Sunday☕️

Trending:
- Yesterday, March 1, 2025, Microsoft experienced a technology outage that disrupted several of its key services, including Outlook, Microsoft 365, Exchange, Teams, and the Microsoft Store. Users started reporting issues in the early afternoon, with Downdetector tracking a rapid increase in complaints. By around 4 p.m. Eastern Time, more than 37,000 users had reported being unable to access their emails, log into accounts, or use Microsoft’s productivity tools.
- The outage affected both individuals and businesses, making it difficult for many to communicate or complete work. Microsoft quickly acknowledged the issue and identified a recent system update as the likely cause. To resolve the problem, they rolled back the update and worked on restoring normal operations. By late afternoon, most services had begun recovering, though some users are still experiencing delays in accessing their accounts.
Economics & Markets:
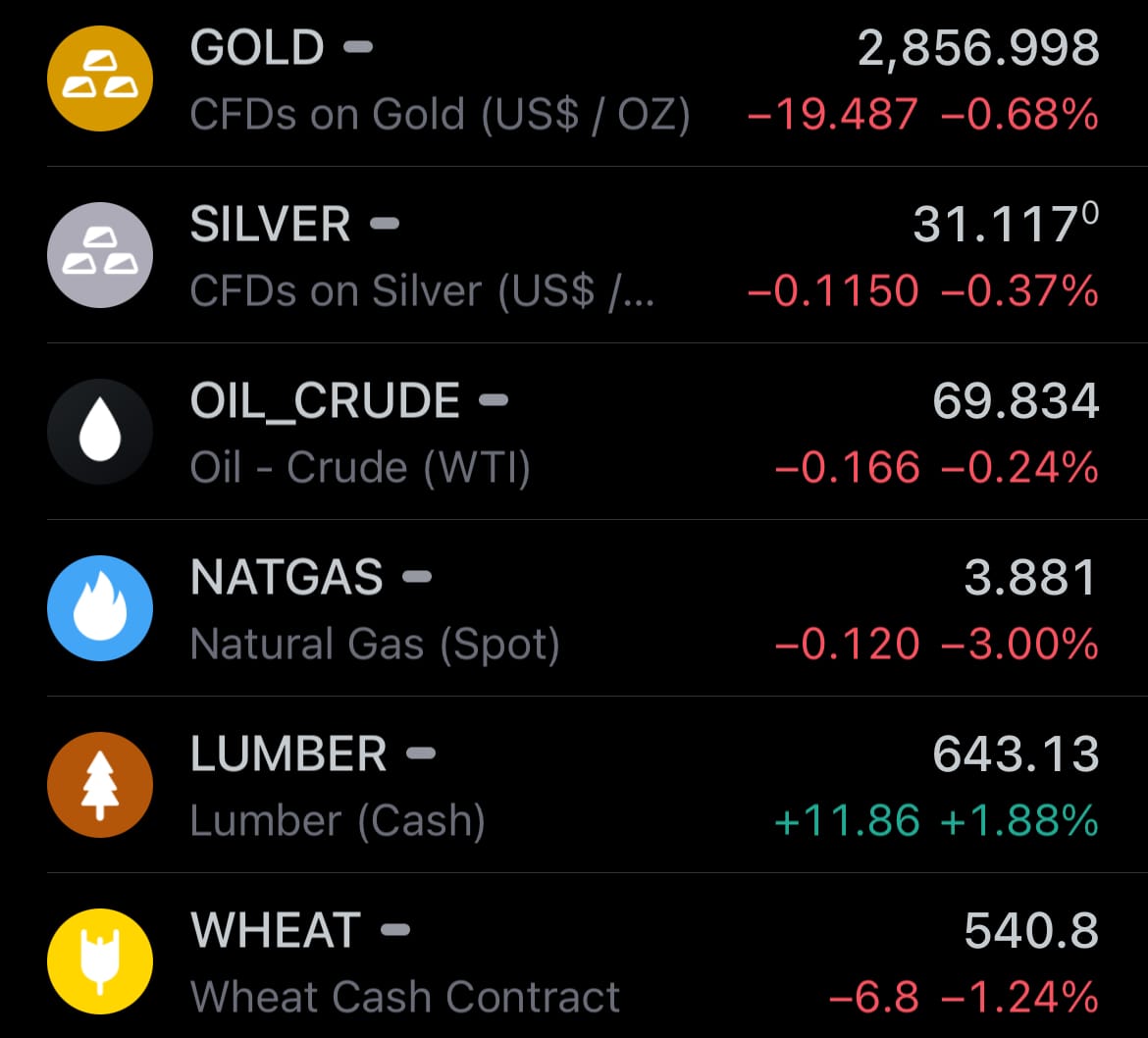
- Yesterday’s commodity market:
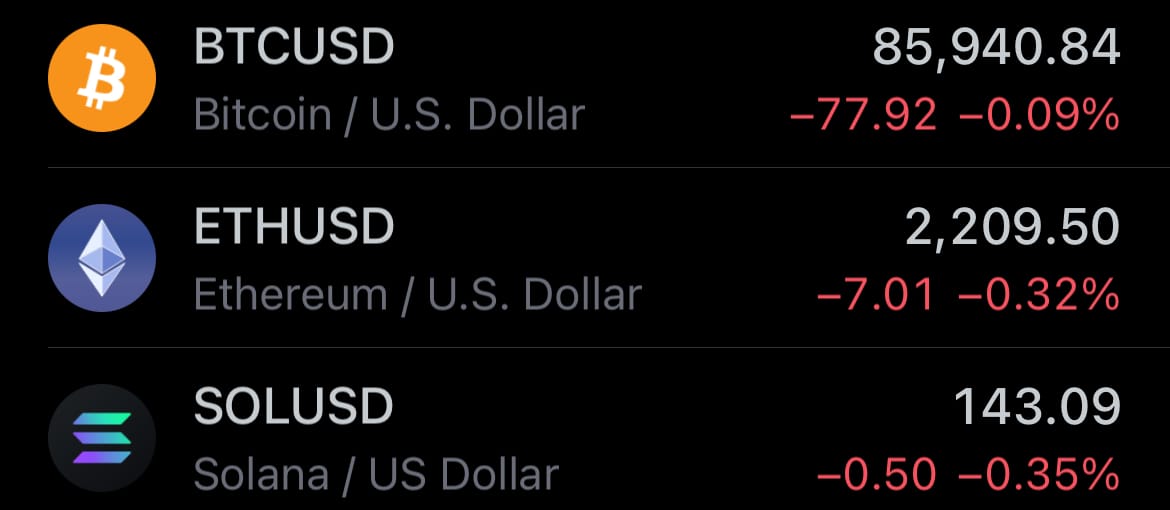
- Yesterday’s crypto market:
