Friday☕️

Economics & Markets:
- Yesterday’s U.S. stock market:

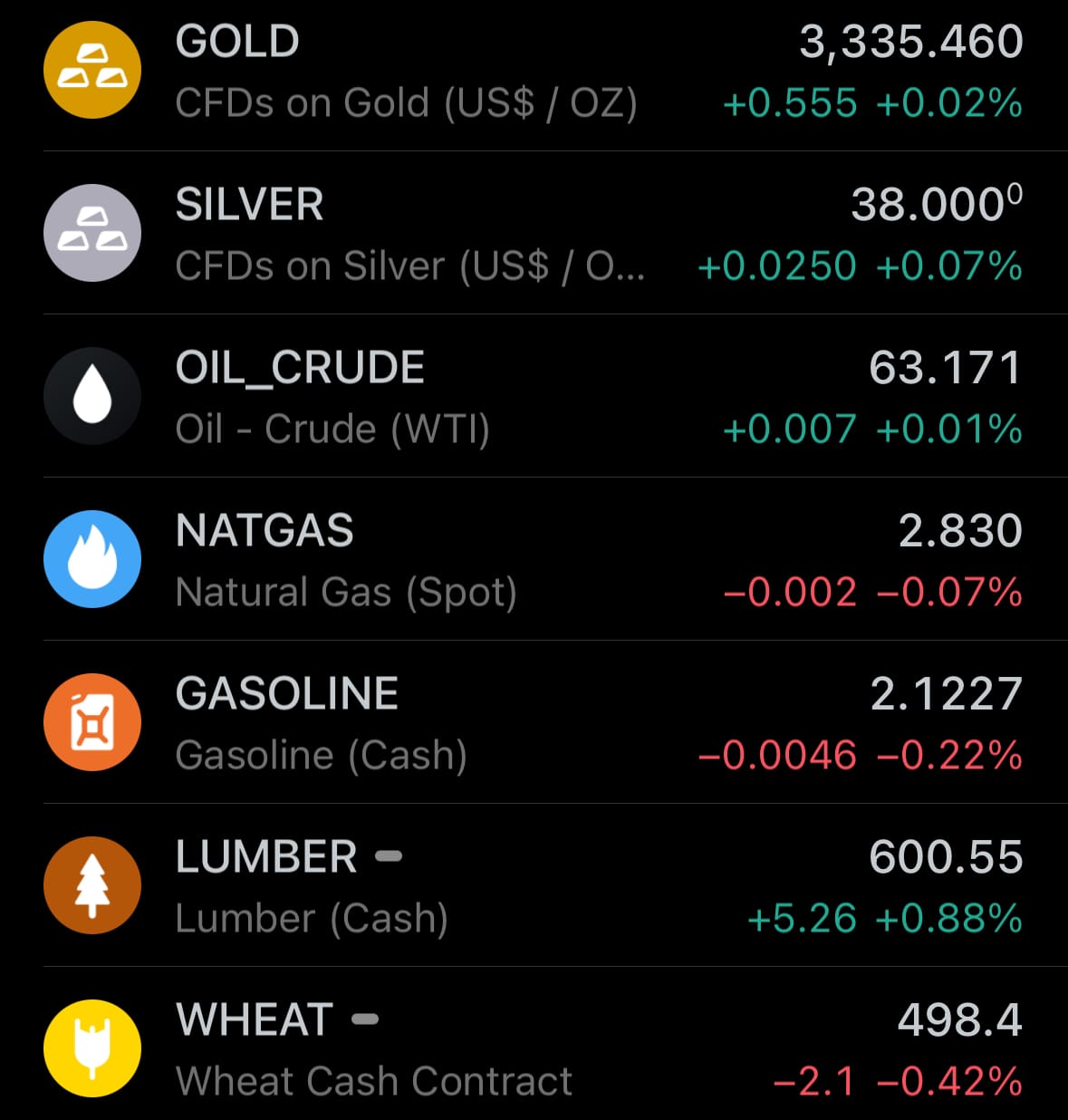
- Yesterday’s commodity market:
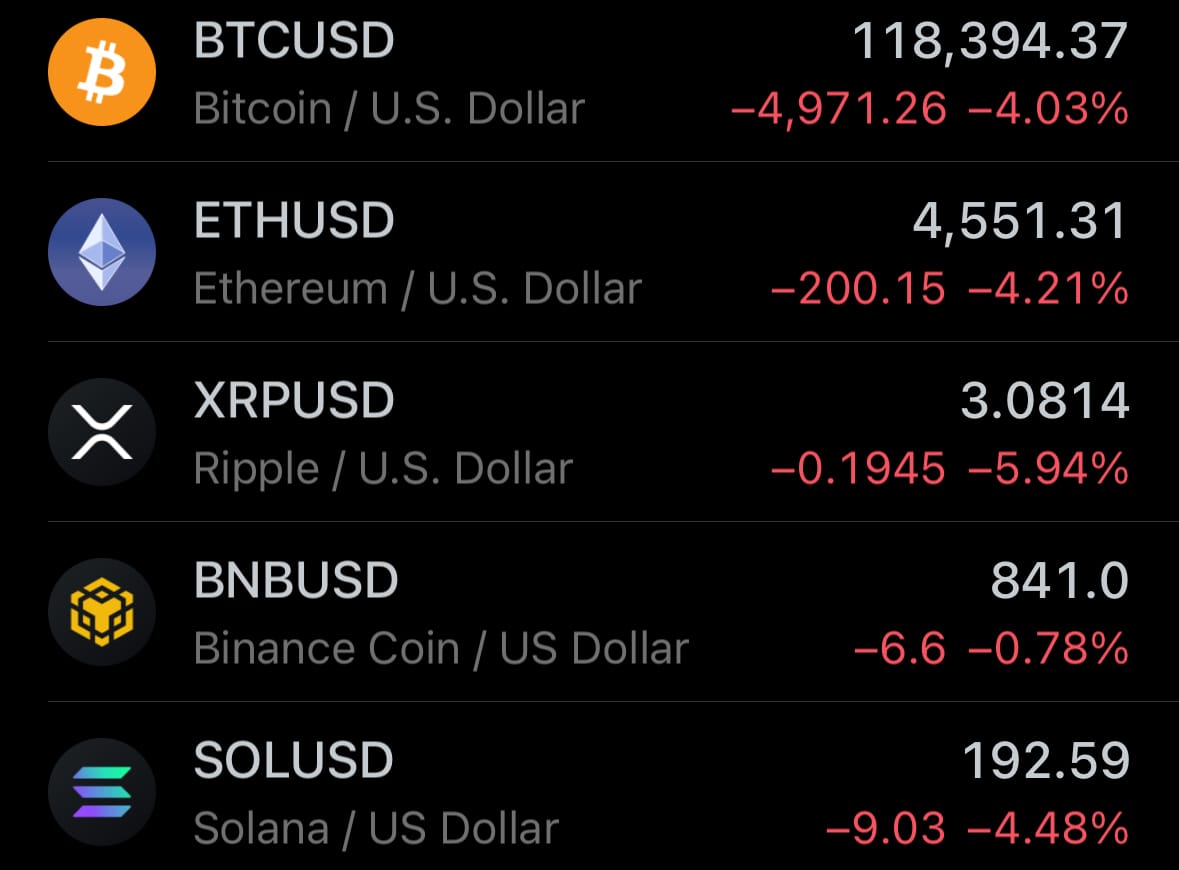
- Yesterday’s crypto market:
Environment & Weather:
- On August 14, 2025, a cloudburst—a sudden, intense rainfall event where clouds release massive amounts of water in a short time, often leading to flash floods in mountainous areas—occurred in Chashoti village, Kishtwar district, Jammu & Kashmir, India, causing flash floods along the Machail Mata pilgrimage route. Reports indicate varying casualty figures, with deaths ranging from 33 to 56, including two CISF personnel; injuries reported between 50 and over 100, many critical; and missing persons estimated from 50 to over 200. The floods affected pilgrims, locals, and infrastructure, washing away houses, bridges, and community facilities in the remote area. Rescue operations involve the Indian Army, NDRF, SDRF, police, and volunteers, using helicopters and ground teams despite difficult terrain and ongoing rain; between 65 and 300 people have been rescued so far, with control rooms set up for coordination.
