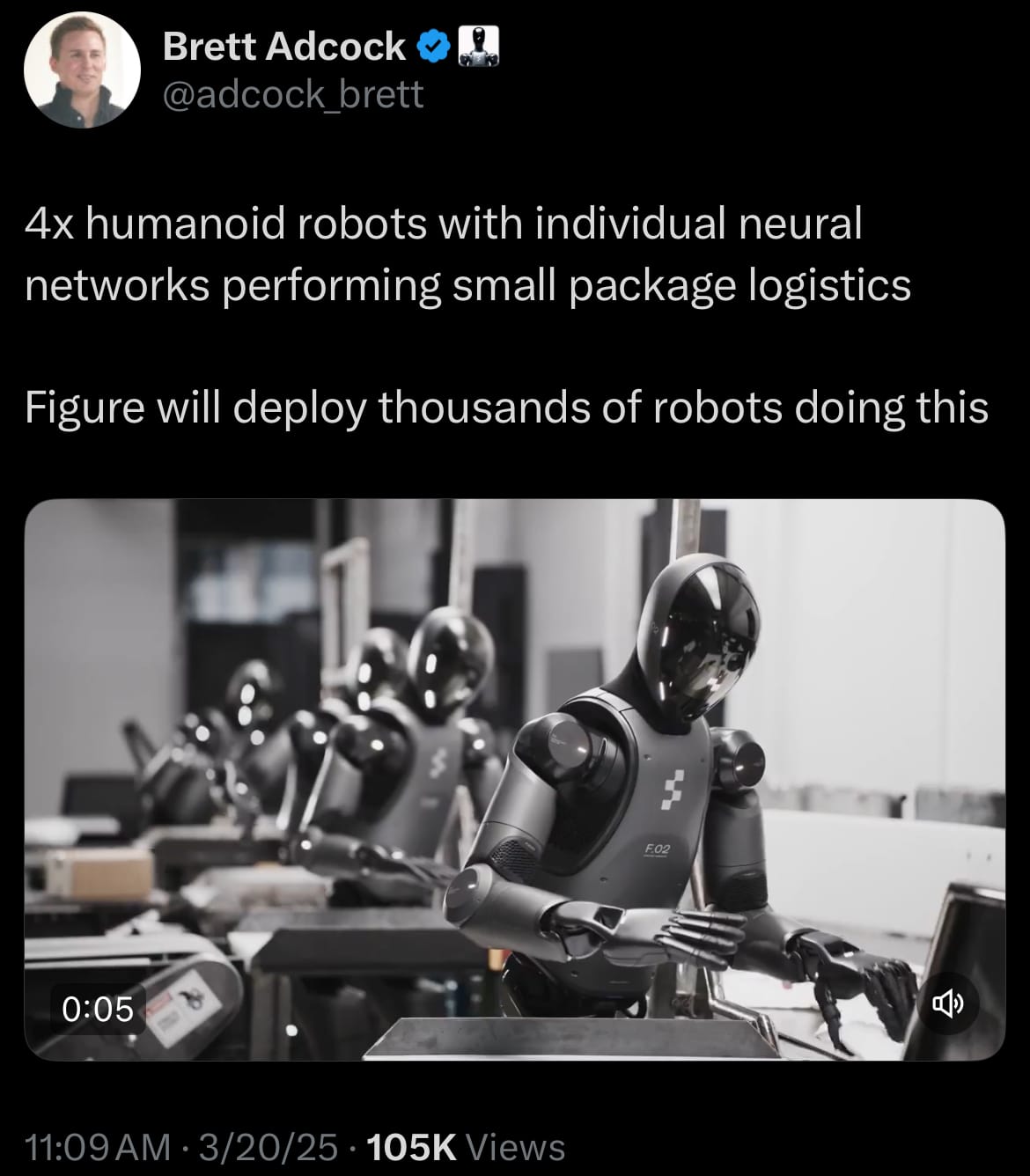
- As of March 21, 2025, Figure is actively developing its Figure 02 humanoid robot, intended for industrial settings. Standing at 5’6” and able to lift up to 44 pounds, Figure 02 uses the company’s Helix AI for speech recognition, visual processing, and task execution without constant human oversight. Figure has launched production at its BotQ facility, aiming for 12,000 units annually, with a long-term goal of reaching 100,000 in four years. Currently, the robot is undergoing trials in controlled environments, such as BMW’s Spartanburg, South Carolina plant, where it handles tasks like pick-and-place and gearbox assembly.
