Monday☕️

Trending:
- As of September 29, 2025, the status of the TikTok situation in the U.S. involves a framework agreement approved by President Trump through an executive order signed on September 25, which deems the proposed divestiture of TikTok's U.S. operations compliant with the 2024 Protecting Americans from Foreign Adversary Controlled Applications Act, thereby avoiding a full nationwide ban that began in January but has faced multiple delays. The deal, estimated at around $14 billion, would see U.S. investors like Oracle and Dell acquiring about 45% ownership, with ByteDance holding less than 20%, and Oracle managing data security, algorithm oversight, and daily operations to mitigate national security risks. This order extends the ban's enforcement delay by 120 days to December 16, 2025, providing time for final approvals from U.S. and Chinese regulators.
- This arrangement stems from recent talks between Trump and Chinese President Xi Jinping, including a phone call noting progress on trade and TikTok matters, amid persistent worries about data privacy and possible foreign influence. The U.S. Supreme Court upheld the law in January 2025, dismissing TikTok's free speech challenge, and the deal seeks to maintain the platform for its 170 million American users under domestic control. Some lawmakers question if it sufficiently eliminates external sway, while others see it as a practical compromise to keep the app running without shutdown. Finalization may extend into 2026, depending on the transfer process, reflecting U.S.-China relations without altering current user access.
Economics & Markets:
- Today’s U.S. stock market:

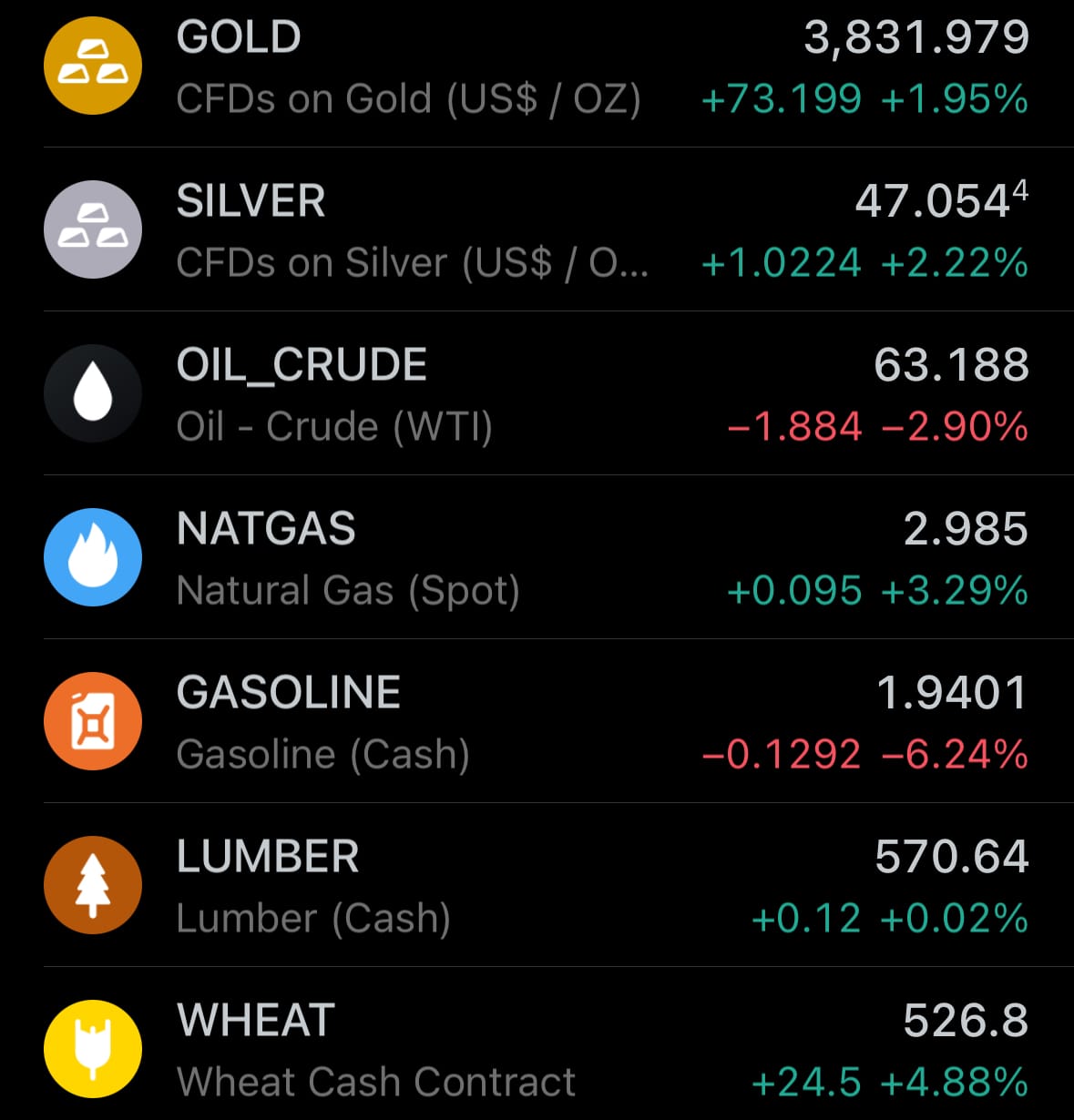
- Yesterday’s commodity market:
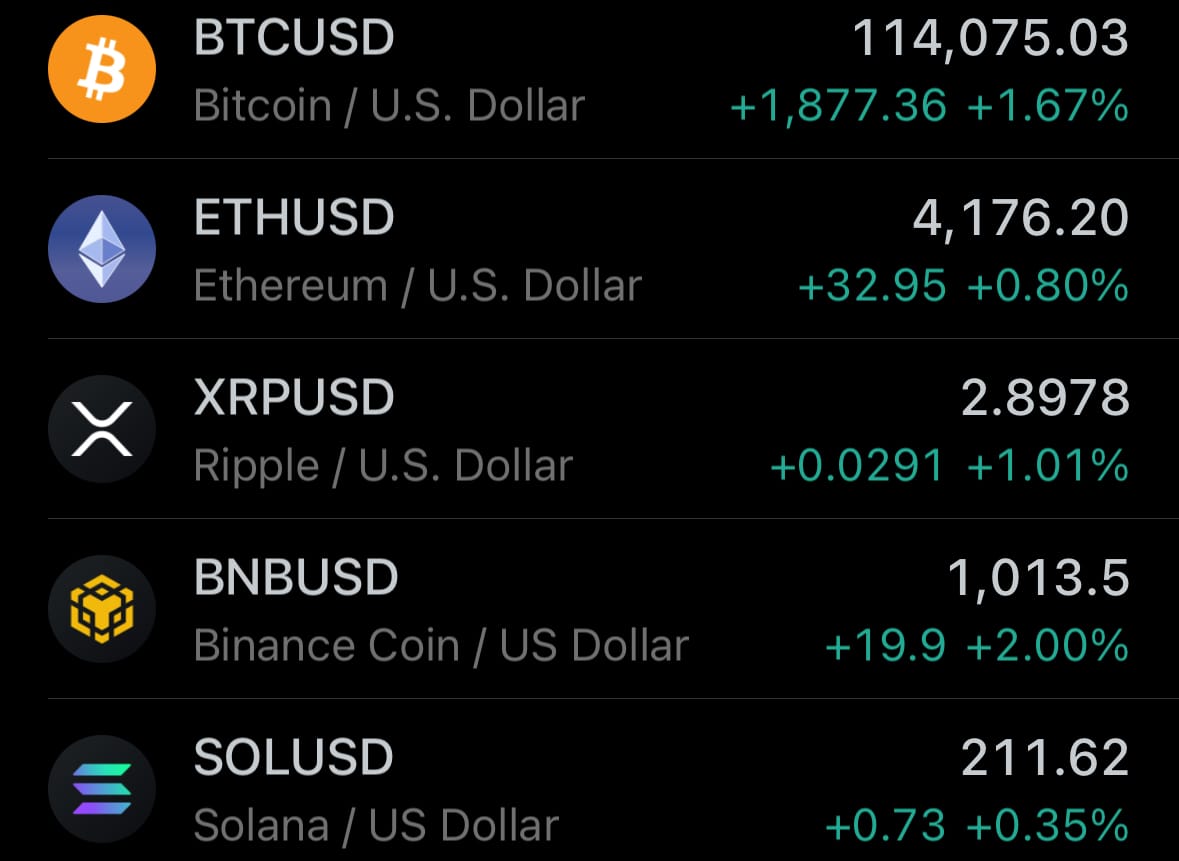
- Today’s crypto market:
Cyber:
- On September 29, 2025, Afghanistan faced a complete nationwide internet blackout as Taliban authorities systematically disconnected multiple networks starting in the morning, expanding from initial restrictions in northern provinces on September 17 intended to curb "immoral activities." Connectivity levels dropped to nearly zero, with telephone services also disrupted, affecting around 40 million people by limiting access to online information, banking, education, and family contacts abroad. Monitoring organizations like NetBlocks confirmed the shutdown, while Taliban officials described it as part of morality enforcement, possibly with provisions for essential alternatives, though no restoration timeline was given. This builds on earlier cuts in areas like Balkh, where fiber-optic services were halted, shifting reliance to costly mobile data and impacting businesses, schools, and especially women's online access.