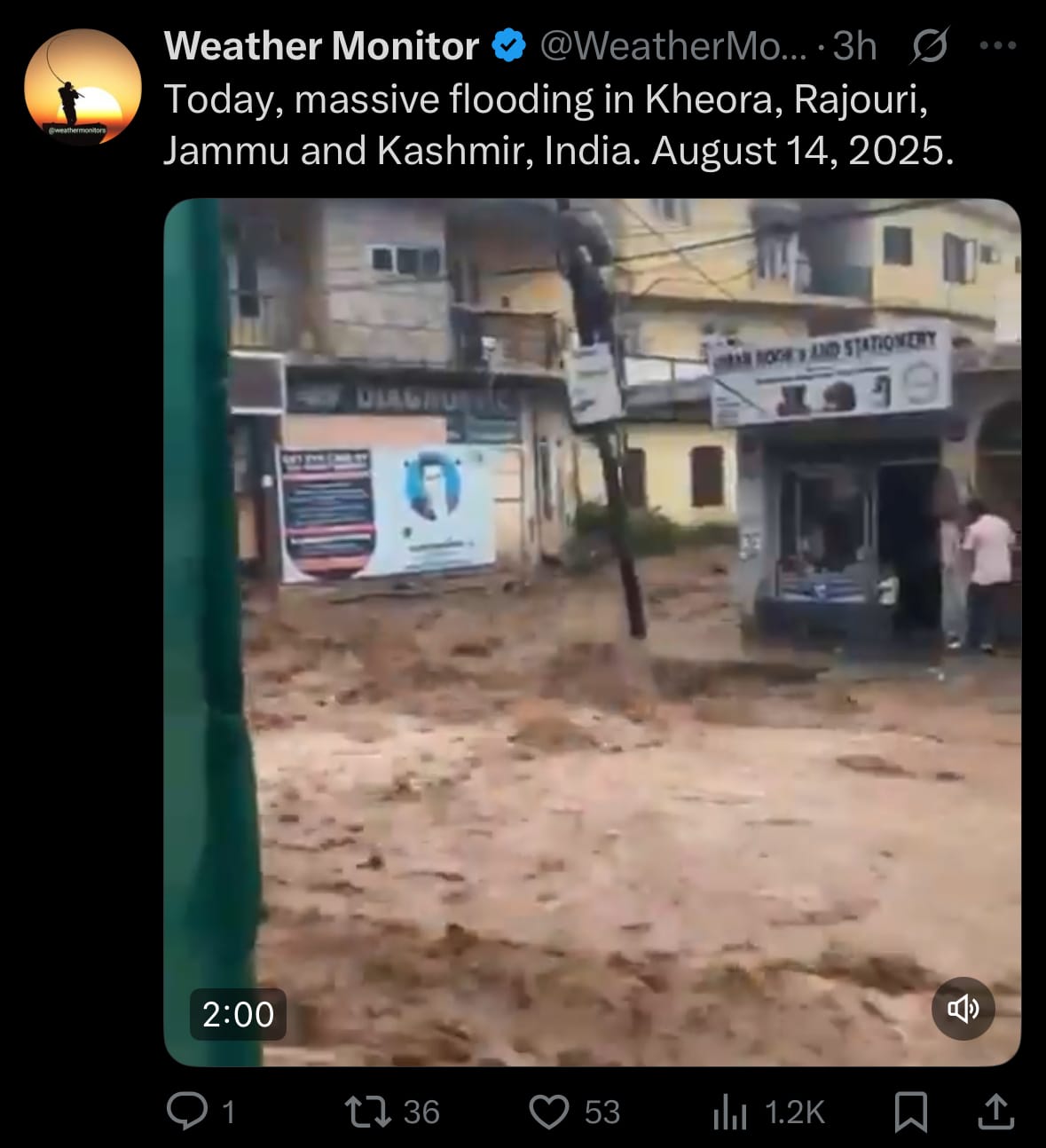
- Authorities, including Chief Minister Omar Abdullah and Union Home Minister Amit Shah, have suspended the pilgrimage and related events while overseeing relief efforts. This incident follows other monsoon-related floods in the Himalayan region, such as recent events in Uttarakhand that also resulted in fatalities. National leaders, including Prime Minister Narendra Modi and President Droupadi Murmu, have expressed condolences and assured support for victims' families and recovery operations. The death toll could increase as searches continue amid debris and damaged areas, with multiple sources providing differing updates on the scale of the disaster.
Cyber:
- On July 25, 2025, the Interlock ransomware group launched a cyberattack on the City of St. Paul, Minnesota, deploying malware that disrupted online payment systems, library services, and recreation center operations; the breach was detected that same day, prompting the city to shut down its IT systems on July 28 to isolate and contain the threat. The city detected the breach and refused to pay the demanded ransom, instead initiating a comprehensive response dubbed Operation Secure St. Paul, with assistance from the FBI, Minnesota National Guard, and local cybersecurity experts to investigate the intrusion and restore systems.
