Monday☕️

Weekend Recap:
- As of January 4, 2026, protests in Iran marked their 8th consecutive day, with demonstrations, strikes, and clashes reported in over 80 cities across 23 provinces. Security forces clashed with protesters in several locations, including western areas like Malekshahi in Ilam Province, where gunfire resulted in deaths (state media reported one security member and two protesters killed; rights groups estimated higher protester casualties). Funerals for earlier victims turned into new rallies in some cities, with slogans against the government.
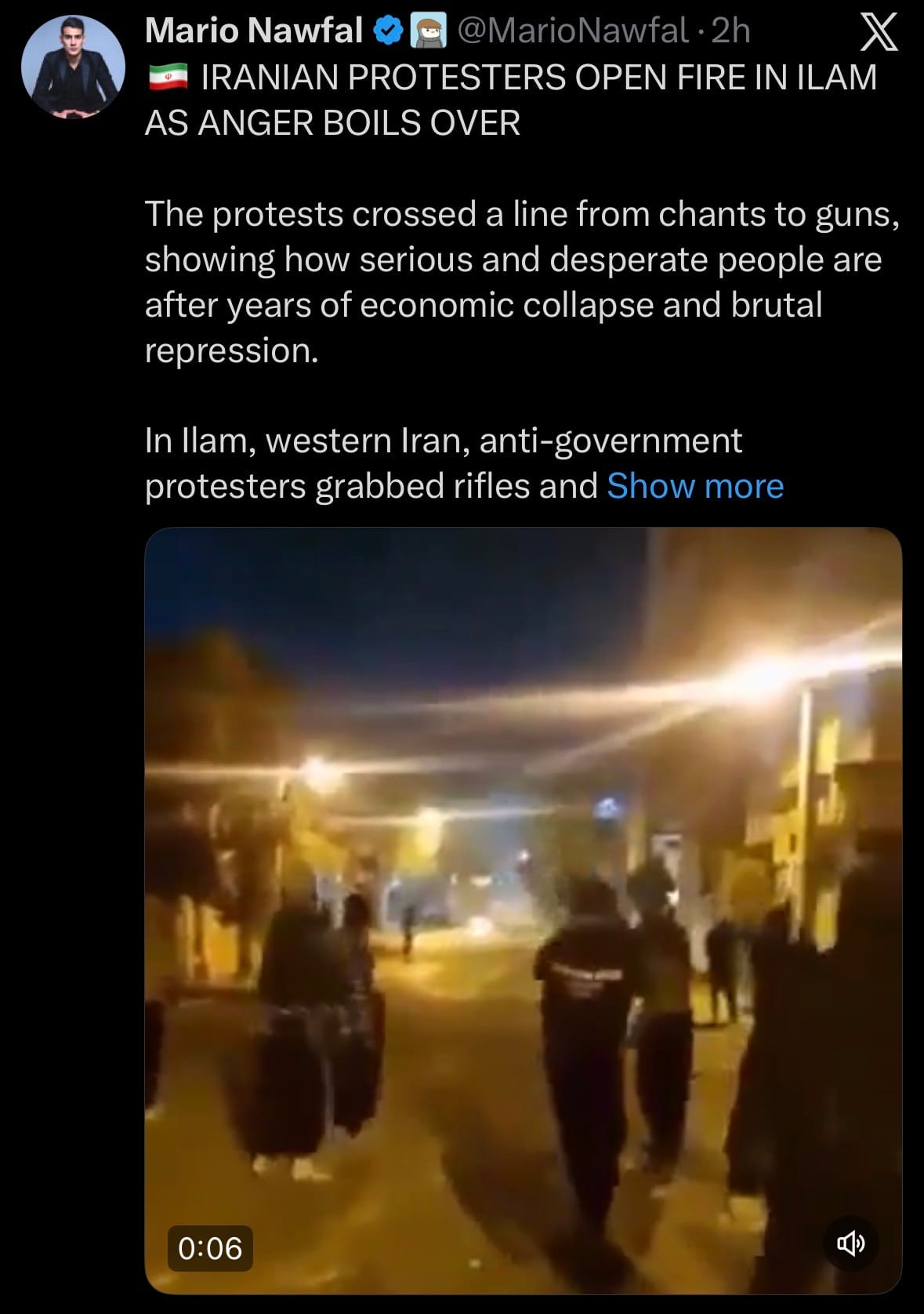
- The unrest began with economic strikes over the rial's collapse and inflation above 40% but has broadened to political demands. Rights groups report at least 16-20 deaths overall, hundreds injured, and over 580 arrests. Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei called for suppressing "rioters" while acknowledging some grievances as valid; President Masoud Pezeshkian urged dialogue. This represents the most widespread protests since 2022, driven by economic hardship amid sanctions and recent conflicts.
