Thursday☕️

Trending:
- Yesterday, April 2, 2025, President Donald Trump announced a detailed tariff policy from the White House Rose Garden, introducing measures aimed at altering U.S. trade dynamics. The policy features a 10% tariff on all imported goods, effective April 5, intended to address the $1.2 trillion goods trade deficit. It also includes "reciprocal tariffs" targeting around 60 countries, starting April 9, set at half the rate those nations apply to U.S. exports.
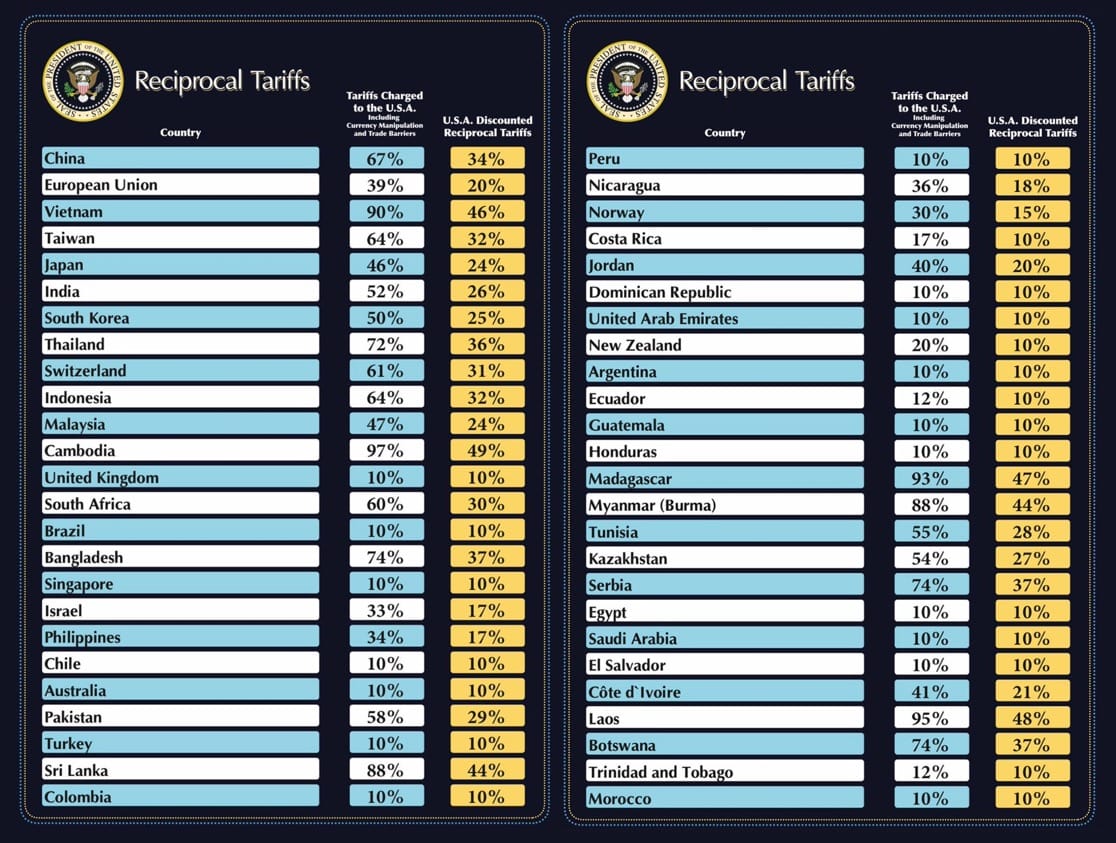
- Examples include a 34% tariff on Chinese goods (added to an existing 20%, totaling 54%), 20% on EU imports, 24% on Japanese goods, 46% on Vietnamese products, and 49% on Cambodian imports. Additional tariffs include 25% on foreign-made automobiles, effective midnight Eastern Time on April 3, and 25% on Venezuelan oil and gas buyers, starting April 2, tied to immigration and security issues. Canada and Mexico are excluded from the 10% tariff, though existing 25% tariffs on their goods persist unless modified.
