Wednesday☕️

Trending:
- On December 9, 2025, Russia's State Duma issued a directive for all employees to transition to remote work amid a nationwide surge in influenza A(H3N2), commonly known as the Hong Kong flu, which now accounts for over 80% of detected cases according to Rospotrebnadzor. The measure aims to curb transmission in crowded government facilities, following a rapid escalation since November that began in the Far East, Siberia, Urals, and central regions before spreading to Moscow and other areas.
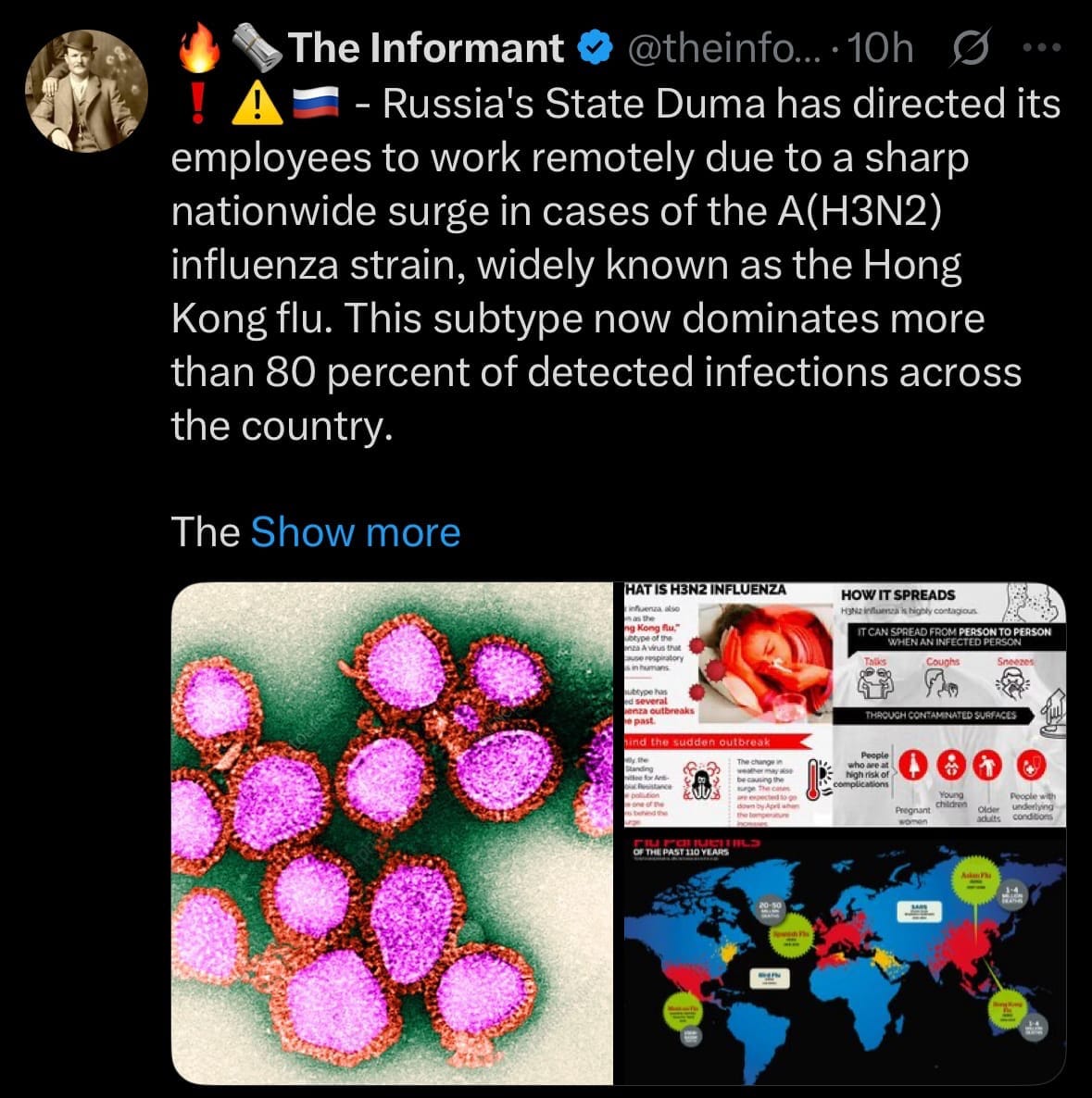
- Rospotrebnadzor reported a several-fold weekly increase in infections, with over 23,400 confirmed influenza cases in recent weeks, and experts anticipate the peak around the New Year holidays in early 2026. The highly transmissible virus spreads via respiratory droplets and can cause severe complications such as pneumonia, sinusitis, ear infections, and neurological issues, posing the highest risks to elderly individuals, young children, pregnant women, and infants.