U.S. Venezuelan Military Operation:
- On January 3, 2026, U.S. forces launched Operation Absolute Resolve, conducting airstrikes on Venezuelan air defense and military targets followed by a ground raid in Caracas. Elite units, including Delta Force and supported by over 150 aircraft, captured President Nicolás Maduro and his wife Cilia Flores from a fortified location in under three hours. Maduro was transported to New York to face U.S. charges on narcoterrorism and drug trafficking, while Vice President Delcy Rodríguez was sworn in as interim leader. President Trump described the action as a law enforcement operation with military support, stating the U.S. would oversee a transition period.

- The operation resulted in dozens of deaths, including Venezuelan military personnel, and reportedly Cuban advisors, with U.S. forces sustaining only minor injuries. Venezuelan officials condemned it as an act of aggression violating sovereignty, while opposition groups welcomed Maduro's removal. International reactions were divided: Brazil, Colombia, Mexico, Cuba, Russia, and China criticized it as illegal intervention, with the UN Secretary-General calling for a Security Council meeting; Argentina's leader expressed support, and European governments urged adherence to international law.
Economics & Markets:
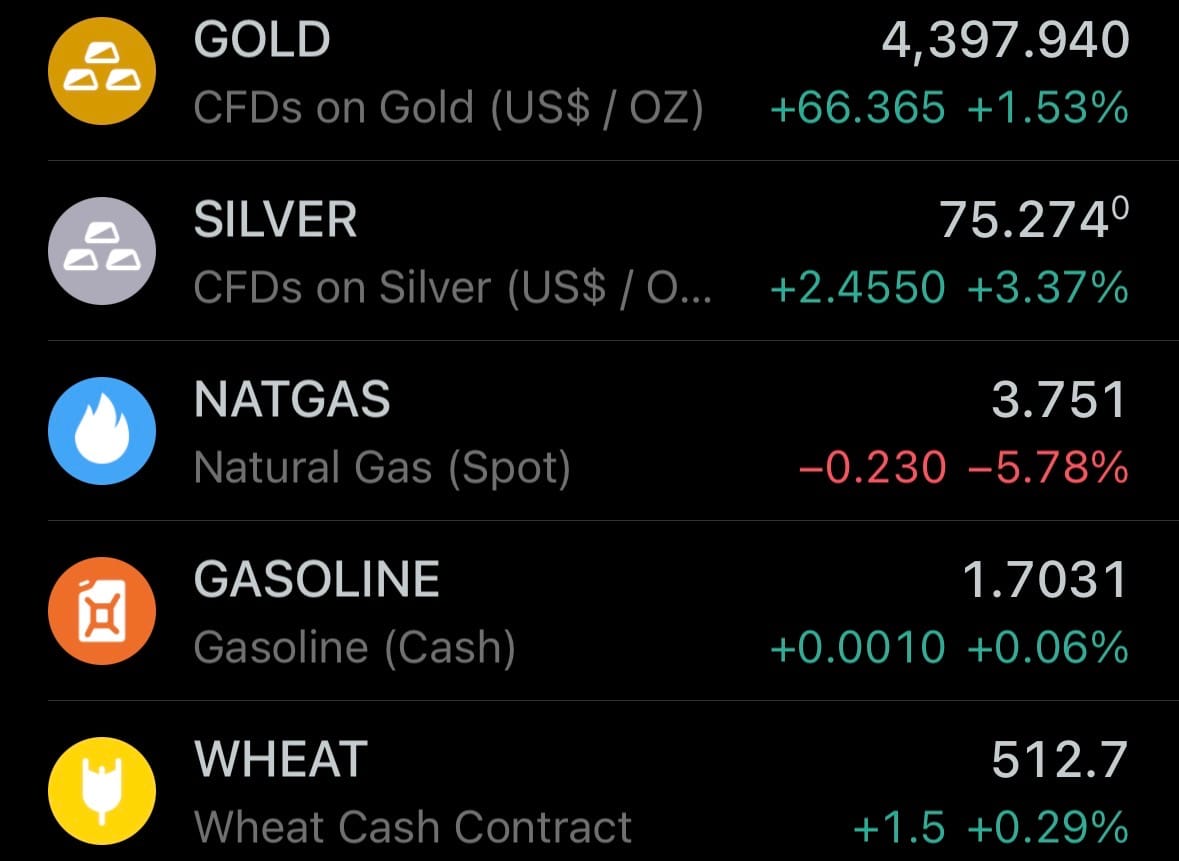
- Yesterday’s commodity market:
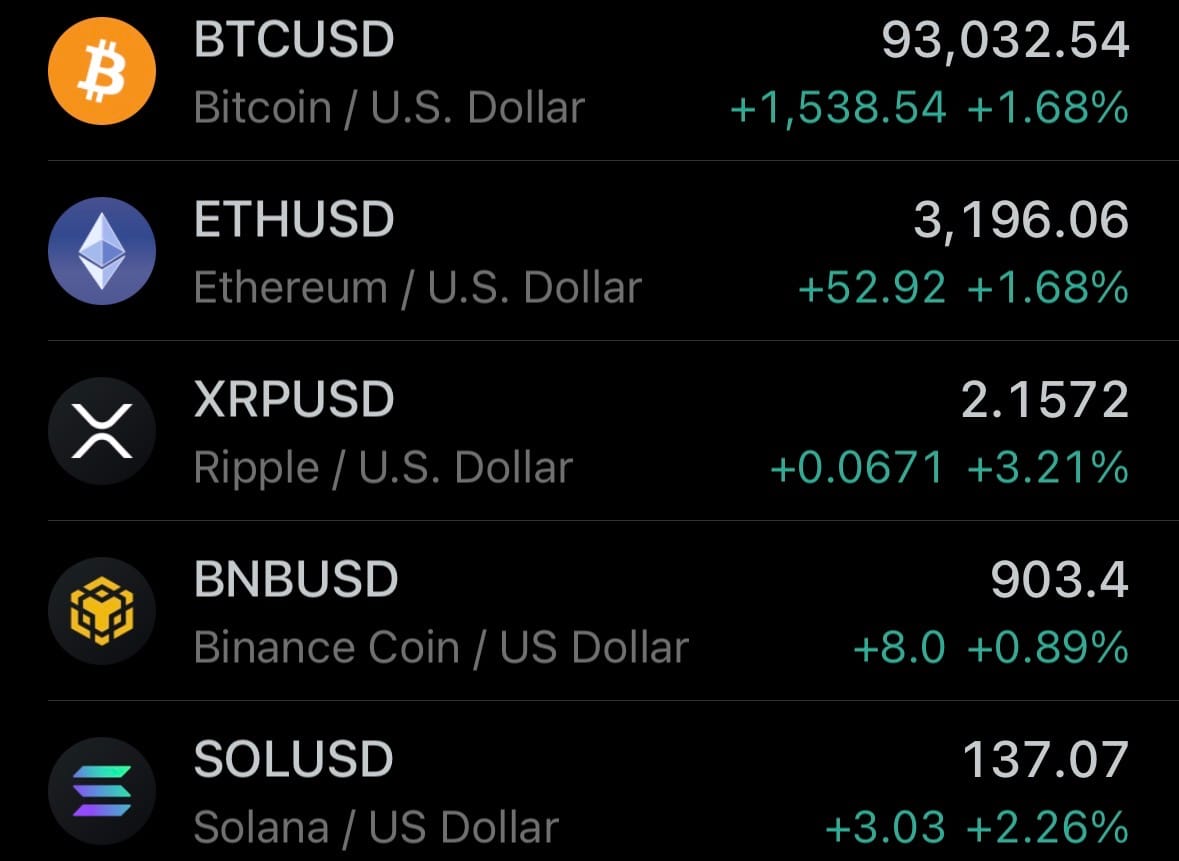
- Yesterday’s crypto market:
Geopolitics & Military Activity:
- On January 3, 2026, French Air Force Dassault Rafale jets and Royal Air Force Eurofighter Typhoon FGR4 aircraft conducted a joint airstrike on an underground Islamic State (ISIS) facility near the ancient city of Palmyra in central Syria. The operation, carried out in the evening, targeted access tunnels to a suspected weapons and explosives storage site in a remote mountainous area with no civilian presence. According to the UK Ministry of Defence, RAF Typhoons—supported by a Voyager tanker—deployed Paveway IV precision-guided bombs, while French Rafales contributed to the mission. Initial assessments confirmed the target was successfully engaged, with no civilian risks and all aircraft returning safely to base.