Economics & Markets:
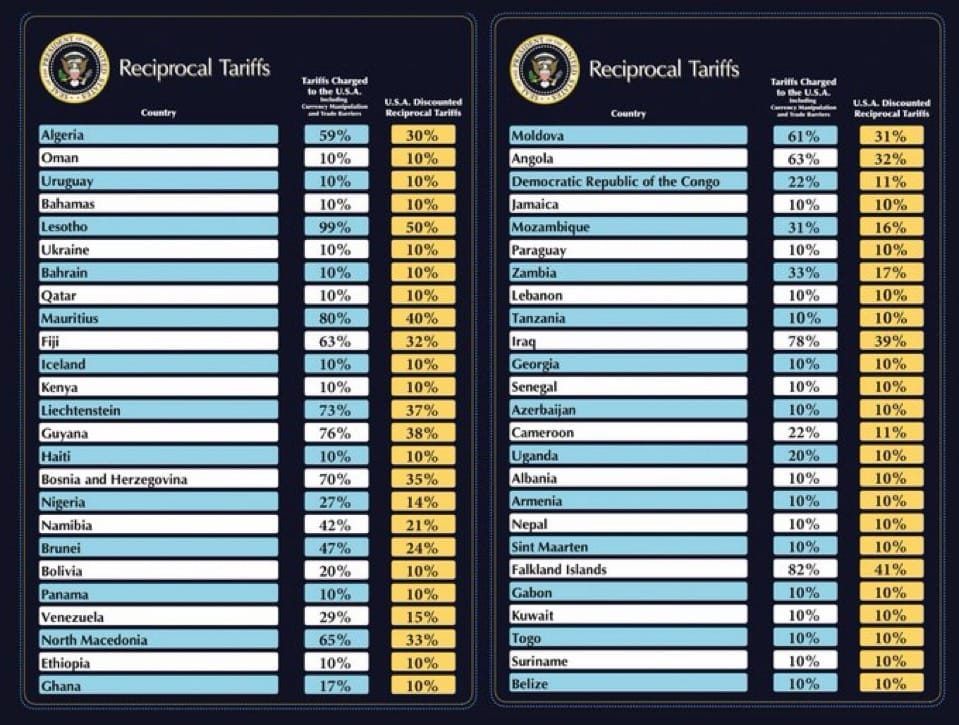
- Yesterday’s U.S. stock market:
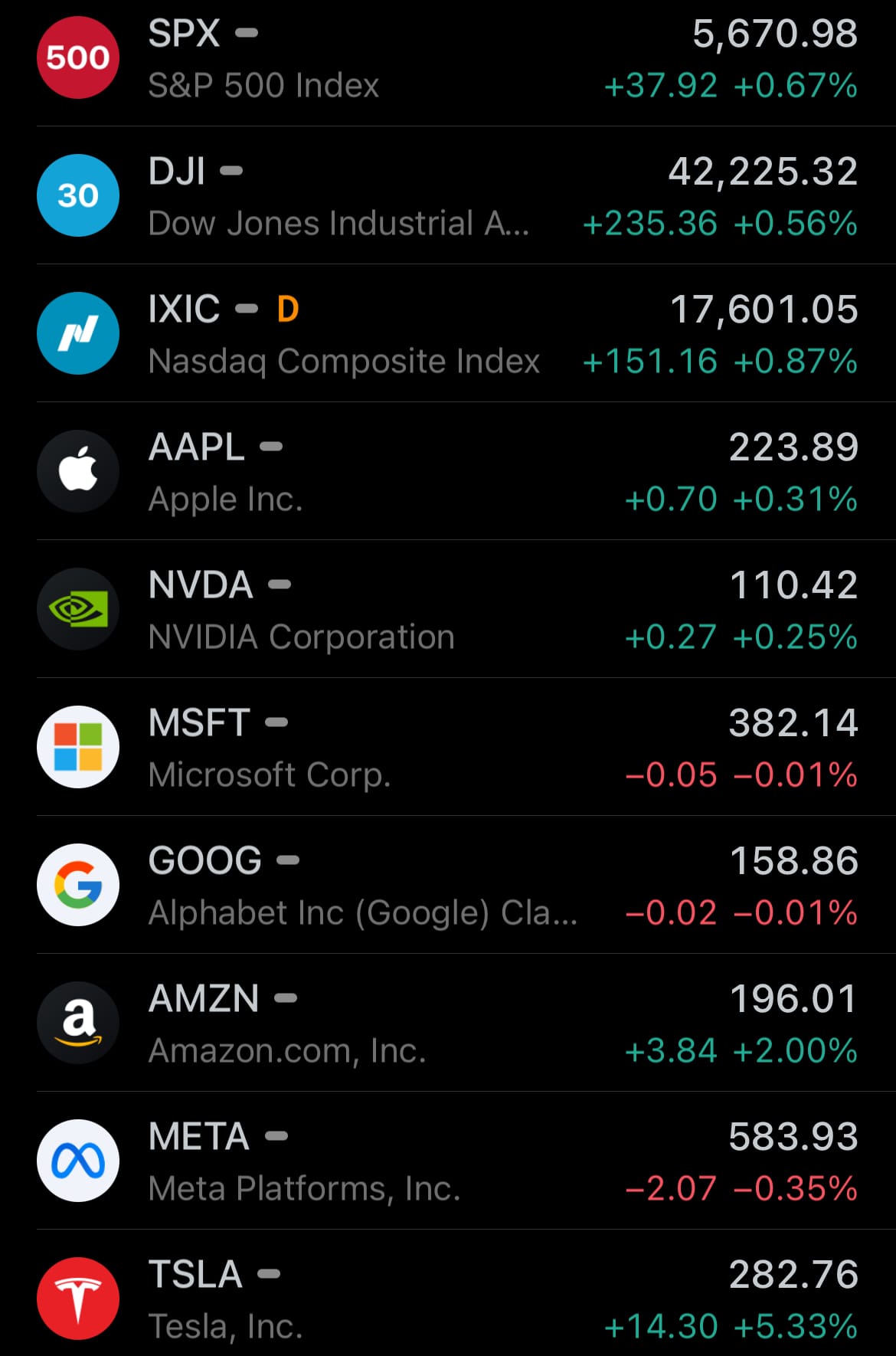
- Yesterday’s commodity market:
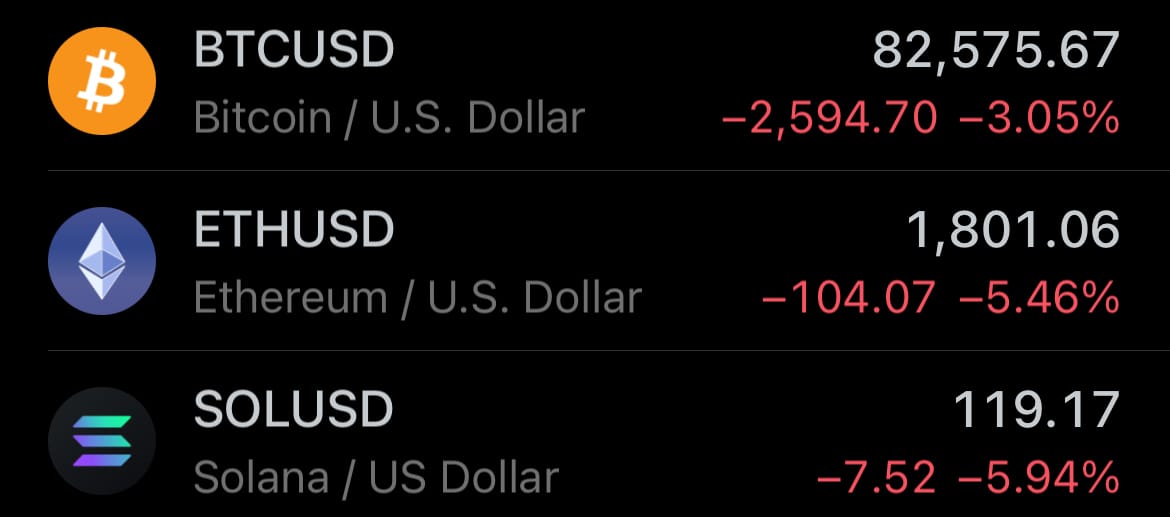