Geopolitics & Military Activity:
- Yesterday, March 1, 2025, a Venezuelan naval vessel entered waters internationally recognized as part of Guyana’s maritime territory and approached an offshore oil facility operated by ExxonMobil. This action escalated ongoing tensions between the two countries, as Venezuela has long disputed Guyana’s control over the Essequibo region and its surrounding waters. Guyana’s government condemned the incursion, calling it a violation of its sovereignty and summoning the Venezuelan ambassador in protest.
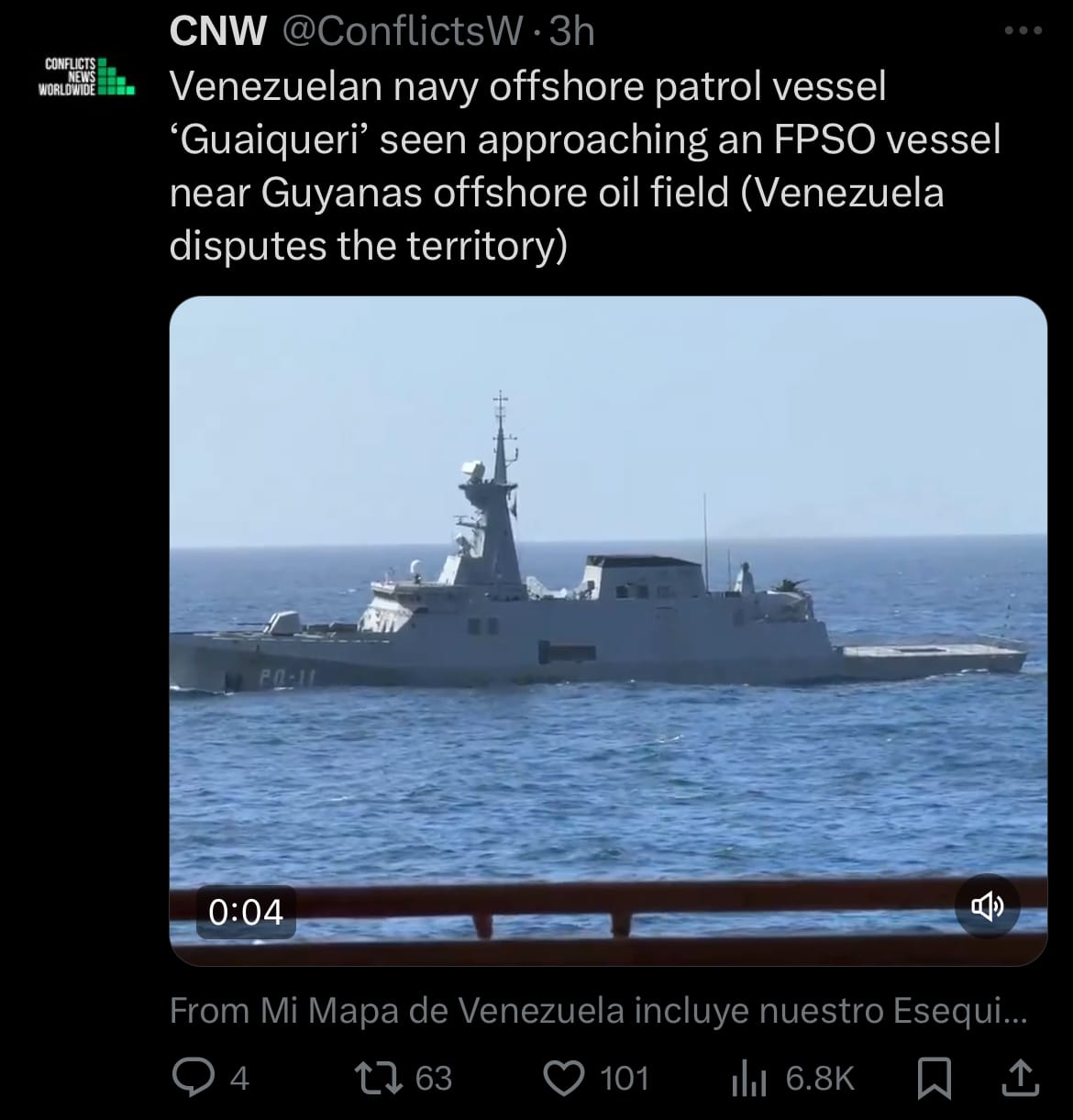
- In response, Guyana increased its military readiness, deploying air and coastguard assets to monitor and protect its waters. International organizations, including the Organization of American States (OAS), along with the United States, denounced Venezuela’s actions, calling for respect of Guyana’s territorial integrity and international law. The dispute over this region dates back to the 19th century, with Venezuela claiming the Essequibo territory despite an 1899 arbitral ruling that awarded the land to Guyana. Tensions have heightened in recent years following significant offshore oil discoveries by ExxonMobil in Guyanese waters.

- The United States reaffirmed its support for Guyana, stating that further Venezuelan provocations could lead to consequences for President Nicolás Maduro’s government. The situation remains a focal point of geopolitical concern, with international powers closely monitoring developments to prevent further escalation and ensure stability in the region.
Environment & Weather:
- As of Yesterday, March 1, 2025, a large wildfire is burning in the Carolina Forest area of Horry County, South Carolina, forcing evacuations in at least two neighborhoods. Firefighters are actively working to contain the blaze and prevent it from spreading further. Dry conditions, low humidity, and strong winds have contributed to the fire’s rapid growth, making it difficult to control. The fire has raised concerns among local officials and residents, who are being urged to follow evacuation orders and stay informed through official emergency updates.