Economics & Markets:
- Yesterday’s U.S. stock market:

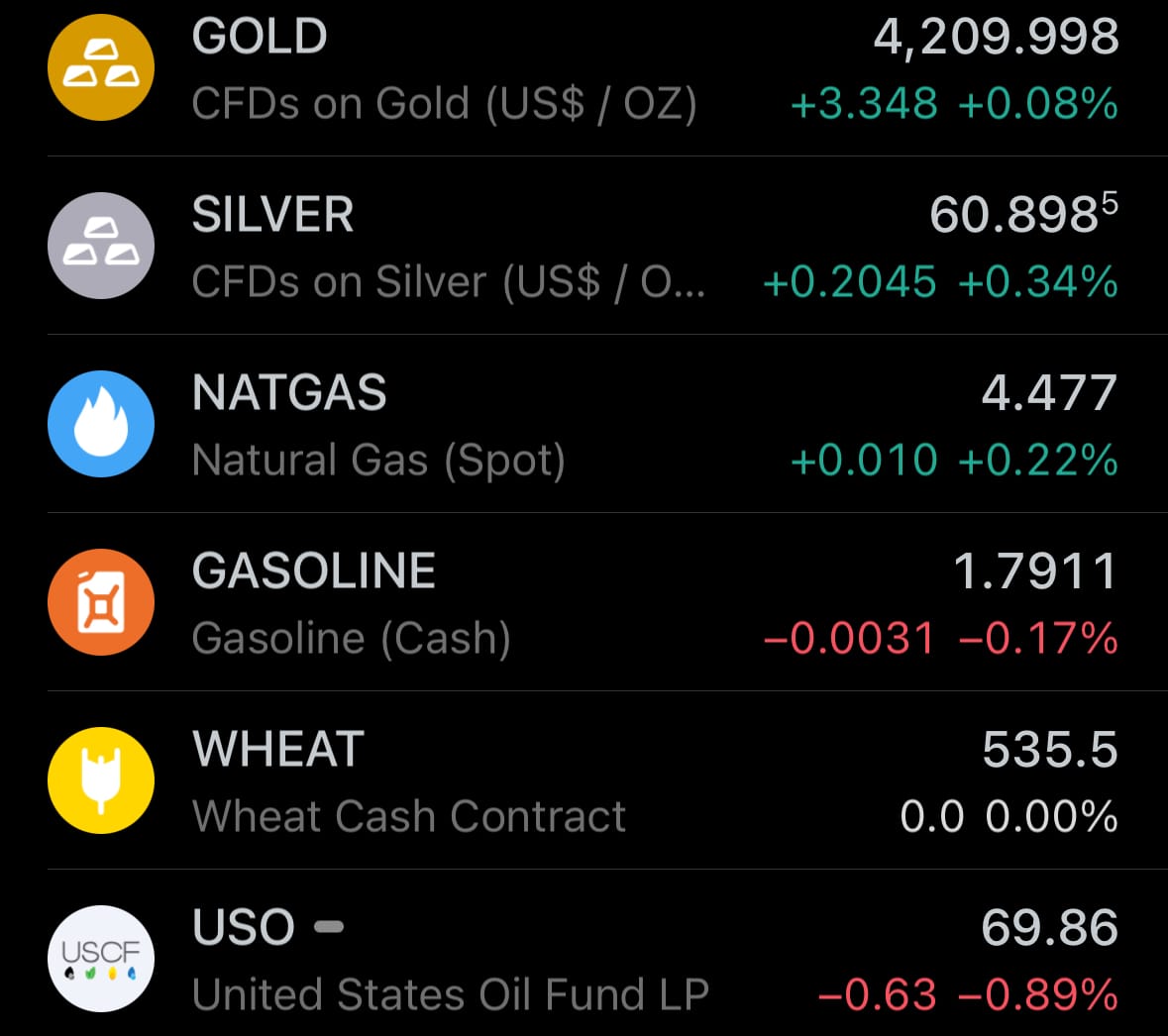
- Yesterday’s commodity market:
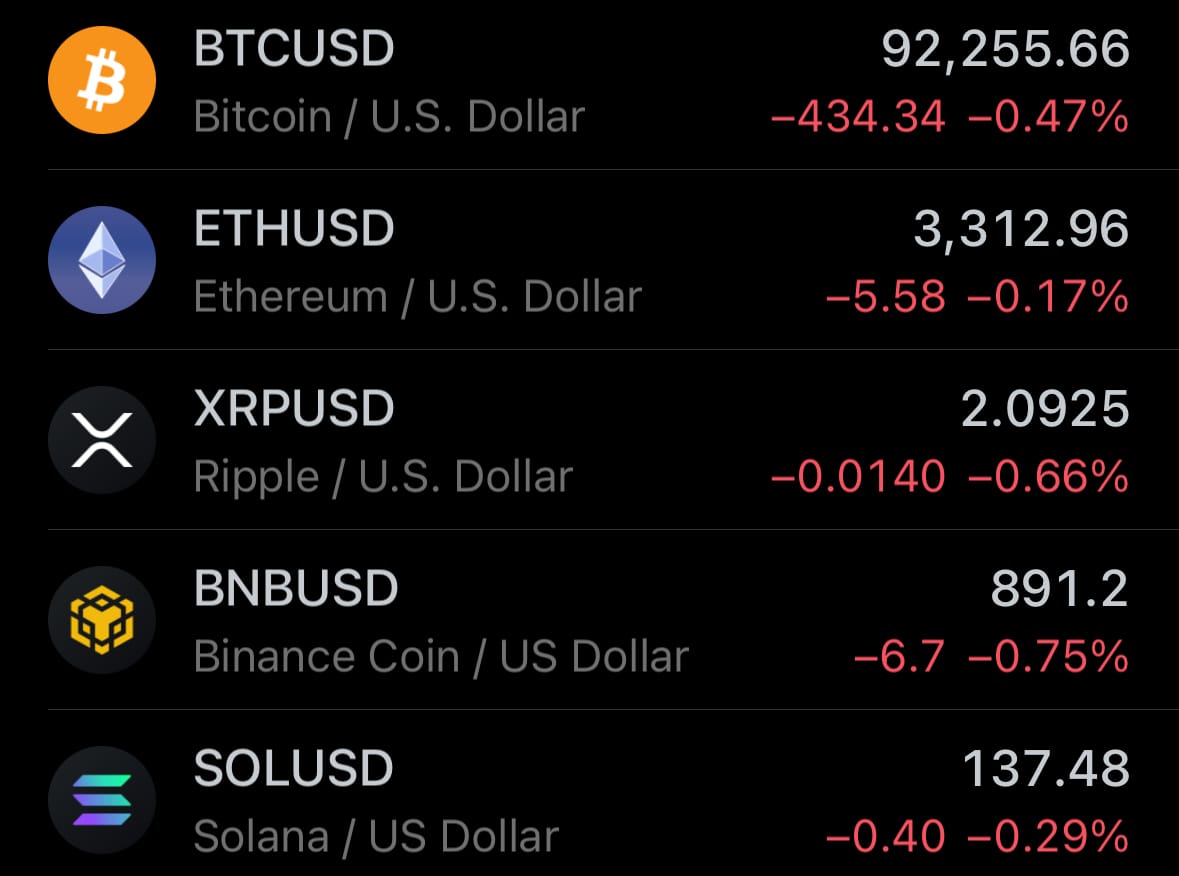
- Yesterday’s crypto market:
Space:
- On December 9, 2025, SpaceX successfully launched the classified NROL-77 mission for the U.S. National Reconnaissance Office aboard a Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Liftoff occurred at 2:16 p.m. EDT (1916 UTC), with the two-stage vehicle ascending on a northeasterly trajectory over the Atlantic Ocean. This was SpaceX's 159th Falcon 9 mission of 2025 and the third NROL launch for the year, partnering with the U.S. Space Force Space Systems Command under the National Security Space Launch program.