- In the wider landscape, Nvidia stands out as a key enabler, providing foundational technology through platforms like GR00T N1, alongside open-sourcing efforts for AI models and training frameworks. These tools offer companies a robust infrastructure for developing humanoid robots, supporting advancements in perception, dexterity, and autonomy across the industry. Alongside this, a range of firms are exploring the field: Agility Robotics deploys Digit robots in Amazon warehouses, Tesla refines Optimus for factory tasks, Boston Dynamics advances Atlas’s mobility, and Sanctuary AI works on Phoenix for task versatility.
- Other players, such as 1X with its EVE robot and Unitree with the G1, are also emerging, focusing on both industrial and potential consumer applications. This collective progress, marks the early stages of a shift that will see humanoid robots increasingly replace human labor, starting in structured environments like manufacturing and potentially expanding to broader roles, though the timeline and scale depend on overcoming technical and economic challenges.
Statistic:
- Largest public semiconductor companies by market capitalization:
- 🇺🇸 NVIDIA: $2.892T
- 🇹🇼 TSMC: $920.45B
- 🇺🇸 Broadcom: $895.90B
- 🇳🇱 ASML: $289.46B
- 🇰🇷 Samsung: $275.47B
- 🇺🇸 QUALCOMM: $174.69B
- 🇺🇸 AMD: $173.61B
- 🇺🇸 Texas Instruments: $164.40B
- 🇬🇧 Arm Holdings: $125.49B
- 🇺🇸 Applied Materials: $125.42B
- 🇺🇸 Micron Technology: $114.75B
- 🇺🇸 Intel: $103.74B
- 🇺🇸 Analog Devices: $102.12B
- 🇰🇷 SK Hynix: $101.33B
- 🇺🇸 Lam Research: $99.54B
- 🇺🇸 KLA: $95.20B
- 🇹🇼 MediaTek: $71.68B
- 🇺🇸 Synopsys: $69.57B
- 🇯🇵 Tokyo Electron: $69.05B
- 🇺🇸 Marvell Technology: $61.04B
- 🇨🇳 SMIC: $60.69B
- 🇳🇱 NXP Semiconductors: $51.39B
- 🇩🇪 Infineon: $48.20B
- 🇯🇵 Advantest: $40.20B
- 🇺🇸 Monolithic Power Systems: $29.15B
History:
- The origins of artificial intelligence trace back to the 1940s, when Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts modeled the brain’s logic through artificial neurons in 1943, planting the early foundations of neural networks. Alan Turing’s Turing Test, proposed in 1950, conceptualized the idea of machines performing intelligent conversation indistinguishable from humans. By the 1956 Dartmouth Conference, the term “artificial intelligence” was officially coined, sparking decades of research into symbolic AI, logic systems, and early expert systems. Throughout the Cold War era, AI quietly embedded itself into defense and aerospace projects, supporting early missile guidance systems, automated target recognition, and war-game simulations. While public-facing AI went through waves of optimism and “AI winters” due to limited computing power, militaries continued advancing machine reasoning, pattern recognition, and control systems behind the scenes. The 1980s and 1990s saw a resurgence in neural networks and machine learning, driving AI’s integration into manufacturing, predictive maintenance, and military platforms like autonomous drones and smart weaponry. Landmark achievements like IBM’s Deep Blue defeating Garry Kasparov in 1997 demonstrated AI’s growing ability to master complex rule-based systems, while real-world applications in air defense networks and signal intelligence pushed machine-driven decision-making capabilities beyond public awareness.
- By the 2000s, the rise of big data, sensor networks, and NVIDIA’s GPU computing breakthroughs significantly accelerated AI’s potential, particularly in image processing, real-time analytics, and complex simulation environments critical to defense and aerospace. Neural networks matured into deep learning systems, enabling advancements in computer vision and autonomous navigation—essential for the development of drones, missile guidance upgrades, and AI-powered surveillance systems. The 2012 ImageNet breakthrough and the 2017 development of the Transformer model ignited the large language model revolution, but AI’s broader evolution was already deeply entrenched in background systems—optimizing logistics, cyber defense, and battlefield decision-making. By the 2020s, AI has split into two powerful trajectories: public-facing AI models like ChatGPT showcasing human-like reasoning, while autonomous physical systems—fighter jets, drone swarms, missile platforms, and humanoid robotics like Figure AI—combine real-time sensor fusion and AI decision-making. As of 2025, the world stands on the edge of extreme automation, where AI systems no longer merely assist but act independently, executing defense missions, controlling supply chains, and accelerating global operations across every domain from finance to warfare, fulfilling visions seeded over eight decades ago.
