Monday☕️

Economics & Markets:
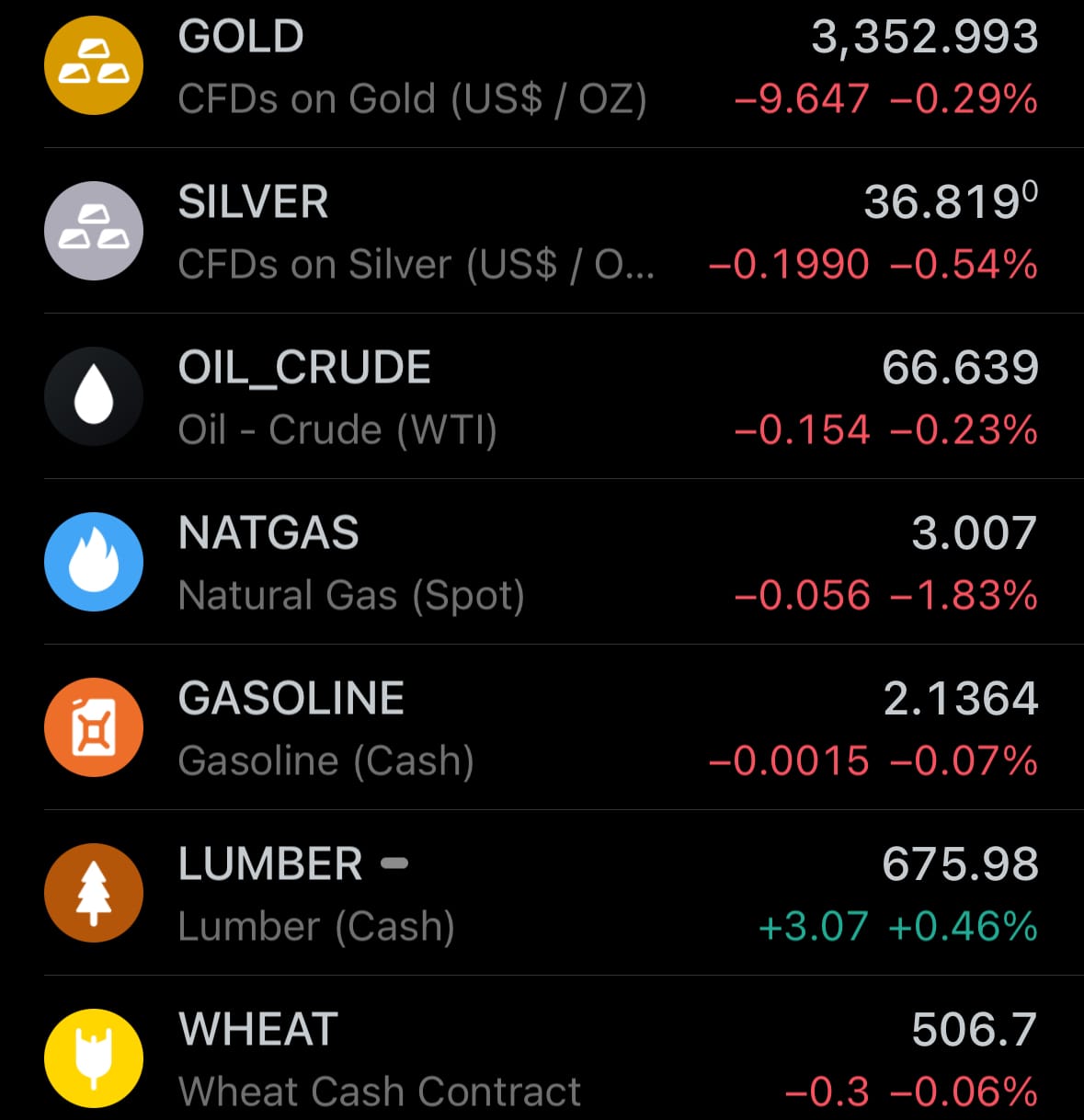
- Yesterday’s commodity market:
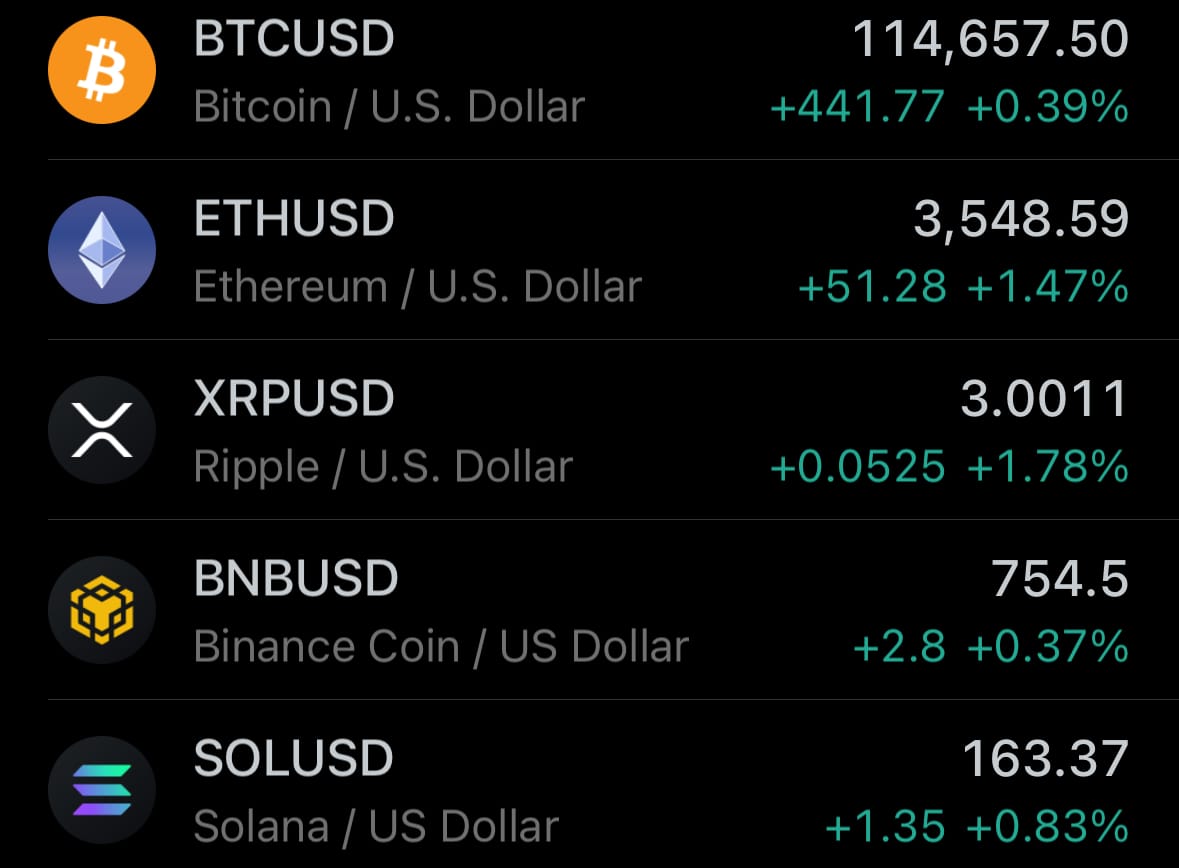
- Yesterday’s crypto market:
Environment & Weather:
- Yesterday, August 3, 2025, heavy rainfall caused severe flooding in the Tuapsinsky district of Russia's Krasnodar Krai. Rivers such as the Shapsukho and Defan overflowed, flooding homes and damaging infrastructure in villages including Lermontovo, Novomikhaylovsky, and Agoy. A waterspout near Agoy worsened the situation, and mudslides blocked the M-4 highway near Dzhubga while causing a bridge collapse in Lermontovo. This isolated more than 300 properties. Videos and reports showed floodwaters carrying away vehicles, including a bus with 25 passengers that entered a river; all passengers were rescued without injury. At least 34 homes were flooded in this Black Sea coastal area, which is known for tourism.