- The NROL-77 payload, designed, built, and operated by the NRO, remains classified, though it is suspected to include a next-generation Naval Ocean Surveillance System (NOSS) satellite for tracking naval vessels and submarines through signals intelligence. The operation highlights the NRO's reliance on commercial launch providers for rapid, assured access to space, completing its 10th and final mission of 2025 amid broader U.S. efforts to modernize reconnaissance capabilities.
TJSW-22
- On December 9, 2025, China conducted a classified launch of the TJSW-22 satellite from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center in Sichuan province aboard a Long March 3B/E rocket. Liftoff occurred at 10:10 a.m. EST (1510 UTC) from Launch Complex 2, with the three-stage vehicle ascending on a southeast trajectory toward geostationary transfer orbit. TJSW-22, or Tongxin Jishu Shiyan Weixing-22 (Communication Technology Experimental Satellite-22), is part of a secretive series suspected by Western analysts of supporting military functions, including signals intelligence gathering, early warning detection, and potential satellite inspection or interference capabilities.
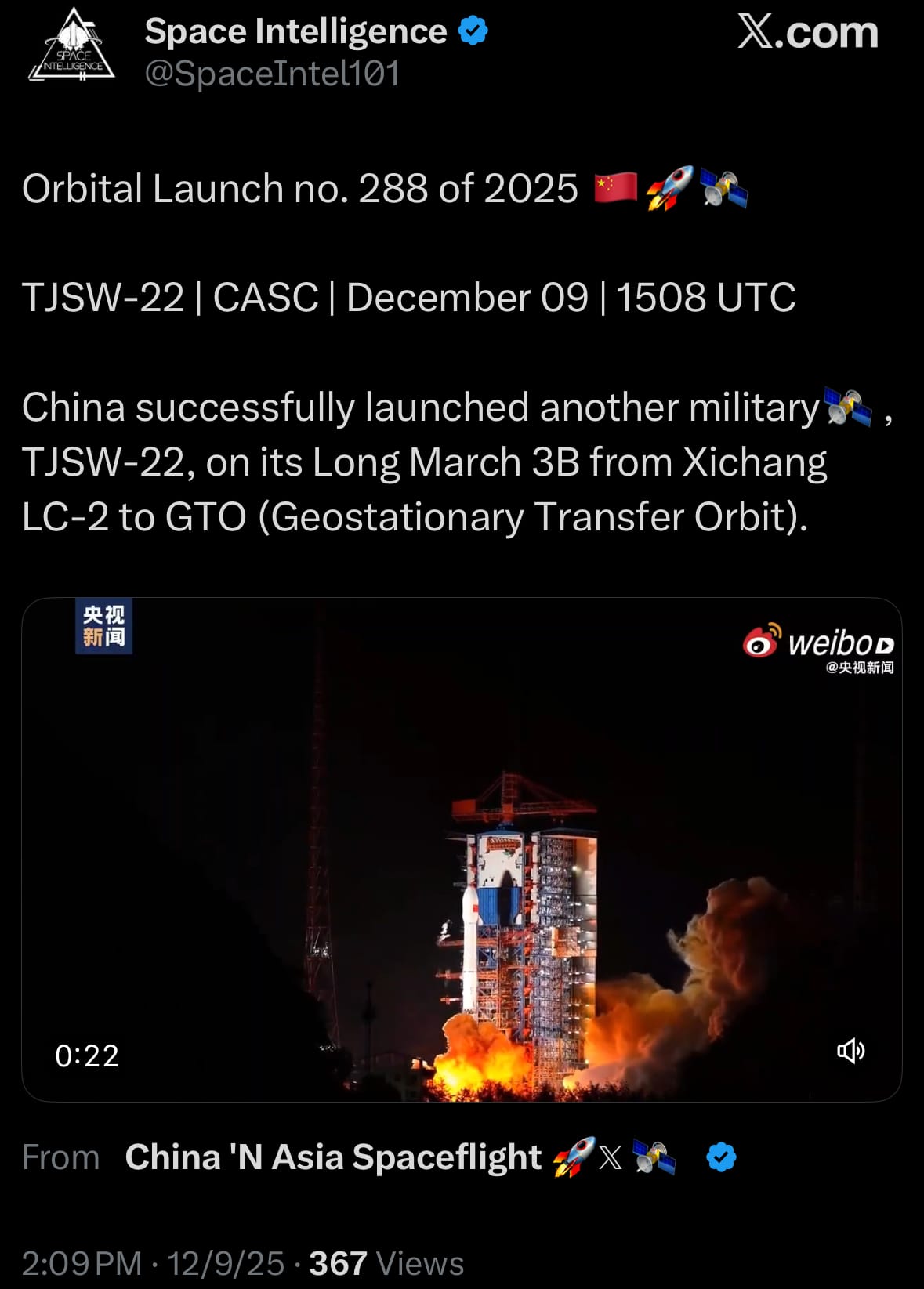
- Built on a geostationary platform with possible large-aperture antennas for broadband Ka-band testing, it follows similar missions like TJSW-21 launched in November and aligns with the People's Liberation Army's efforts to enhance space-based reconnaissance. Specific orbital details and capabilities remain undisclosed, consistent with the program's opacity.