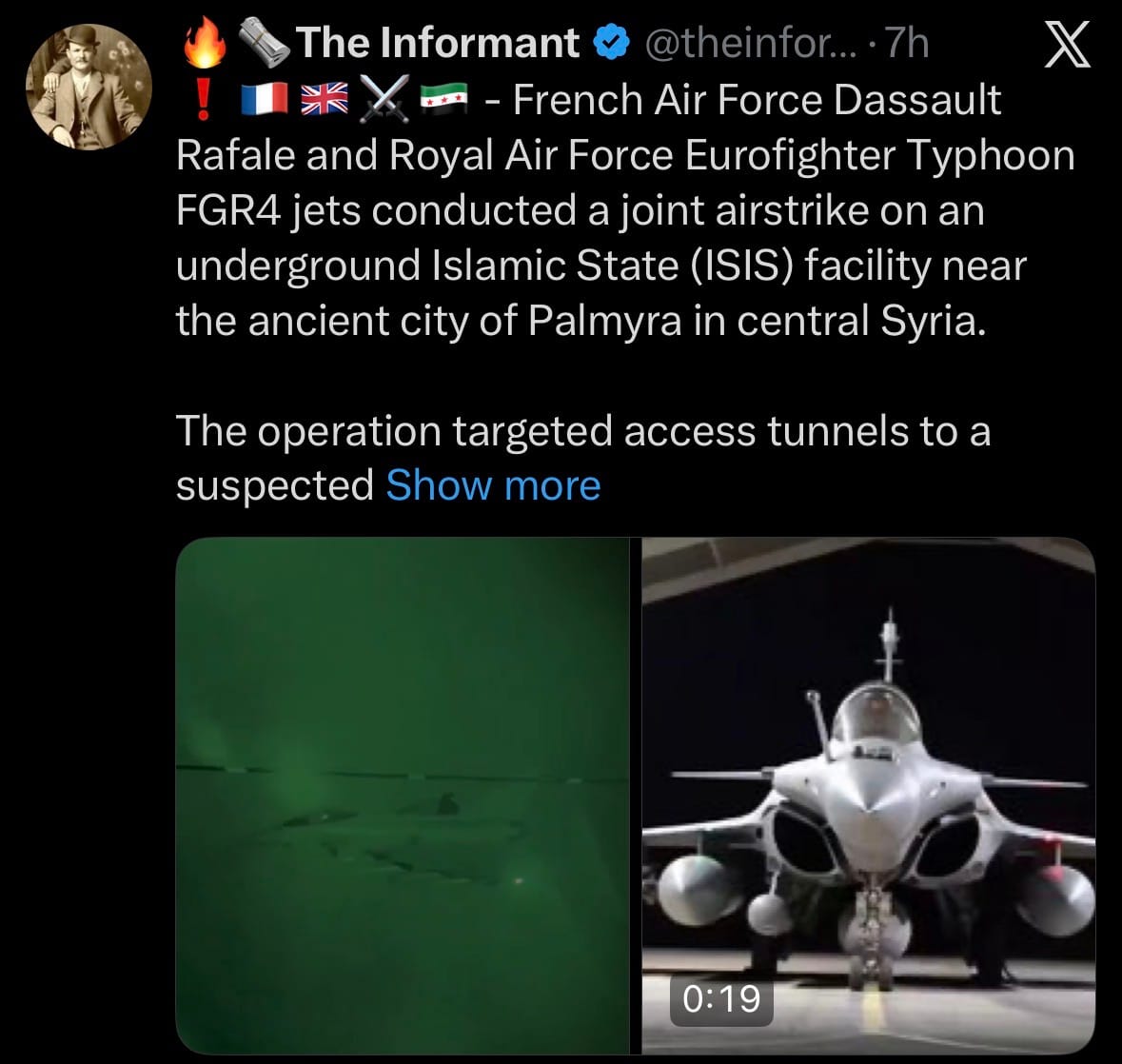
- The strike is part of multinational efforts to prevent an ISIS resurgence following the group's territorial defeat in 2019, amid ongoing threats in Syria. It follows recent U.S. strikes in the region after an ISIS ambush in December 2025 that killed American personnel near Palmyra. This collaborative action between France and the UK demonstrates continued coalition commitment to counterterrorism operations in Syria, focusing on degrading ISIS capabilities through precision strikes while minimizing collateral damage.