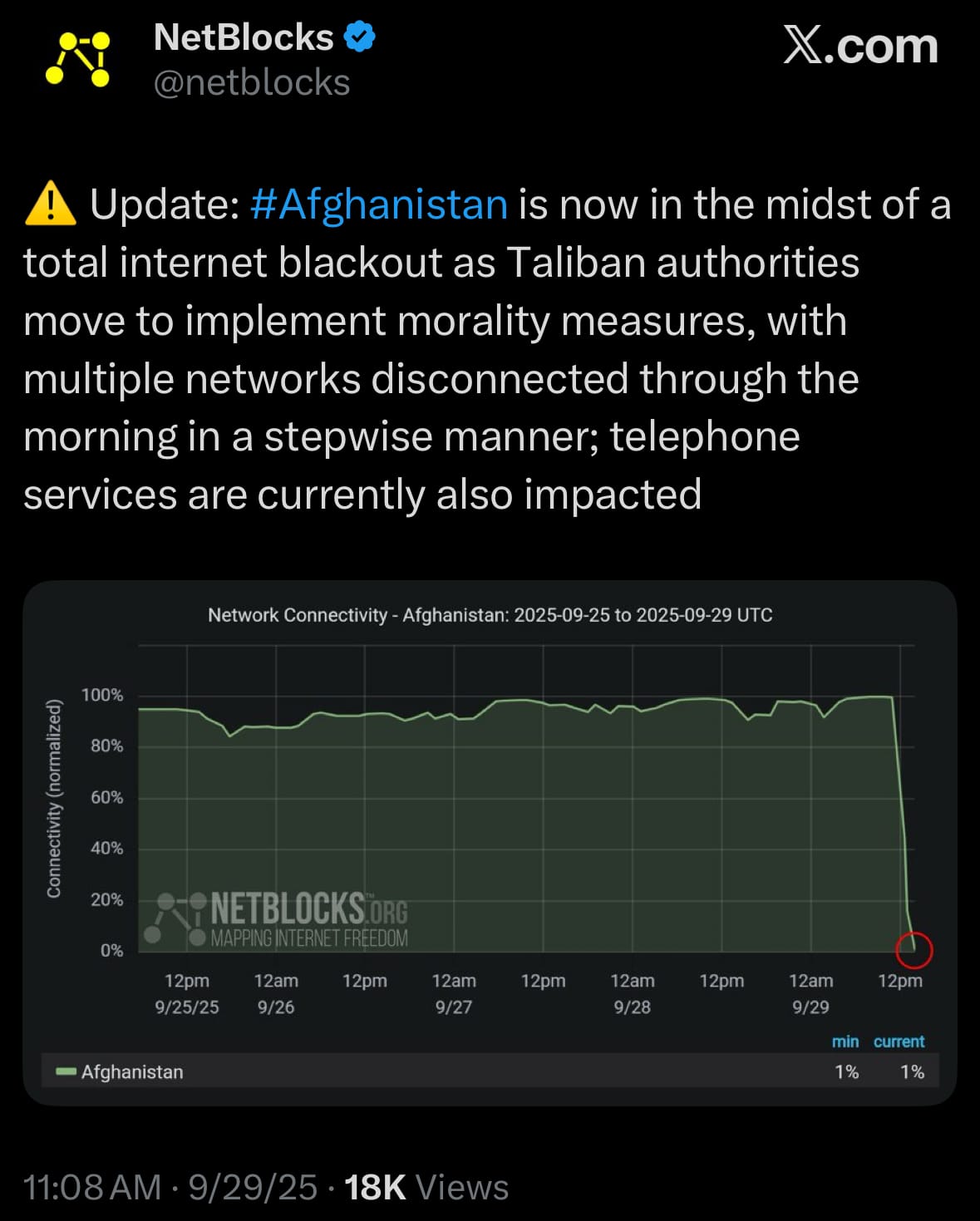
- Human rights groups and media observers have expressed concerns that the blackout may infringe on freedoms, suppress dissent, and control information flow under Taliban governance since 2021, with reports of interruptions to humanitarian aid, media streaming, and economic activities, including some Afghan TV networks' online availability. Suggestions for alternatives like satellite internet have emerged, but no official actions have been noted. Responses from Afghans and the international community highlight increased isolation, with difficulties in family communication and potential challenges in tracking human rights and relief efforts.