Science & Technology:
- On December 9, 2025, U.S. Secretary of War Pete Hegseth announced the launch of GenAI.mil, a new Department of War platform providing generative AI tools to approximately 3 million military personnel, civilians, and contractors. The initiative, described by Hegseth as embedding frontier AI models directly into daily operations, begins with Google Cloud's Gemini for Government as the primary model, accessible via a secure website requiring a Common Access Card for authentication. Hegseth stated in a video and memo that the platform aims to enhance efficiency in tasks like research, document formatting, video and imagery analysis, and administrative workflows, while emphasizing that all tools are certified for Controlled Unclassified Information (IL-5 level) and do not use DoW data to train public models.
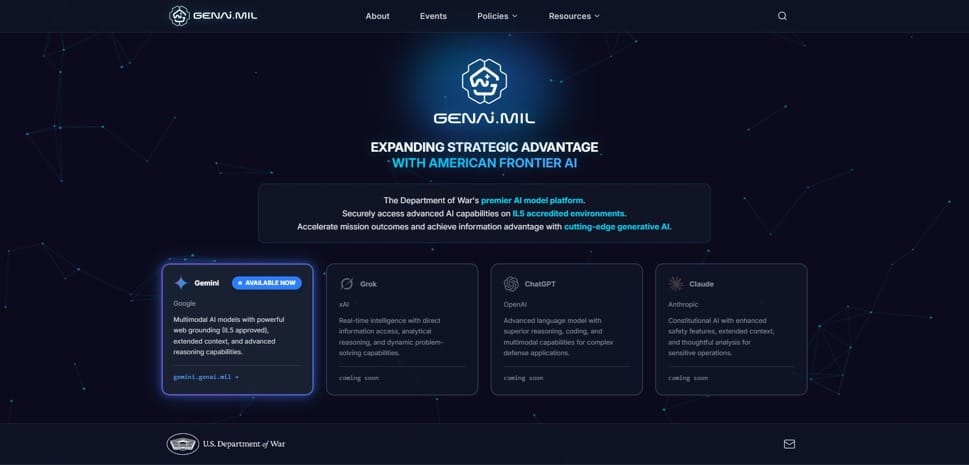
- The rollout includes free training for all users and plans to integrate additional AI capabilities from partners like xAI, OpenAI, and Anthropic, following a July 2025 Google contract and President Trump's mandate for AI superiority. Under Secretary for Research and Engineering Emil Michael highlighted its potential for intelligence analysis, logistics, and simulations, positioning it as a "culture change" to counter adversaries' technological advances.