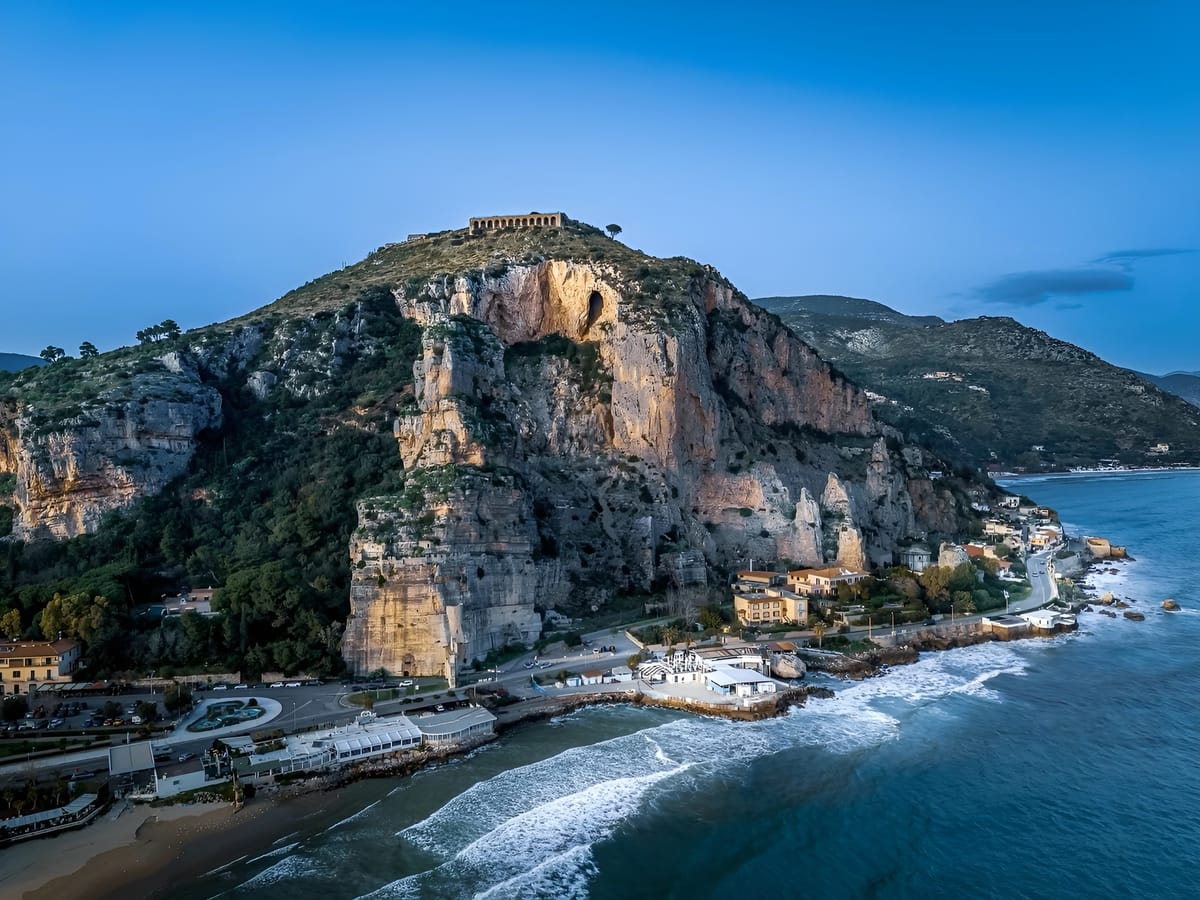
Image of the day:

Thanks for reading!
Earth is complicated, we make it simple.
Click image to view the Earth Intelligence System:


Support/Suggestions Email:
earthintelligence@earthintel.news