Space:
- On September 28, 2025 (PDT), China successfully launched the Shiyan-30 01 and 02 satellites aboard a Long March-2D rocket from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center in Sichuan Province at 8:00 PM PDT, equivalent to September 29 at 03:00 UTC or 11:00 local time. The mission placed the two experimental satellites into low Earth orbit, where they are intended for technology demonstration and Earth observation purposes, though specific details remain classified by the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation. The launch marked another milestone in China's active space program, with no reported anomalies during ascent or deployment.
- These Shiyan-series satellites, part of a broader experimental lineup, typically test new payloads, sensors, or orbital capabilities, contributing to advancements in remote sensing and space applications without disclosed military or civilian specifics. The event underscores China's rapid launch cadence in 2025, amid global monitoring of its space activities, but does not indicate any immediate international implications or deviations from routine operations.
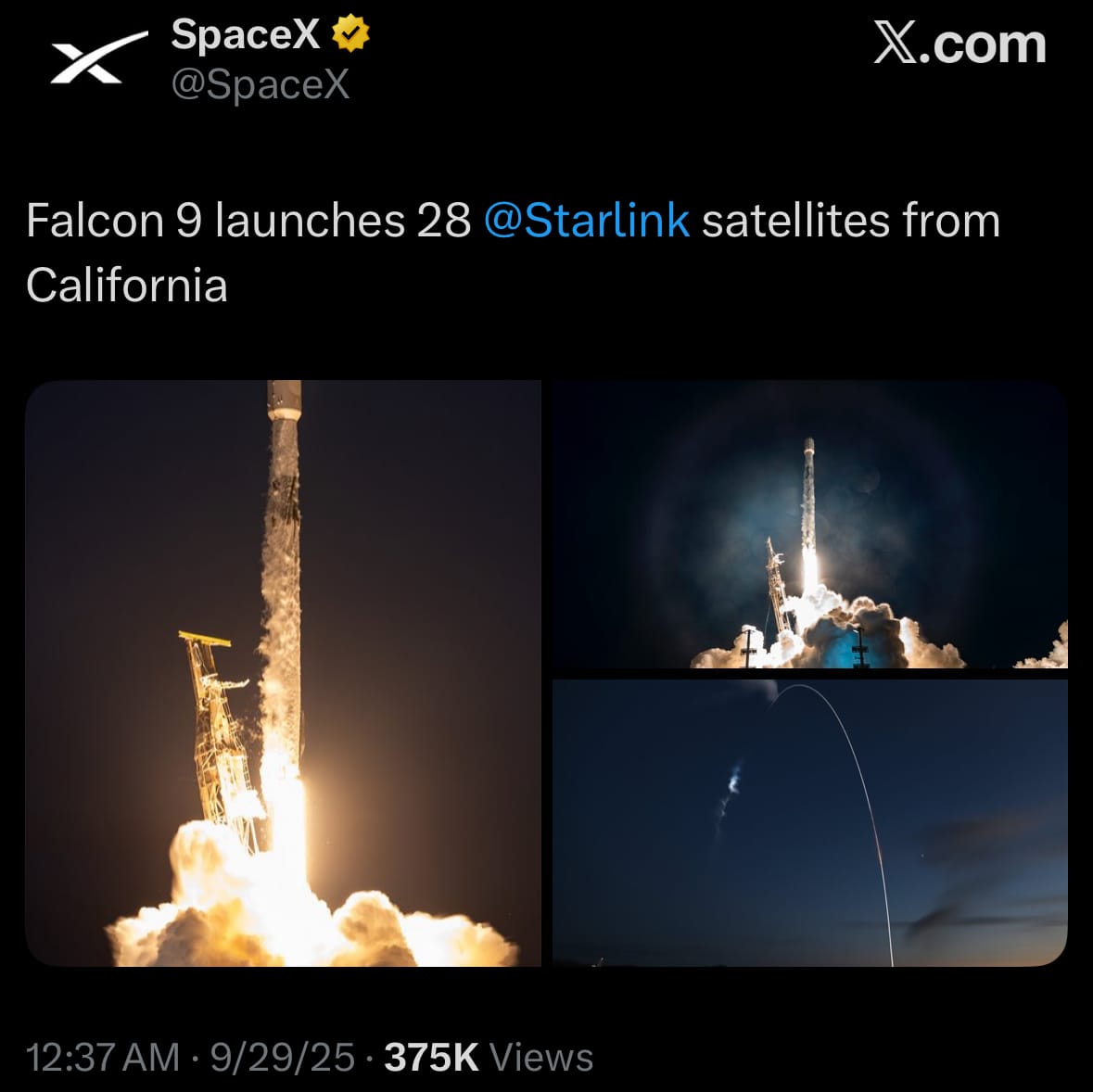
- On September 29, 2025 (02:04 UTC), SpaceX successfully launched the Starlink Group 11-20 mission using a Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4E at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, deploying 28 Starlink V2 Mini satellites into low Earth orbit to enhance global broadband coverage. The launch occurred at 7:04 p.m. local time on September 28 (PDT), with the first-stage booster, separating as planned and landing on the droneship Of Course I Still Love You in the Pacific Ocean. No anomalies were reported during ascent or satellite deployment, marking another step in SpaceX's routine operations.
- This mission contributes to the expanding Starlink constellation, aimed at providing internet access to underserved areas worldwide, with the satellites equipped for improved signal strength and capacity. It reflects SpaceX's high launch cadence in 2025, supporting both commercial and potential government applications, while highlighting ongoing advancements in reusable rocket technology without indicating any shifts in broader space industry dynamics.
Statistic:
- Largest assets on Earth by market capitalization:
- Gold: $25.916T
- 🇺🇸 NVIDIA: $4.427T
- 🇺🇸 Microsoft: $3.825T
- 🇺🇸 Apple: $3.767T
- 🇺🇸 Alphabet (Google): $3.003
- Silver: $2.659T
- 🇺🇸 Amazon: $2.360T
- Bitcoin: $2.269T
- 🇺🇸 Meta Platforms: $1.877T
- 🇸🇦 Saudi Aramco: $1.651T
- 🇺🇸 Broadcom: $1.571T
- 🇺🇸 Tesla: $1.468T
- 🇹🇼 TSMC: $1.430T
- 🇺🇸 Berkshire Hathaway: $1.075T
- 🇺🇸 JPMorgan Chase: $865.91B
- 🇺🇸 Walmart: $819.40B
- 🇺🇸 Oracle: $803.09B
- 🇨🇳 Tencent: $771.72B
- 🇺🇸 Visa: $658.81B
- 🇺🇸 Eli Lilly: $651.25B
- SPDR S&P 500 ETF Trust (SPY): $608.90B
- 🇺🇸 Netflix: $515.52B
- 🇺🇸 Mastercard: $513.39B
- Ethereum: $502.38B
- 🇺🇸 Exxon Mobil: $487.84B
History:
- The H-1B visa was established under the Immigration Act of 1990 to allow U.S. employers to temporarily hire foreign workers in “specialty occupations” that require at least a bachelor’s degree or equivalent, particularly in science, technology, engineering, and related fields. Over the years, Congress and federal agencies have made adjustments to the program—such as adding exemptions for higher education institutions, introducing portability between employers, and modifying prevailing wage rules. The program has consistently been debated in U.S. politics: supporters view it as essential for attracting global talent and supporting economic competitiveness, while critics argue it can be misused to undercut wages or displace U.S. workers.
- Under the Trump administration, several significant changes and proposals have been introduced to reshape the H-1B system. A major policy announced in 2025 requires new H-1B petitions to include a $100,000 payment, intended to discourage lower-wage usage of the program. Additional changes under consideration or implementation include raising prevailing wage requirements, prioritizing higher-paid roles in the lottery selection process, increasing audits and compliance reviews, and removing automatic deference for renewals so each application undergoes full scrutiny. The administration has also considered limiting spousal work authorizations tied to H-1B holders. These reforms are intended to make the program more selective and focused on high-wage, high-skill roles, but they also increase costs and administrative challenges for employers and could limit access for entry-level or lower-paying specialty occupations.