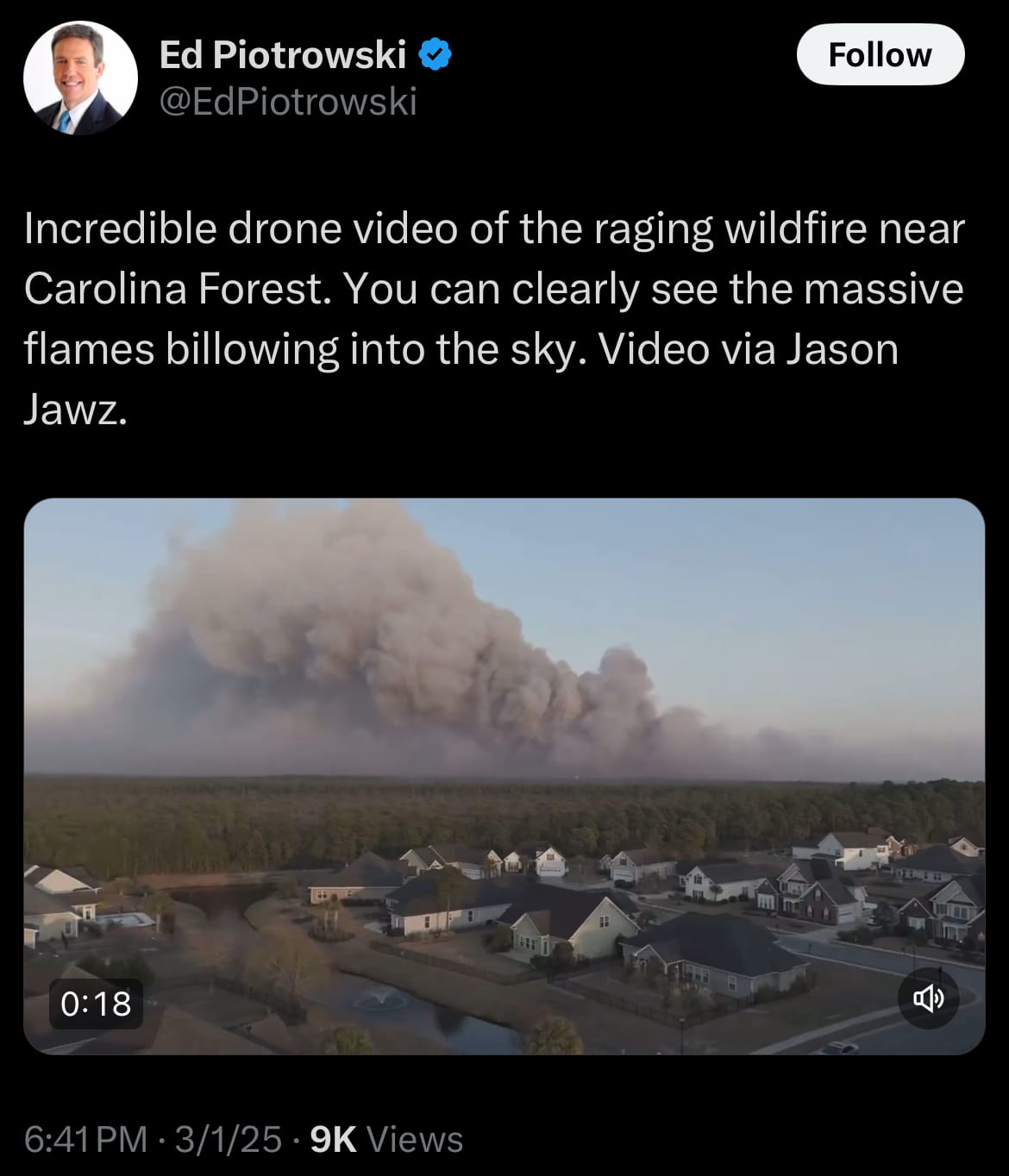
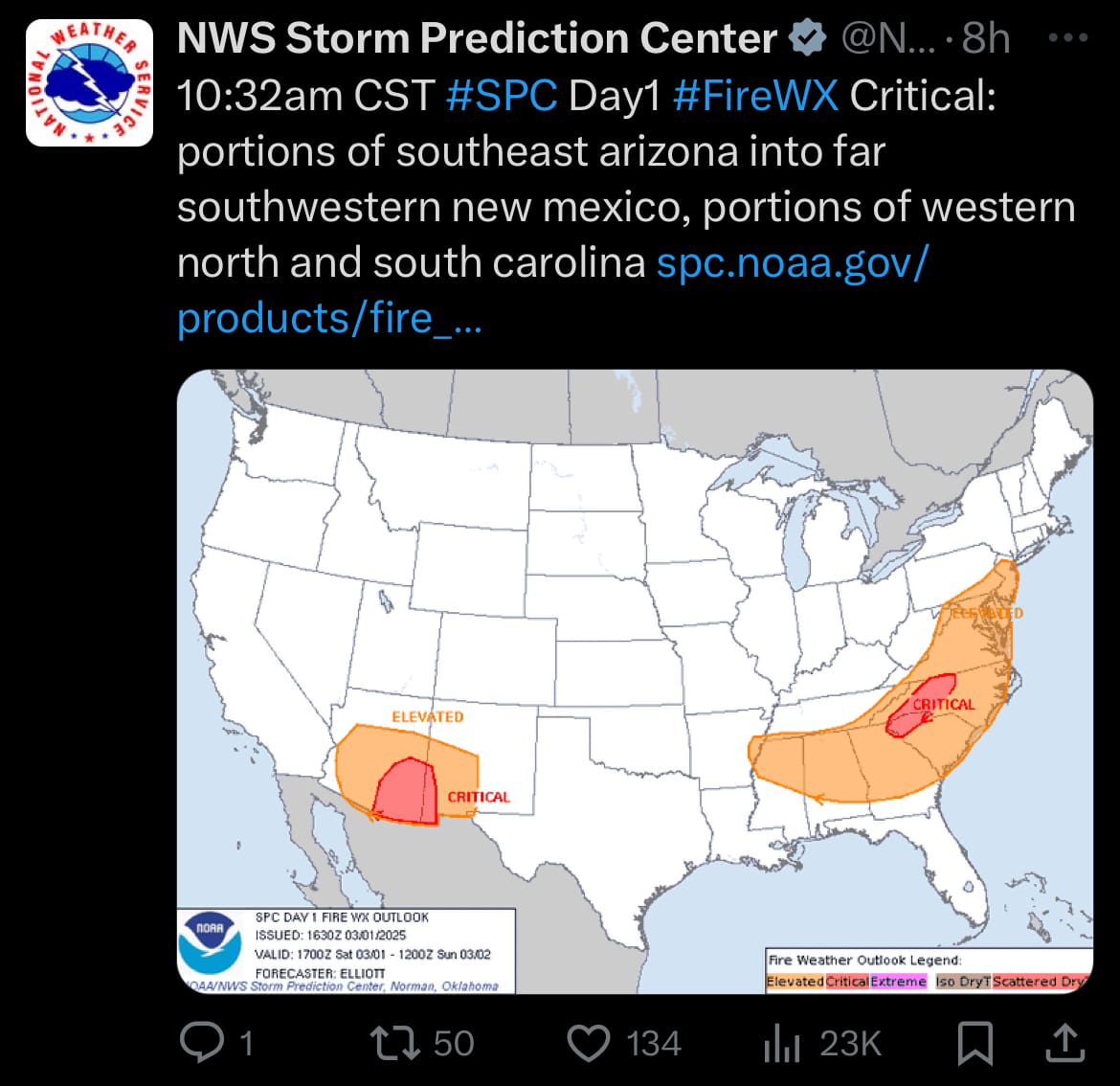
- The National Weather Service has issued Red Flag Warnings for parts of North and South Carolina due to elevated fire weather conditions. These warnings highlight the risk of wildfires spreading quickly due to warm temperatures, gusty winds, and dry vegetation. In addition to the fire threat in the Carolinas, the National Weather Service has also reported critical fire weather conditions in southeast Arizona and southwestern New Mexico. These regions are experiencing similar dry and windy conditions, increasing the risk of wildfires. Officials are urging residents in all affected areas to take extra precautions, avoid outdoor burning, and remain alert to any fire warnings or evacuation notices.
Privacy & Security:
- On March 1, 2025, cybersecurity researchers reported that ransomware gangs are using a weakness in Paragon Partition Manager’s BioNTdrv.sys driver to take control of Windows systems. This driver is a piece of software that helps the operating system communicate with storage drives. However, hackers have found a flaw in it that allows them to install it on a computer and then use it to gain full administrative access. This type of attack is called Bring Your Own Vulnerable Driver (BYOVD) because the attackers introduce a legitimate but flawed driver into the system to disable security protections. Once inside, they can install ransomware, which locks files and demands payment to restore access, or other harmful programs without being detected. Microsoft has identified five security flaws in this driver, and at least one of them is already being used in real-world cyberattacks.
- This technique has been used by ransomware groups before because it is very effective at avoiding detection. One example is the BlackByte ransomware gang, which previously used this method to disable over 1,000 security-related drivers, making it almost impossible for antivirus programs to stop the attack. The discovery of this new exploit highlights the ongoing risk of outdated or vulnerable software being used by hackers. To protect against these attacks, cybersecurity experts recommend keeping all drivers up to date, closely monitoring systems for unusual activity, and blocking known vulnerable drivers from being installed. These steps can help prevent cybercriminals from gaining control of a computer or network.