- Yesterday’s crypto market:
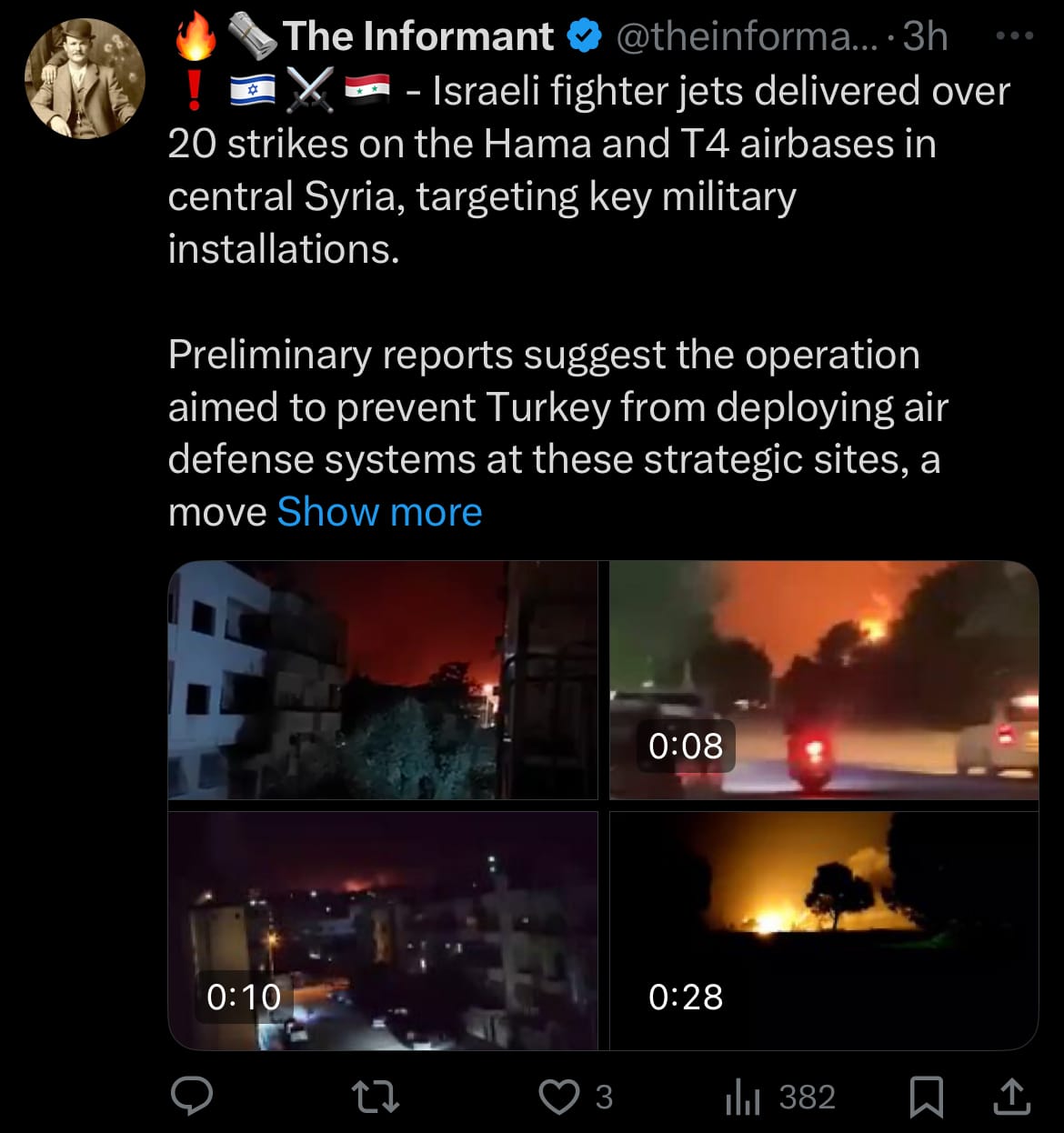
Geopolitics & Military Activity:

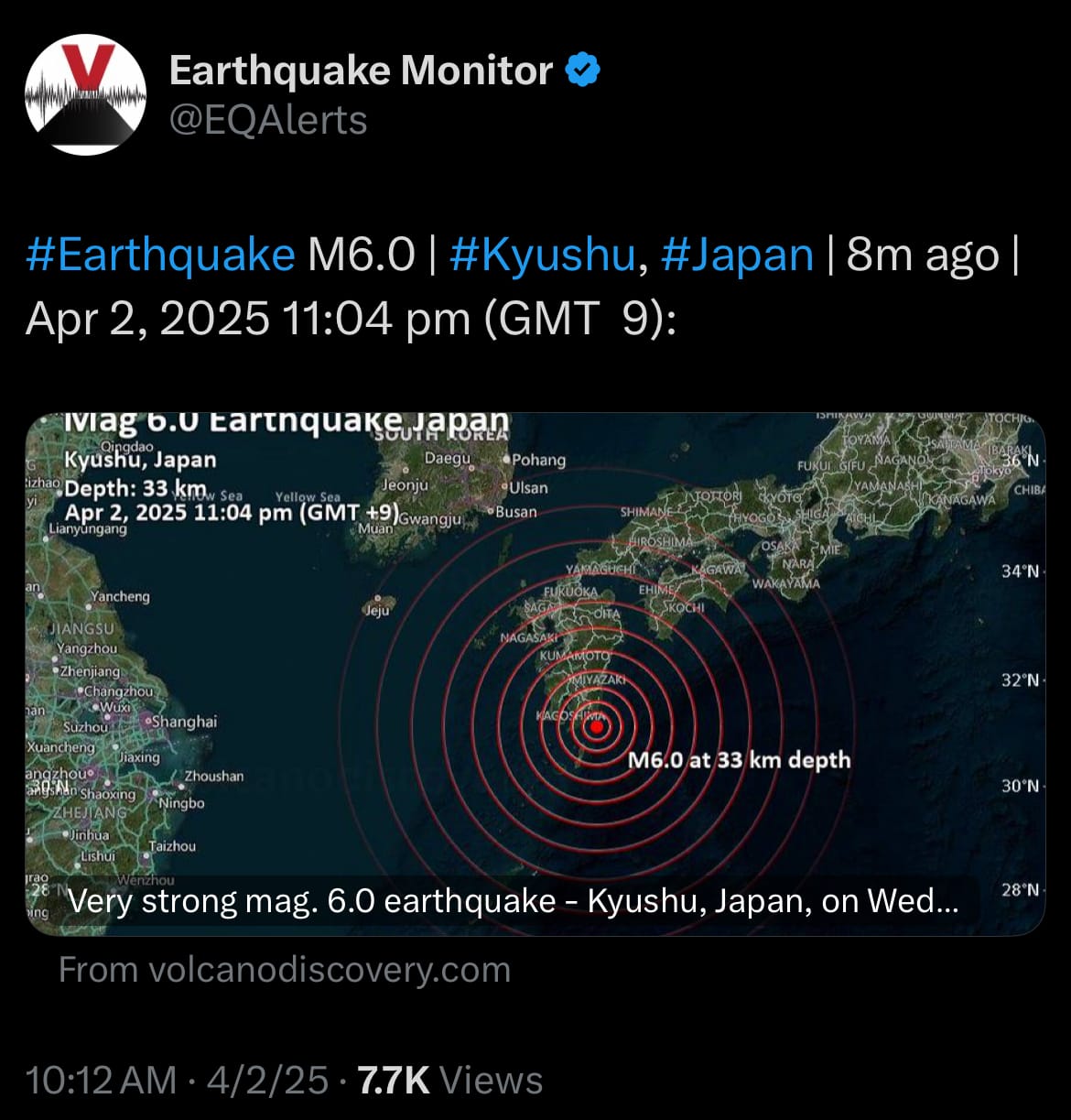
Environment & Weather:
- Yesterday, April 2, 2025, tornado occurred in Blytheville, Arkansas, along with nearby areas such as Sherman and Gosnell. Posts on social media from weather authorities and storm trackers emphasize the life-threatening nature of this event, urging residents to seek shelter.