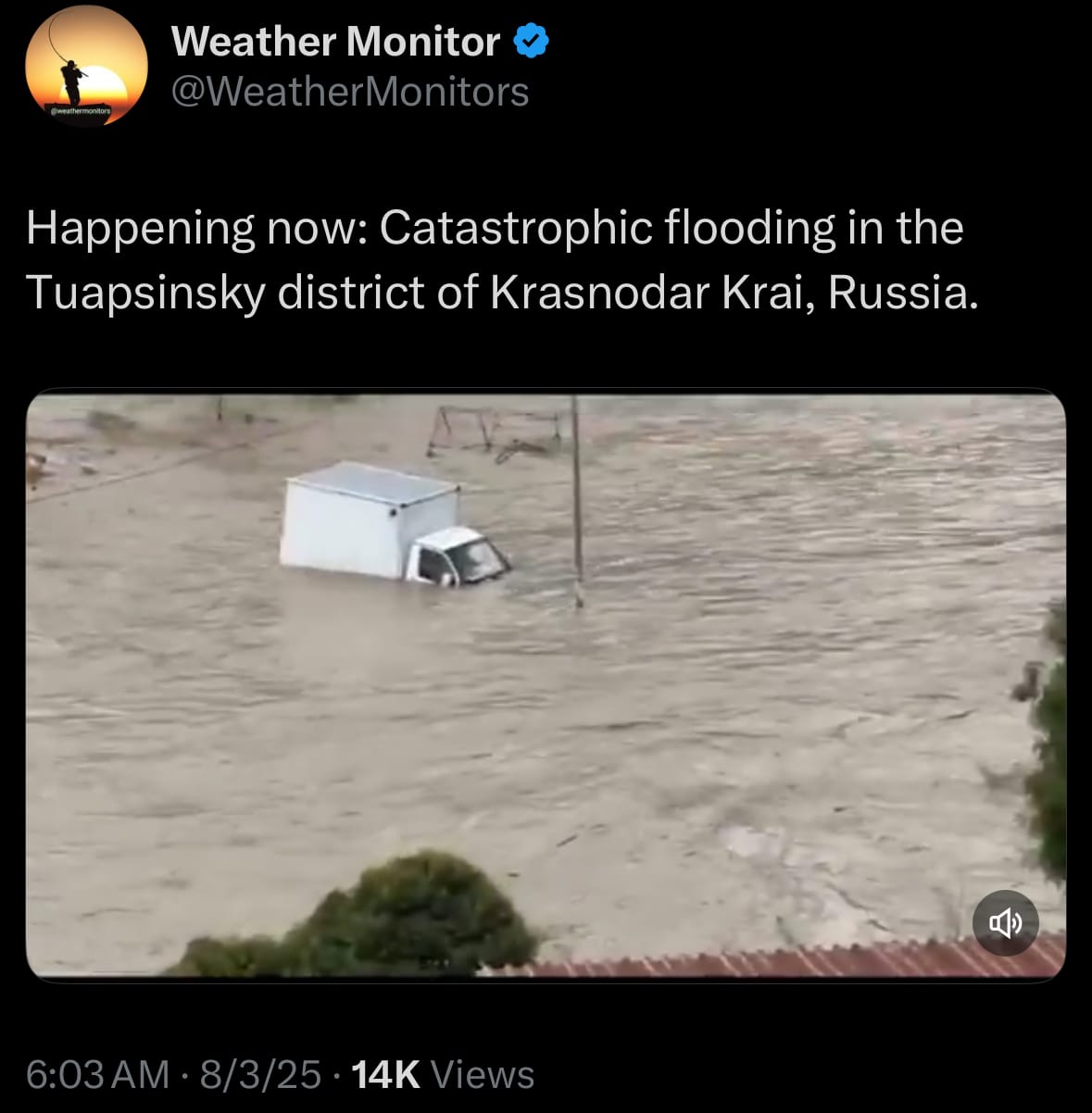
- Authorities declared a state of emergency in the Tuapse district and began evacuating residents and tourists, including children from group tours, to shelters in local schools in Novomikhaylovsky and Dzhubga. Emergency teams are carrying out rescue operations, with two deaths confirmed and several people reported missing. Weather forecasts predict more heavy rain through August 4, which could lead to additional landslides and flooding. Officials are recommending that people move to higher ground.
Space:
- Yesterday, August 3, 2025, Blue Origin launched its New Shepard NS-34 mission from Launch Site One in West Texas, marking the 34th flight of the reusable suborbital vehicle and the 14th crewed one. The launch occurred at about 7:30 AM CDT (12:30 UTC), sending six civilian passengers on an 11-minute suborbital flight that crossed the Kármán line at roughly 100 kilometers altitude. The crew comprised Arvinder Singh Bahal, an 80-year-old India-born real estate investor; Gökhan Erdem, a Turkish businessman; Deborah Martorell, a Puerto Rican meteorologist and journalist; Lionel Pitchford, a British educator; James "J.D." Russell, an American entrepreneur and repeat flyer from NS-28; and Justin Sun, TRON blockchain founder, who won his seat in a 2021 auction for $28 million to benefit space charities. The mission offered brief weightlessness and Earth views, demonstrating reliability for commercial space tourism.