Science & Technology:
- A biotech company called Loyal is developing an anti-aging pill for dogs, and on February 26, 2025, the FDA confirmed that the pill, LOY-002, has a “reasonable expectation of efficacy.” This means it has shown promise in helping older dogs, specifically those aged 10 years or more and weighing at least 14 pounds, live healthier for longer. Loyal has been working on similar treatments for years. In November 2023, another drug, LOY-001, designed for large and giant dog breeds, also received FDA recognition for its potential effectiveness. Loyal expects to receive conditional FDA approval for LOY-002 by the end of 2025, with plans to make it available to veterinarians in 2026.
- Scientists believe that extending lifespan in dogs could provide useful insights for human longevity. Since dogs experience similar age-related diseases and environmental factors as humans, studying how to slow their aging process could contribute to advancements in human medicine. Other research efforts, like the Dog Aging Project, are testing drugs such as rapamycin, which has already been shown to extend life in mice. These studies are part of the growing longevity field, which explores ways to improve health and lifespan across different species. While it is still uncertain how these findings may apply to humans, ongoing research continues to expand our understanding of aging and its potential treatments.
Statistic:
- Largest public pharmaceutical companies by market capitalization:
- 🇺🇸 Eli Lilly: $826.88B
- 🇩🇰 Novo Nordisk: $408.87B
- 🇺🇸 Johnson & Johnson: $397.30B
- 🇺🇸 AbbVie: $369.01B
- 🇨🇭 Roche: $265.90B
- 🇬🇧 AstraZeneca: $236.27B
- 🇺🇸 Merck: $233.02B
- 🇨🇭 Novartis: $215.78B
- 🇺🇸 Amgen: $165.49B
- 🇺🇸 Pfizer: $149.77B
- 🇺🇸 Gilead Sciences: $142.46B
- 🇫🇷 Sanofi: $138.86B
- 🇺🇸 Vertex Pharmaceuticals: $123.20B
- 🇺🇸 Bristol-Myers Squibb: $120.98B
- 🇺🇸 CVS Health: $82.85B
- 🇯🇵 Chugai Pharmaceutical: $81.92B
- 🇦🇺 CSL: $78.16B
- 🇬🇧 GlaxoSmithKline: $76.66B
- 🇺🇸 Regeneron Pharmaceuticals: $76.38B
- 🇺🇸 Zoetis: $74.88B
- 🇩🇪 Merck KGaA: $61.31B
- 🇯🇵 Takeda Pharmaceutical: $45.99B
- 🇨🇭 Lonza: $45.39B
- 🇮🇳 Sun Pharmaceutical: $43.73B
- 🇯🇵 Daiichi Sankyō: $43.07B
History:
- The Essequibo dispute between Guyana and Venezuela is one of the longest-running border conflicts in South America, dating back to colonial times. The Essequibo region, which makes up about two-thirds of modern-day Guyana, was originally claimed by both Spain and Britain in the 18th and 19th centuries. When Venezuela gained independence from Spain in 1811, it took over Spain’s claim and argued that the Essequibo River was the natural border between the two countries. However, Britain, which controlled what was then British Guiana, believed the boundary extended much farther west. In the late 19th century, gold was discovered in the Essequibo region, increasing tensions as both sides wanted control over the valuable resources. With no clear agreement, an international tribunal was set up to decide the rightful owner of the land.
- In 1899, the tribunal ruled in favor of British Guiana, awarding the Essequibo region to Britain. Venezuela accepted the decision at the time, but in 1962, it declared the ruling unfair, claiming that the judges had been biased. Around this time, British Guiana was moving toward independence, and Venezuela sought to challenge its territorial claims before it became a sovereign nation. On May 26, 1966, British Guiana officially became the independent nation of Guyana, inheriting the borders established by the 1899 ruling. However, Venezuela refused to recognize Guyana’s sovereignty over Essequibo and has continued to claim the region. Guyana, on the other hand, maintains that the 1899 ruling is final and that its borders are internationally recognized. The dispute remains unresolved today, with Venezuela challenging Guyana’s sovereignty in the International Court of Justice (ICJ) while tensions continue over the region’s oil-rich waters.
Image of the day:

Thanks for reading!
Earth is complicated, we make it simple.
Click image to view the Earth Intelligence System:


Support/Suggestions Email:
earthintelligence@earthintel.news