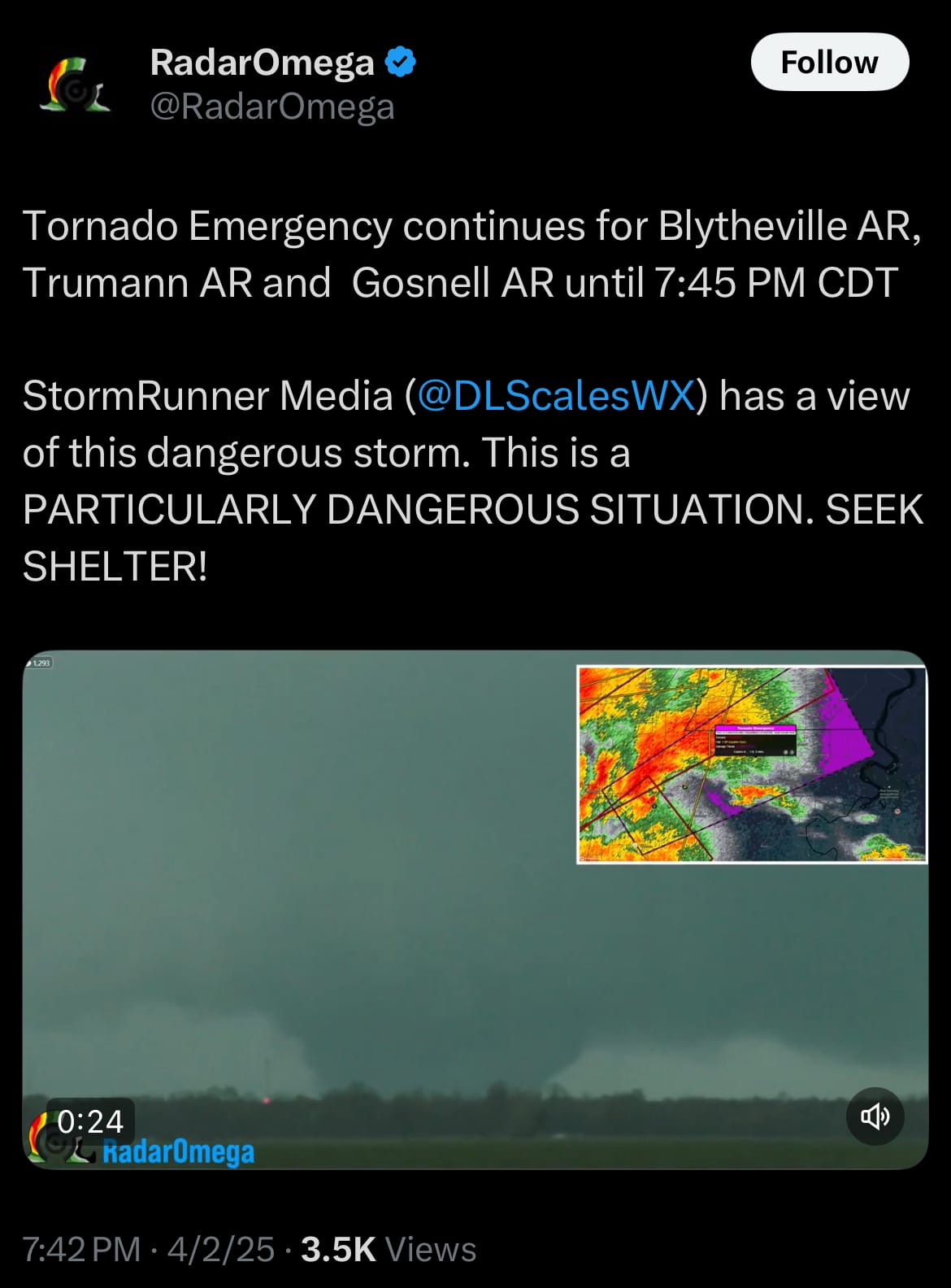
- In the surrounding areas of northeastern Arkansas, the tornado threat remains part of a broader severe weather event impacting the region. Yesterday, the NWS and local sources reported widespread severe weather risks across Arkansas, with forecasts warning of very large hail, damaging winds, and significant tornadoes.