Image of the day:
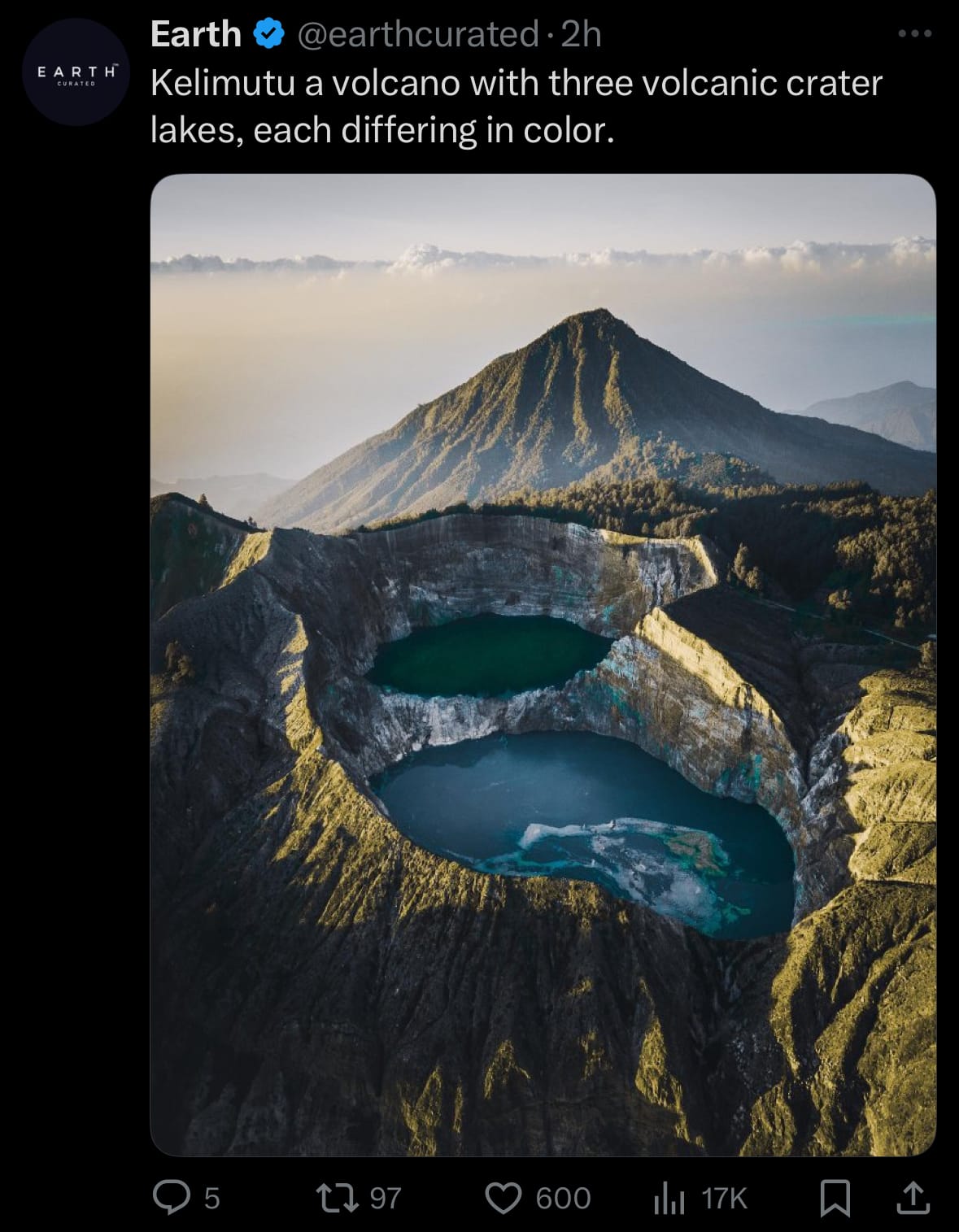
Article:

Thanks for reading!
Earth is complicated, we make it simple.
Monitor the planet with the Earth Intelligence System. Click the image below to view the Earth Intelligence System:



Support/Suggestions Email:
earthintelligence@earthintel.news