- Interlock subsequently claimed to have exfiltrated and leaked 43GB of data from the Parks and Recreation department's network, including human resources files, financial documents, employee identification, payroll information, W2 forms, trespass notices, and network configurations; the attack was publicly confirmed as ransomware on August 10, with the group identified on August 12 and the data leak occurring that same day. In response, the city mandated a full password reset for all employees and issued public warnings about heightened phishing risks, while emphasizing that critical services like emergency response remained unaffected; as of August 13, recovery efforts continue with systems expected to begin coming back online this week, though officials note the city is "not out of the woods yet" amid ongoing investigations and enhanced security measures.
- This incident highlights the growing threat of ransomware attacks on municipal governments, with Interlock identified as a sophisticated, profit-driven group targeting public sector entities and large organizations. City officials, including Mayor Melvin Carter, have stated that the breach affected only a fraction of the city's vast data holdings—43GB out of 153 terabytes—and no evidence of widespread personal data compromise has been confirmed yet, though investigations continue amid concerns of ongoing risks. The attack prompted the deployment of National Guard resources for enhanced security measures and has drawn national attention to the need for robust cyber defenses in local administrations, with recovery efforts ongoing and no ransom paid to deter future extortion attempts.
Space:
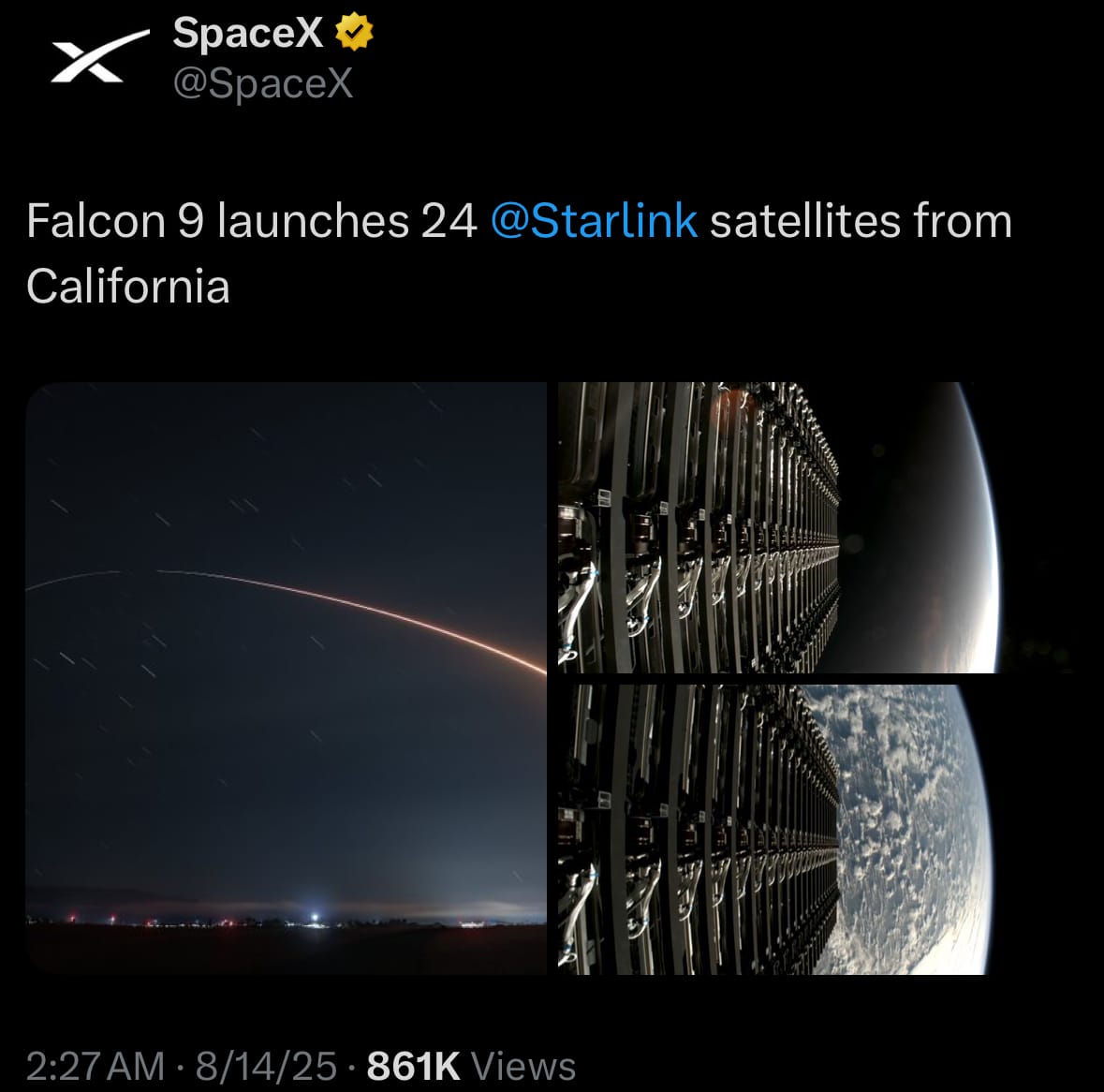