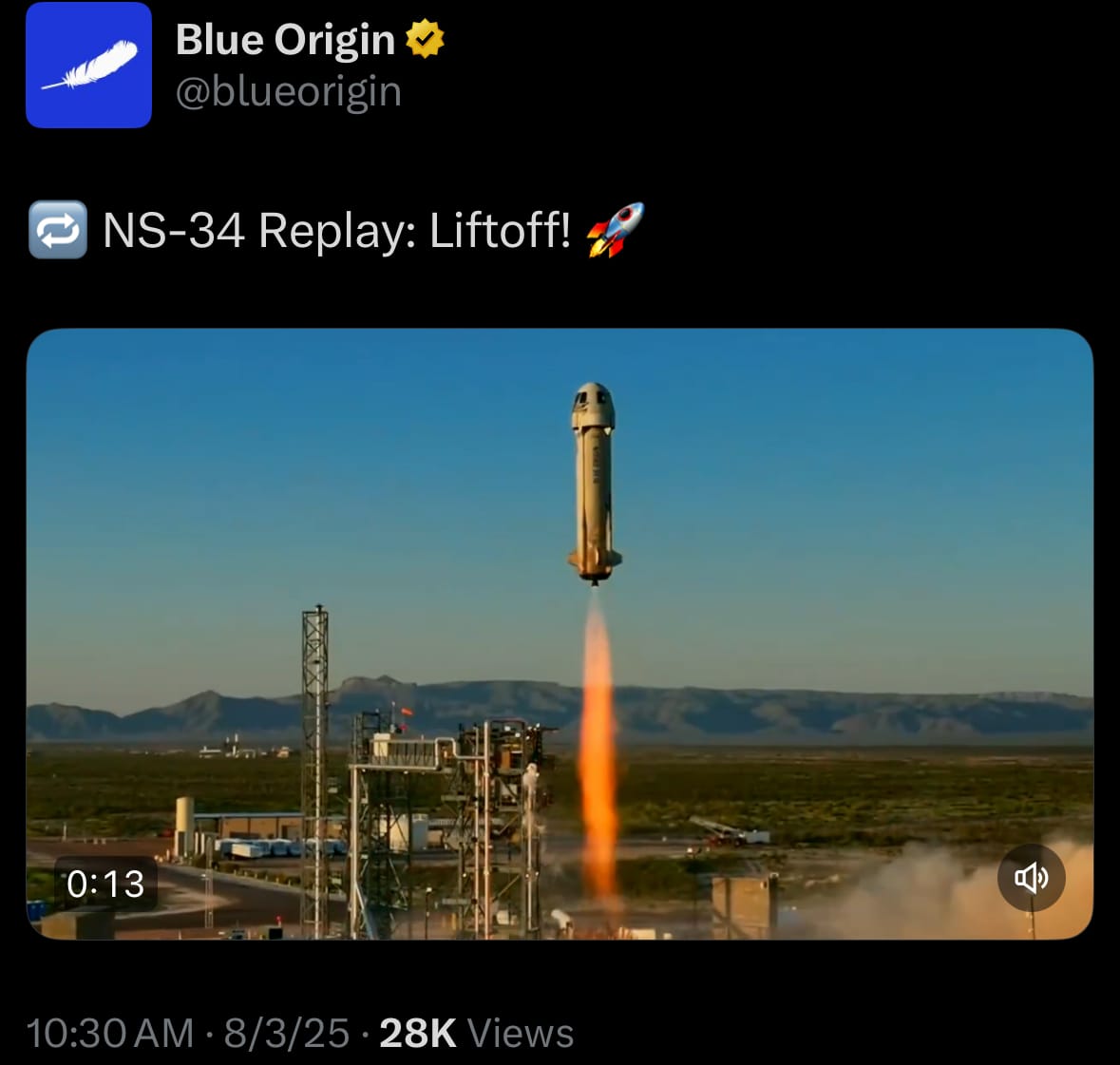
- The flight went smoothly, reaching apogee for microgravity before the capsule parachuted safely back near the launch site. All passengers emerged uninjured, with Sun carrying 1,000 TRON community postcards to symbolize blockchain in space. This brought Blue Origin's total flyers to 75, including repeats, and highlighted crew diversity from fields like journalism and philanthropy, showing growing private space access.