Space:
- On January 4, 2026, SpaceX successfully launched the Starlink Group 6-88 mission using a Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida. Liftoff occurred at 1:48 a.m. EST (06:48 UTC), deploying 29 Starlink V2 Mini satellites into low Earth orbit.
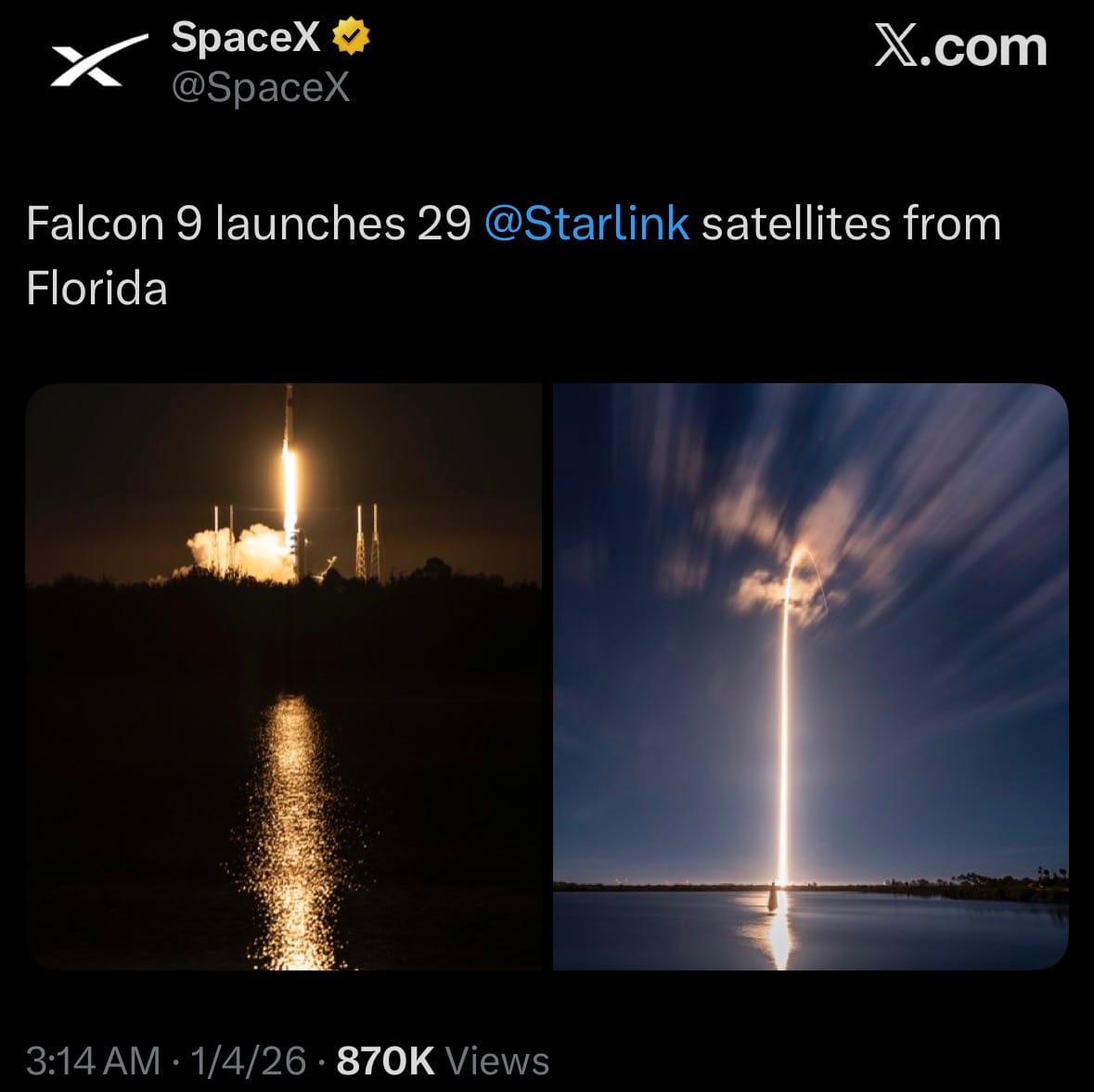
- This mission was the first Starlink deployment of 2026 and Florida's inaugural orbital launch of the year, following a brief pause after an in-orbit anomaly affected one satellite in December 2025. The launch contributes to SpaceX's ongoing efforts to densify the network while preparing for next-generation Version 3 satellites later in 2026.