- On August 14, 2025, SpaceX successfully conducted the Starlink Group 17-4 mission, launching a Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California at 1:05 a.m. EDT (10:05 p.m. PDT on August 13 local time). The rocket's ascent was nominal, reaching space in about nine minutes, and the upper stage was on track to deploy 24 Starlink satellites into low-Earth orbit approximately one hour later. The first-stage booster, designated B1093 on its fifth flight—all dedicated to Starlink missions—landed precisely on the drone ship "Of Course I Still Love You" in the Pacific Ocean, marking another milestone in reusable rocket technology. No issues were reported, and SpaceX provided a live broadcast of the event.
- On August 14, 2025, SpaceX successfully conducted the Starlink Group 10-20 mission, launching a Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida at 8:29 a.m. EDT (12:29 UTC). The rocket's ascent was nominal, reaching space in about nine minutes, and the upper stage was on track to deploy 28 Starlink satellites into low-Earth orbit approximately one hour later. The first-stage booster, designated B1085 on its 10th flight—including previous missions such as NASA’s Crew-9, Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Mission 1, and Fram2—landed precisely on the drone ship "Just Read the Instructions" in the Atlantic Ocean, marking another milestone in reusable rocket technology. No issues were reported, and SpaceX provided a live broadcast of the event.
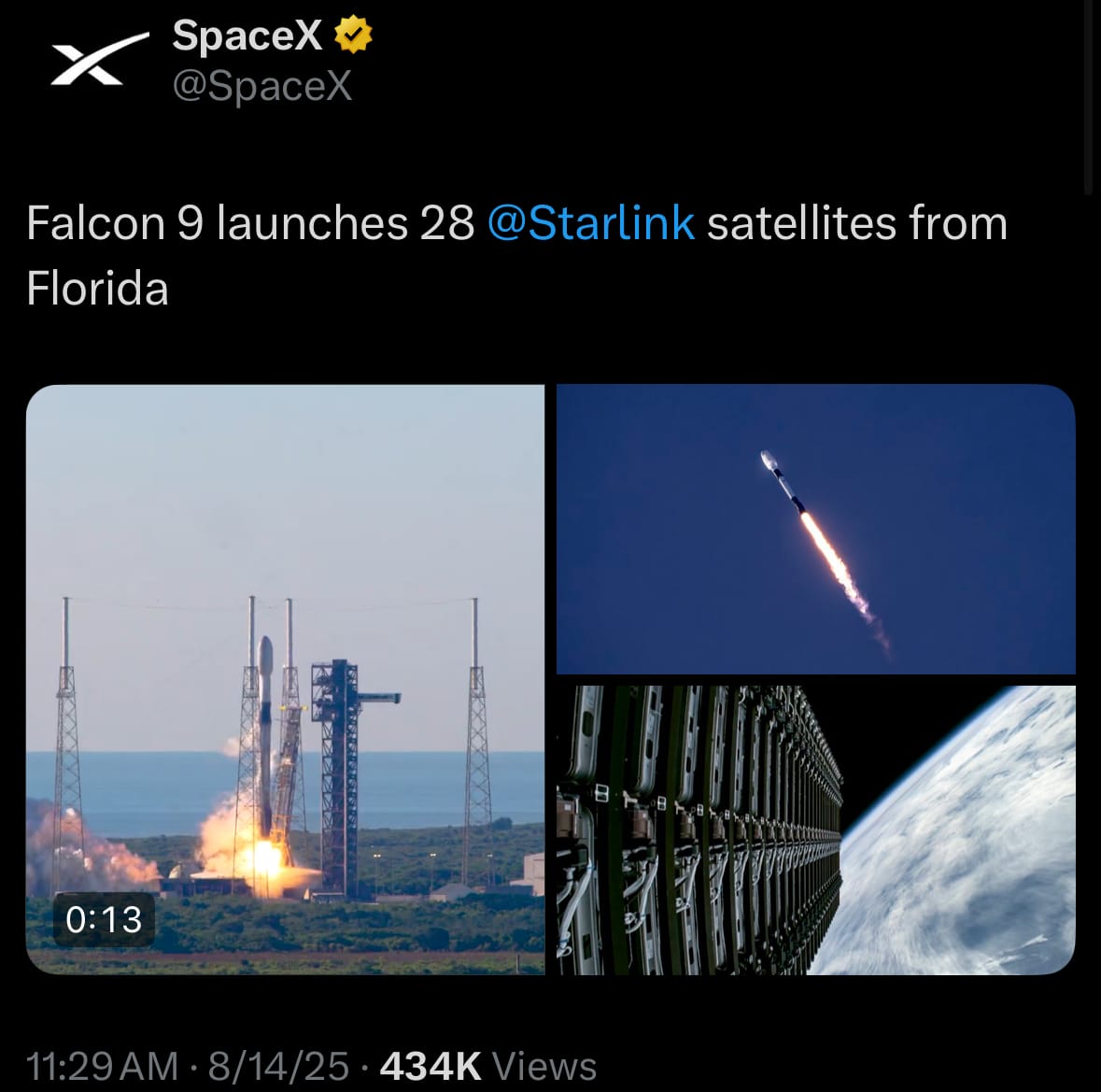
- This launch adds to SpaceX's megaconstellation, now boasting over 8,100 active Starlink satellites out of nearly 9,400 launched since 2018, enhancing global broadband internet coverage, particularly in underserved areas. It represented the 99th Falcon 9 mission of 2025, the 517th overall since 2010, and the 453rd booster reuse, highlighting the company's aggressive pace and efficiency in expanding orbital infrastructure while reducing costs through reusability.