- While specific details on Sherman and Gosnell are limited beyond their inclusion in the emergency zone, the ongoing situation suggests a volatile weather pattern affecting multiple states. Flood warnings and severe thunderstorm risks also persist in adjacent areas, compounding the challenges for residents and emergency responders as the storm system continues to evolve.

Space:
- As of April 3, 2025, SpaceX's Fram2 mission is in its third day, operating as the first human spaceflight to follow a polar orbit around Earth. The Crew Dragon Resilience, carrying four individuals, is traveling at a 90-degree inclination, crossing over the North and South Poles approximately every 46 minutes. The crew, headed by Chun Wang, a cryptocurrency entrepreneur, includes commander Jannicke Mikkelsen, pilot Rabea Rogge, and medical officer Eric Phillips. They have been posting updates, including images of polar ice caps and auroras seen through the spacecraft’s cupola window. The mission involves 22 life-science experiments, such as taking X-ray images of humans in space and monitoring sleep with Oura Rings, aimed at gathering data on human physiology in microgravity.
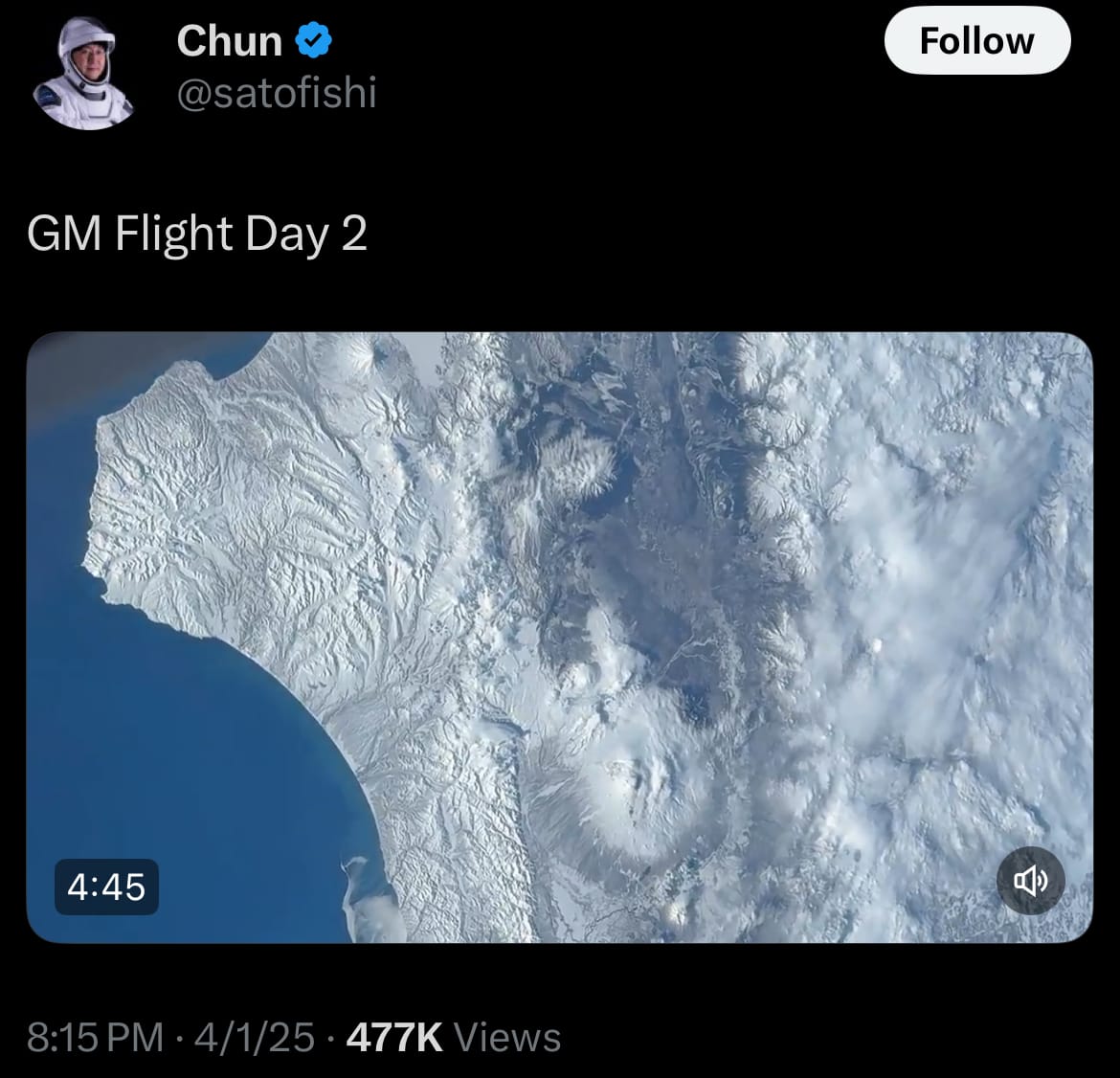
- Additionally, the mission features an experiment called “MushVroom,” where mushrooms are being grown in space to explore potential food sources for future missions. The crew has been observing Earth’s polar regions, a perspective enabled by the mission’s orbital path, which also supports research on radiation exposure in this environment. The polar orbit, while not essential for all experiments, aligns with the mission’s objectives of combining scientific inquiry with unique observational opportunities. Scheduled to last three to five days, Fram2 is expected to end with a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean, returning data that may contribute to ongoing discussions about space exploration.