Science & Technology:
- On August 1, 2025, Google DeepMind introduced Gemini 2.5 Deep Think, an AI model focused on improved reasoning and problem-solving. It is accessible to subscribers of Google AI Ultra through the Gemini app. The model uses a multi-agent approach to process ideas in parallel, exploring various reasoning paths before providing outputs. It applies reinforcement learning methods to refine its processes and handles multiple input types, such as text, audio, images, and video, with a context capacity of up to 1 million tokens. This version draws from demonstrations at Google I/O 2025 and incorporates input from initial users to boost precision in demanding tasks.
- Gemini 2.5 Deep Think performed well in evaluations, achieving 87.6% on the LiveCodeBench V6 for coding and 34.8% on Humanity’s Last Exam, showing strengths in math-related areas compared to similar models. A specialized edition earned scores equivalent to a gold medal at the 2025 International Mathematical Olympiad, though it is restricted to select users like researchers and developers. Subscription costs $249.99 per month, with a reduced rate of $124.99 for the first three months for new subscribers, and includes limits on daily usage. The model supports uses in fields like design, planning, and research analysis.
Statistic:
- Largest automakers on Earth by market capitalization:
- 🇺🇸 Tesla: $976.11B
- 🇯🇵 Toyota: $235.47B
- 🇨🇳 Xiaomi: $175.15B
- 🇨🇳 BYD: $133.89B
- 🇮🇹 Ferrari: $88.31B
- 🇩🇪 BMW: $57.65B
- 🇩🇪 Mercedes-Benz: $54.49B
- 🇩🇪 Volkswagen: $52.81B
- 🇺🇸 General Motors: $50.01B
- 🇮🇳 Maruti Suzuki India: $44.34B
- 🇩🇪 Porsche: $44.03B
- 🇮🇳 Mahindra & Mahindra: $43.45B
- 🇯🇵 Honda: $43.12B
- 🇺🇸 Ford: $43.06B
- 🇰🇷 Hyundai: $35.71B
- 🇨🇳 Seres Group: $29.09B
- 🇰🇷 Kia: $28.53B
- 🇨🇳 SAIC Motor: $27.65B
- 🇮🇳 Tata Motors: $27.39B
- 🇳🇱 Stellantis: $26.10B
- 🇨🇳 Li Auto: $25.91B
- 🇨🇳 Geely: $22.68B
- 🇨🇳 Great Wall Motors: $22.56B
- 🇯🇵 Suzuki Motor: $22.04B
- 🇮🇳 Hyundai Motor India: $20.31B
History:
- The history of our understanding of electromagnetic fields has played a central role in shaping how we interact with the physical world. In the 18th century, electricity was seen more as a curiosity than a usable force. That began to shift in the early 1800s when Hans Christian Ørsted discovered the connection between electric currents and magnetic fields. Michael Faraday soon showed that changing magnetic fields could induce electric currents, forming the basis of electromagnetic induction. These discoveries enabled the development of motors and generators. In 1864, James Clerk Maxwell unified these ideas into a set of equations that described electricity, magnetism, and light as aspects of the same phenomenon: electromagnetic waves. This led to the first practical use of wireless communication, as demonstrated by Guglielmo Marconi’s transatlantic radio signal in 1901. By the mid-20th century, electromagnetic theory was applied across infrastructure, computing, medicine, and defense—powering everything from radar systems and X-ray machines to television and early computing hardware. The invention of the transistor in 1947 at Bell Labs was a turning point, enabling the precise manipulation of electrical signals on tiny silicon chips, which would become the foundation of all digital electronics.
- In recent decades, our use of electromagnetic fields has grown more advanced and fine-tuned. Modern wireless communication—from Wi-Fi and Bluetooth to 5G cellular networks—is built on densely packed segments of the radio and microwave spectrum, requiring highly coordinated global standards and infrastructure. In consumer electronics, smartphones contain multiple antennas and sensors that continuously transmit and receive electromagnetic signals across various frequencies. In medicine, MRI systems use pulsed radiofrequency fields combined with magnetic gradients to image soft tissue in high detail, while functional MRI tracks brain activity through subtle electromagnetic shifts. At the quantum scale, technologies such as superconducting qubits and spin-based systems use extremely precise electromagnetic pulses to manipulate and read quantum states, forming the basis for experimental quantum computing platforms developed by companies like IBM, Google, and Rigetti.
- Electromagnetic sensing has also advanced in geophysics, climate monitoring, and surveillance, with satellites and drones using hyperspectral, radar, and thermal imaging to detect information invisible to the human eye. Directed energy systems, like high-powered microwave weapons and laser-based defense platforms, are being actively developed for both military and space applications. Even areas like wireless energy transfer—once limited to short-range charging pads—are expanding into mid-range, beam-steered systems that aim to safely transmit power across greater distances. These examples reflect a continuing trend: as tools improve, we access finer layers of electromagnetic behavior. This progression invites open questions about whether other fields—gravitational, quantum vacuum, or entirely unknown interactions—might one day be understood and used with similar precision, just as electromagnetic waves moved from theory to everyday utility over the past two centuries.