Statistic:
- Largest public semiconductor companies by market capitalization:
- 🇺🇸 NVIDIA: $4.439T
- 🇺🇸 Broadcom: $1.463T
- 🇹🇼 TSMC: $1.249T
- 🇰🇷 Samsung: $339.43B
- 🇳🇱 ASML: $296.94B
- 🇺🇸 AMD: $293.65B
- 🇺🇸 Texas Instruments: $176.10B
- 🇺🇸 QUALCOMM: $170.57B
- 🇺🇸 Applied Materials: $151.06B
- 🇬🇧 Arm Holdings: $148.87B
- 🇺🇸 Micron Technology: $140.21B
- 🇰🇷 SK Hynix: $137.34B
- 🇺🇸 Lam Research: $135.90B
- 🇺🇸 KLA: $126.07B
- 🇺🇸 Analog Devices: $117.21B
- 🇺🇸 Synopsys: $114.05B
- 🇺🇸 Intel: $104.43B
- 🇹🇼 MediaTek: $73.76B
- 🇺🇸 Marvell Technology: $68.14B
- 🇯🇵 Tokyo Electron: $67.19B
- 🇨🇳 SMIC: $64.39B
- 🇳🇱 NXP Semiconductors: $58.37B
- 🇯🇵 Advantest: $55.47B
- 🇩🇪 Infineon: $55.38B
- 🇨🇳 Cambricon Technologies: $55.30B
History:
- Semiconductors are materials—typically silicon or compounds like gallium arsenide—that have electrical conductivity between that of a conductor (like copper) and an insulator (like glass). This unique property allows them to control the flow of electricity in precise ways, making them the foundation of nearly all modern electronic devices. The early understanding of semiconducting behavior began in the 19th century, when scientists discovered that certain materials could conduct electricity under some conditions but not others. This led to inventions like the crystal detector (used in early radios) and eventually to the development of the transistor at Bell Labs in 1947. The transistor replaced fragile vacuum tubes, allowing electrical signals to be amplified and switched more efficiently. This innovation gave rise to the integrated circuit (IC) in the late 1950s, which combined multiple transistors into a single chip. With ICs, engineers could build compact, reliable, and low-power electronic systems—fueling the birth of computers, calculators, and digital communications.