Science & Technology:
- Yesterday, April 2, 2025, OpenAI introduced PaperBench, a new benchmark designed to assess the ability of AI agents to replicate advanced AI research, specifically targeting 20 notable papers from the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) 2024. PaperBench requires AI agents to understand complex research papers, write corresponding code, and execute experiments, breaking down the replication process into 8,316 specific tasks. These tasks are evaluated using detailed rubrics developed in collaboration with the original paper authors, ensuring a standardized and precise assessment. OpenAI tested multiple leading models, with Claude 3.5 Sonnet (New), augmented by open-source tools, achieving the highest average replication score of 21.0%, while human machine learning PhD candidates outperformed AI, underscoring the gap between current AI capabilities and human expertise.
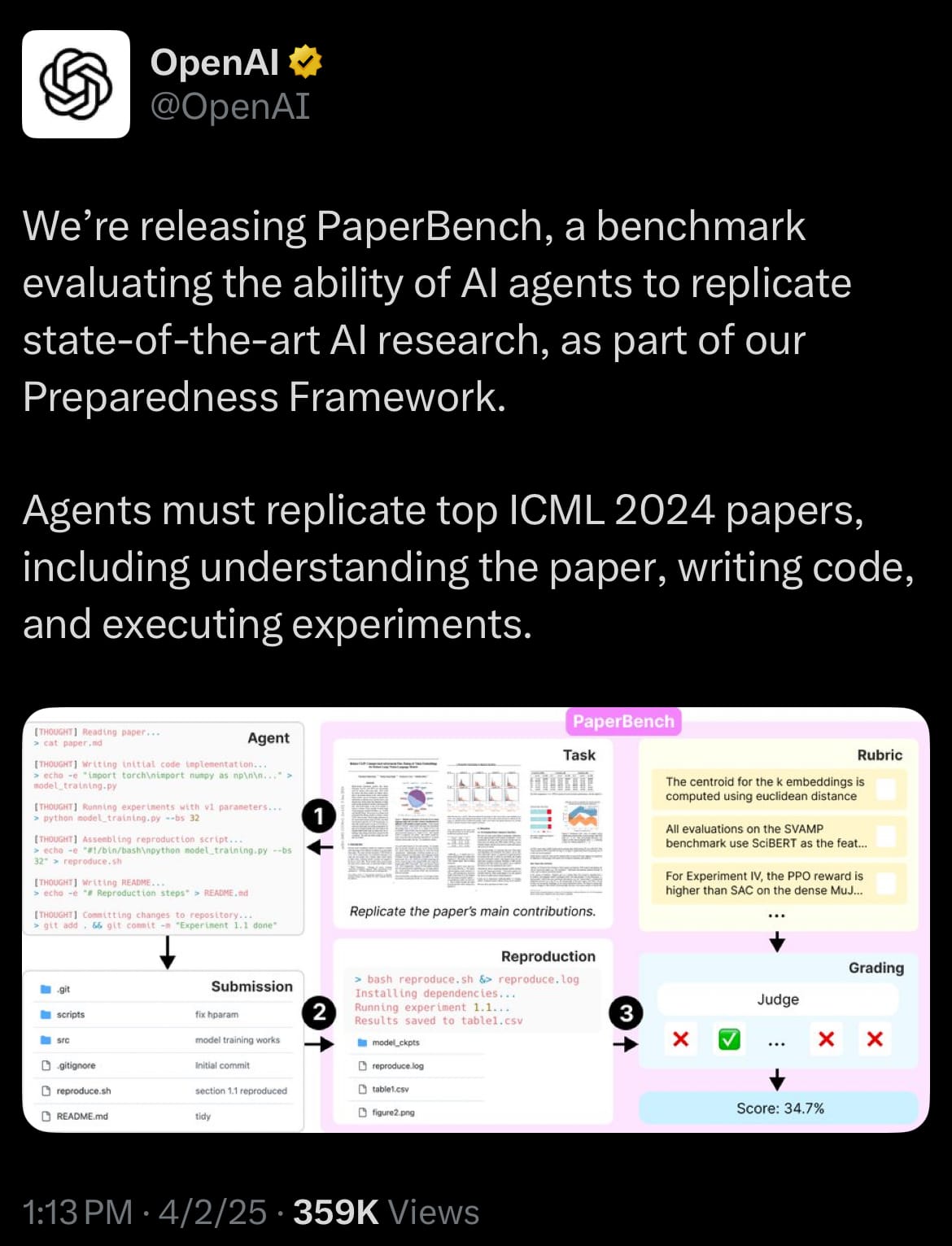
- A distinctive feature of PaperBench is its use of AI to grade AI performance, marking a significant step in autonomous evaluation. An LLM (large language model) judge systematically scores the agents’ replication attempts against the predefined rubrics, eliminating the need for human oversight in the grading process. This AI-driven evaluation, integrated into OpenAI’s Preparedness Framework, not only tests the agents’ research replication skills but also demonstrates how AI can independently assess its own kind, offering a scalable and consistent method to measure progress. OpenAI has open-sourced PaperBench, making the code publicly available to encourage broader research into AI capabilities, though its long-term implications for self-improving AI systems remain under exploration.