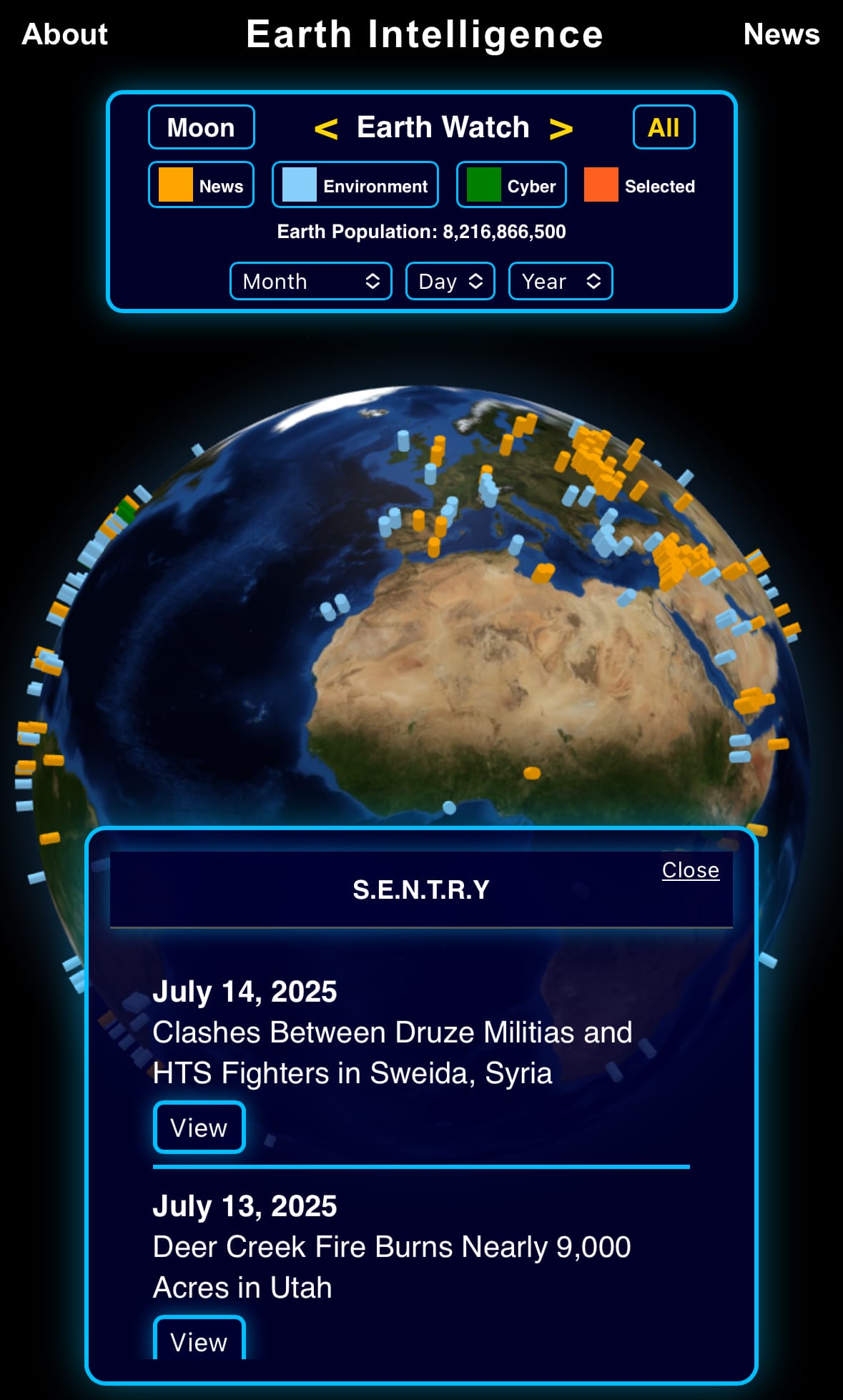
Image of the day:

Thanks for reading!
Earth is complicated, we make it simple.
Click image to view the Earth Intelligence System:


Support/Suggestions Email:
earthintelligence@earthintel.news