- Throughout the 1970s to the present, semiconductor technology evolved rapidly, driven by Moore’s Law—the observation that the number of transistors on a chip would double approximately every two years. This led to exponential increases in processing power, memory capacity, and energy efficiency. Semiconductors today form the core of central processing units (CPUs), graphics processors (GPUs), memory chips (RAM and flash), sensors, and networking components. They’re used in everything from smartphones and laptops to spacecraft, self-driving cars, AI systems, and military equipment. Advanced manufacturing now involves etching nanoscale features onto silicon wafers using techniques like extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUV). The industry has also diversified into specialized chips like ASICs (application-specific integrated circuits) and SoCs (systems-on-chip). As of today, semiconductors are not only the backbone of the global digital economy but also a strategic asset—central to national security, innovation, and technological leadership across the world.
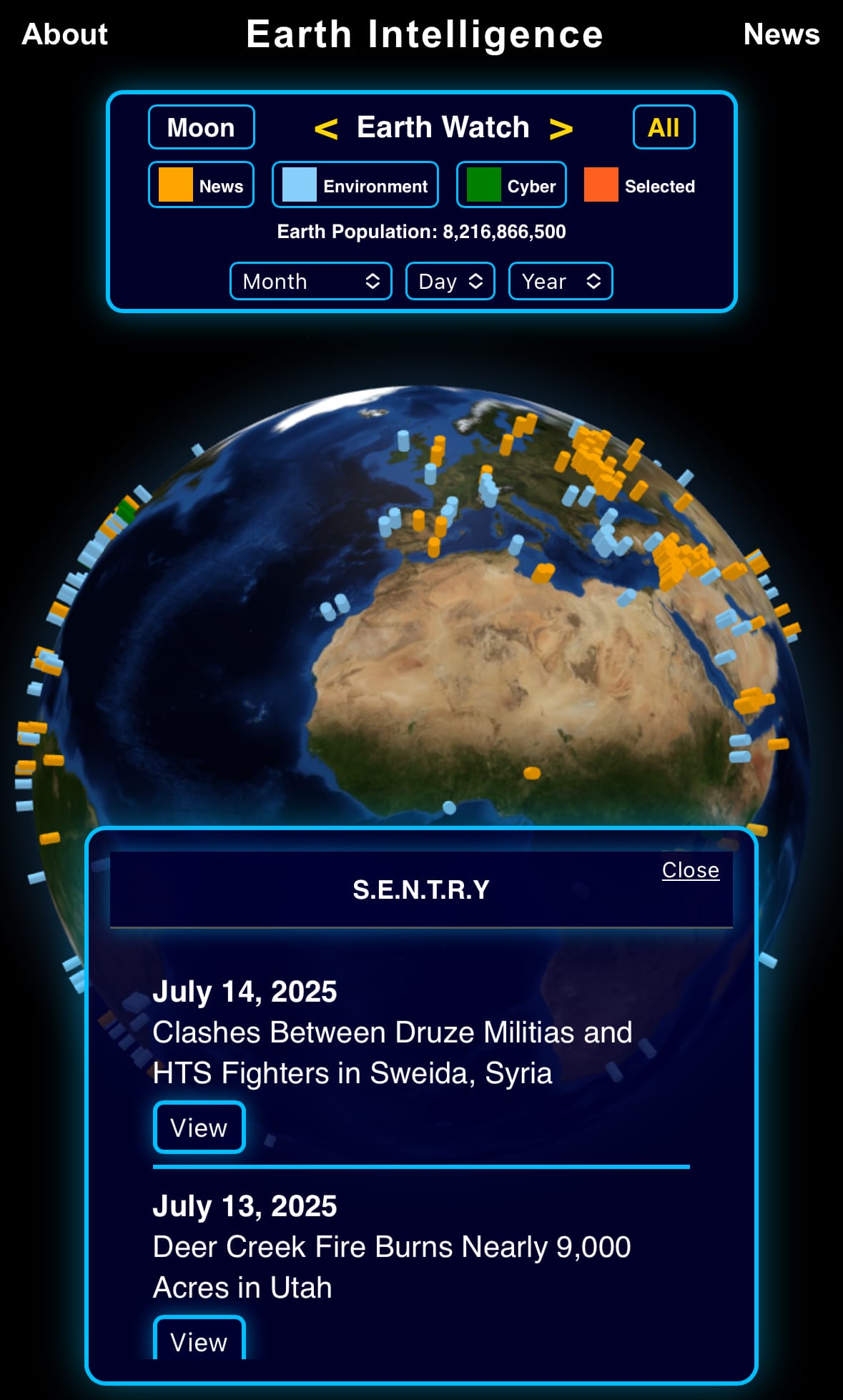
Image of the day:
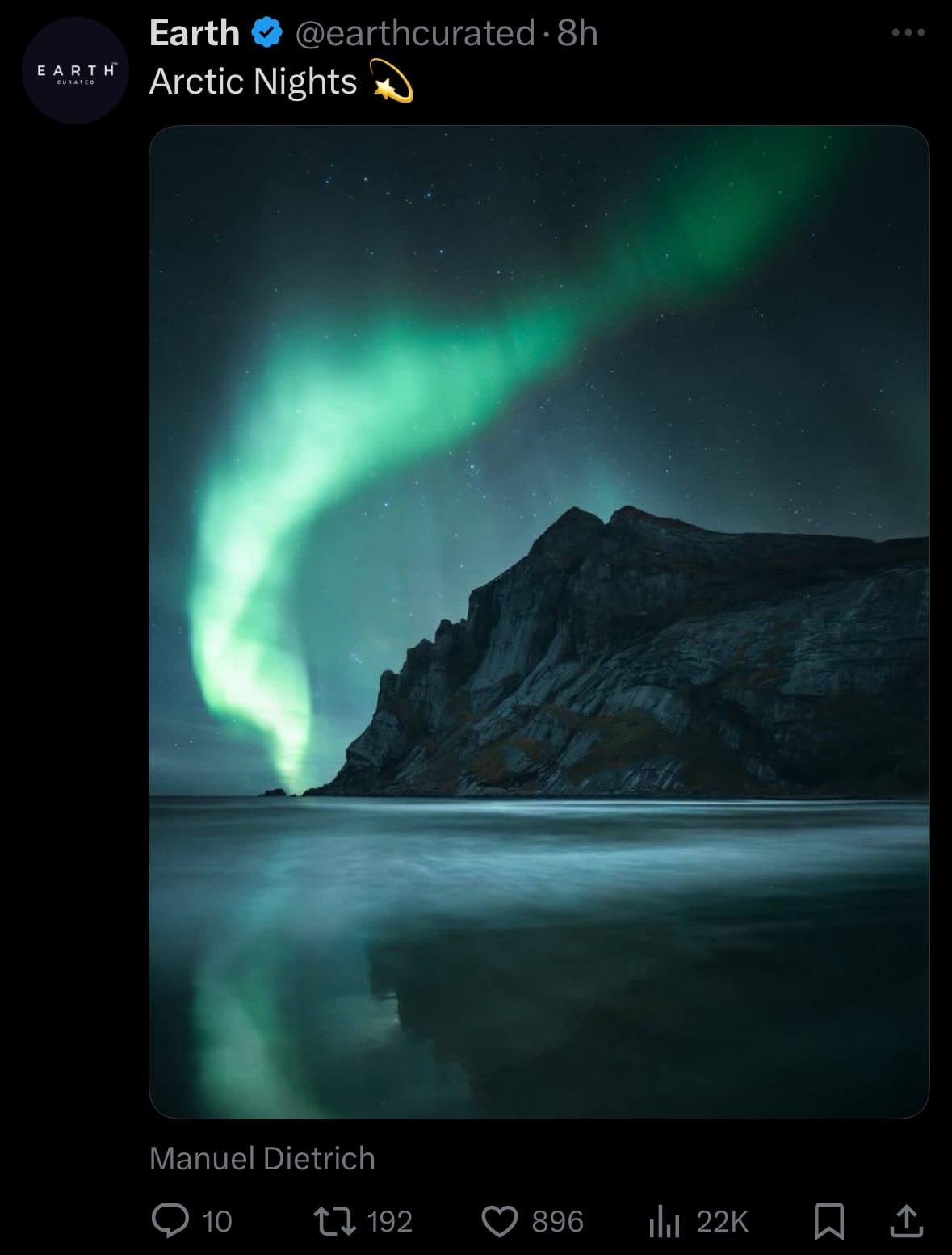

Thanks for reading!
Earth is complicated, we make it simple.
Click image to view the Earth Intelligence System:


Support/Suggestions Email:
earthintelligence@earthintel.news