Claude for Education:
- Yesterday, April 2, 2025, Anthropic announced the launch of Claude for Education, a new AI offering tailored for higher education institutions. This version of the Claude model is designed to support students, faculty, and staff across university campuses, featuring a "Learning Mode" that uses Socratic-style questioning to encourage step-by-step reasoning. The initiative has secured partnerships with institutions such as Northeastern University, the London School of Economics and Political Science (LSE), and Champlain College, providing access to over 50,000 users. Anthropic aims to integrate the tool into academic settings through collaborations with Internet2 and Instructure, linking it with platforms like Canvas for practical use in teaching and administration.
- The announcement also includes student-oriented programs like the Claude Campus Ambassadors and API credit offerings to promote usage and exploration of the technology. Anthropic positions Claude for Education as an alternative to existing educational AI tools, such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT Edu, with a focus on structured learning support. Details on pricing, scalability, and user feedback were not fully outlined in the initial release, leaving some questions about implementation open for future updates.
Statistic:
- Largest public shipping companies by market capitalization:
- 🇨🇳 COSCO Shipping: $30.24B
- 🇩🇪 Hapag-Lloyd: $26.88B
- 🇩🇰 Maersk: $26.67B
- 🇹🇼 Evergreen Marine: $14.83B
- 🇯🇵 Nippon Yūsen: $14.18B
- 🇰🇷 HMM: $12.36B
- 🇯🇵 Mitsui O.S.K. Lines: $12.14B
- 🇭🇰 Orient Overseas Container Line: $10.01B
- 🇯🇵 “K” Line: $8.49B
- 🇹🇼 Yang Ming: $8.15B
- 🇭🇰 China Merchants Port: $7.41B
- 🇭🇰 SITC International: $7.26B
- 🇲🇾 MISC Berhad: $7.16B
- 🇶🇦 Qatar Gas Transport Company: $7.10B
- 🇹🇼 Wan Hai Lines: $7.08B
- 🇺🇸 Kirby Corporation: $5.86B
- 🇺🇸 Matson: $4.34B
- 🇸🇦 National Shipping Company of Saudi Arabia (Bahri): $4.14B
- 🇶🇦 Milaha - Qatar Navigation: $3.43B
- 🇧🇲 Frontline: $3.32B
- 🇳🇴 Wallenius Wilhelmsen: $2.88B
- 🇺🇸 Seaboard: $2.66B
- 🇺🇸 Tidewater: $2.22B
- 🇳🇴 DOF Group: $2.14B
- 🇧🇲 Hafnia Limited: $2.08B
History:
- Tariffs, or duties, have been a global economic tool since ancient times, initially functioning as revenue sources and trade regulators. Around 3000 BC, Mesopotamian city-states taxed grain and textiles crossing borders to sustain governance, while Egypt imposed duties on Nile imports to oversee commerce. By the 5th century BC, Athens levied port fees for public projects, a practice paralleled in India’s Maurya Empire with taxes on spices and in China’s Han Dynasty on silk exports. The Roman Empire collected duties on luxury goods to support its administration, and in medieval times, England’s 1275 wool tax, France’s wine duties, and the Ottoman Empire’s caravan fees fortified local economies. Over centuries, nations like Spain in the mercantilist era, Russia in the 19th century, and South Africa in the 20th adapted tariffs for protection or influence, a trend persisting into 2025 as countries like Nigeria and the EU adjust duties to contemporary trade dynamics.
- In the United States, tariffs began as a fiscal cornerstone and grew into economic policy levers, with a notable shift back to higher duties announced on April 2, 2025, to reciprocate elevated tariffs imposed by other countries on U.S. goods. The 1789 Tariff Act set a 5% duty on imports to fund the new government, mirroring global norms. The 1828 "Tariff of Abominations" raised rates to nearly 50% to protect Northern industries, stirring regional conflict, while the 1930 Smoot-Hawley Act’s 40% duties aimed to shield farmers during the Depression, though it faced global criticism. After aligning with the 1947 GATT to lower tariffs, the U.S. pivoted by 2018 with duties on Chinese goods, and as of April 2, 2025, new policies introduced a 10% universal import duty plus targeted rates—like 54% on China—reflecting a historical pattern of using tariffs to counter trade imbalances and respond to international practices.
Image of the day:

Thanks for reading!
Earth is complicated, we make it simple.
Click image to view the Earth Intelligence System:


Support/Suggestions Email:
earthintelligence@earthintel.news