Statistic:
- Largest assets on Earth by market capitalization:
- Gold: $30.672T
- 🇺🇸 NVIDIA: $4.597T
- Silver: $4.240T
- 🇺🇸 Apple: $4.021T
- 🇺🇸 Alphabet (Google): $3.806T
- 🇺🇸 Microsoft: $3.515T
- 🇺🇸 Amazon: $2.421T
- Bitcoin: $1.857T
- 🇹🇼 TSMC: $1.657T
- 🇺🇸 Broadcom: $1.648T
- 🇺🇸 Meta Platforms: $1.639T
- 🇸🇦 Saudi Aramco: $1.515T
- 🇺🇸 Tesla: $1.456T
- 🇺🇸 Berkshire Hathaway: $1.071T
- 🇺🇸 Eli Lilly: $968.49B
- 🇺🇸 Walmart: $899.01B
- 🇺🇸 JPMorgan Chase: $894.98B
- 🇺🇸 Vanguard S&P 500 ETF: $823.52B
- 🇺🇸 iShares Core S&P 500 ETF: $761.70B
- 🇨🇳 Tencent: $727.18B
- 🇺🇸 SPDR S&P 500 ETF: $709.08B
- 🇺🇸 Visa: $668.67B
- 🇰🇷 Samsung: $627.25B
- 🇺🇸 Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF: $567.34B
- 🇺🇸 Oracle: $562.30B
- Platinum: $550.02B
History:
- The story of GPS (Global Positioning System) begins long before satellites, rooted in humanity’s struggle to know where it is on a round, moving planet. Latitude was the first problem solved: as early as 600 BC, Greek thinkers like Thales and later Eratosthenes (c. 240 BC) understood Earth as a sphere and used the angle of the Sun or stars to determine north–south position. Longitude, however, defeated civilizations for centuries because it required accurate timekeeping. Knowing longitude means knowing the time difference between your location and a fixed reference point. This problem plagued navigation until the 18th century, when British clockmaker John Harrison built the first reliable marine chronometers. In 1761, Harrison’s H4 clock proved ships could calculate longitude accurately at sea, anchoring global navigation to time and establishing the Greenwich Meridian as the prime reference. By the 19th century, latitude–longitude grids were standardized, nautical charts improved, and navigation became a precise science—but it still depended on celestial observation, dead reckoning, and later radio beacons. The next leap came during the Cold War, when space and physics entered navigation. In 1957, scientists tracking Sputnik noticed its radio signal shifted frequency as it moved—revealing that position could be calculated from Doppler effects. This insight led the U.S. Navy to develop TRANSIT (operational 1964), the first satellite navigation system, primarily for ballistic missile submarines that needed accurate positioning without surfacing.
- Modern GPS emerges in the 1970s as a unified, global solution. The U.S. Department of Defense launched the Navstar GPS program in 1973, combining precise atomic clocks, satellite ranging, and trilateration. The first experimental satellite launched in 1978, and by 1995, a full constellation of 24 satellites provided continuous global coverage. GPS works by measuring the time it takes for signals from multiple satellites—each broadcasting its precise position and time—to reach a receiver, allowing exact calculation of location in three dimensions. Initially reserved for military use, GPS was gradually opened to civilians, with full accuracy unlocked in 2000 when the U.S. removed “Selective Availability.” Since then, GPS has become foundational infrastructure: aviation, maritime navigation, smartphones, banking timestamps, power grids, telecommunications, agriculture, and military operations all depend on it. Other global systems followed—Russia’s GLONASS, Europe’s Galileo, China’s BeiDou—but GPS remains the dominant reference standard worldwide. Today, GPS is evolving beyond simple positioning into a resilient, multi-layered system integrated with inertial sensors, ground augmentation, encrypted military signals, and AI-based correction models. What began as star-gazing and timekeeping has become a planet-spanning synchronization engine—one that ties location, time, and motion into a single invisible grid wrapped around Earth, enabling modern civilization to function with precision measured not in miles, but in centimeters and nanoseconds.
Image of the day:

Thanks for reading! Earth is complicated, we make it simple.
- Click below if you’d like to view our free EARTH WATCH globe:
- Download our mobile app:



Click below to view our previous newsletters:

Support/Suggestions Email:
earthintelligence@earthintel.news