Statistic:
- Largest public financial service companies by market capitalization:
- 🇺🇸 JPMorgan Chase: $826.32B
- 🇺🇸 Visa: $633.71B
- 🇺🇸 Mastercard: $485.95B
- 🇨🇳 Agricultural Bank of China: $398.40B
- 🇺🇸 Bank of America: $396.56B
- 🇨🇳 ICBC: $351.40B
- 🇨🇳 China Construction Bank: $345.94B
- 🇺🇸 Morgan Stanley: $285.47B
- 🇺🇸 Wells Fargo: $284.75B
- 🇨🇳 Bank of China: $266.42B
- 🇺🇸 Goldman Sachs: $265.35B
- 🇺🇸 American Express: $253.23B
- 🇬🇧 HSBC: $243.03B
- 🇨🇦 Royal Bank Of Canada: $229.28B
- 🇺🇸 Citigroup: $201.44B
- 🇮🇳 HDFC Bank: $180.33B
- 🇯🇵 Mitsubishi UFJ Financial: $177.45B
- 🇦🇺 Commonwealth Bank: $171.66B
- 🇺🇸 Charles Schwab: $170.92B
- 🇯🇵 SoftBank: $170.68B
- 🇨🇳 CM Bank: $168.51B
- 🇪🇸 Santander: $162.04B
- 🇨🇦 Toronto Dominion Bank: $152.60B
- 🇺🇸 S&P Global: $149.81B
- 🇺🇸 Capital One: $147.60B
History:
- Charles Schwab’s history begins in 1971, when Charles R. Schwab founded a small investment advisory newsletter called Investment Indicator in San Francisco. Later that year he restructured it into First Commander Corporation, a brokerage subsidiary that offered investment services at a time when Wall Street was tightly regulated and operated under fixed, universally mandated trading commissions. Schwab believed that small investors were underserved, and when the U.S. government deregulated brokerage commissions on May 1, 1975 (“May Day”), he acted faster than almost anyone else. He transformed his small firm into one of the country’s first discount brokerages, cutting fees drastically and focusing on execution rather than salesmanship—an approach that contrasted sharply with the entrenched, relationship-driven model used by major firms like Merrill Lynch and Dean Witter. Through the late 1970s and 1980s, Schwab pioneered multiple consumer-facing innovations: “no-advice” trading, toll-free 24-hour order entry (1979), computer-automated quote systems, and by 1984, the Schwab One account, which combined checking, a debit card, and a brokerage account into a single financial instrument. By 1987, Schwab became the largest discount broker in the United States. During the 1990s, the company accelerated its technological focus—launching TeleBroker in 1989, Mutual Fund Marketplace, and Schwab.com online trading in 1996, giving retail investors tools that previously existed only for professionals. Throughout these decades Schwab grew not by speculation or high-risk strategies but by systematically lowering barriers to entry for individual investors.
- From the early 2000s to today, Schwab evolved into a diversified financial giant. It expanded into banking during the early 2000s, added institutional custody services for independent advisors, and pushed aggressively into index-based investing and ETFs. After the 2008 financial crisis, Schwab strengthened its advisory services and launched Schwab Intelligent Portfolios in 2015, one of the first large-scale automated investment platforms (“robo-advisors”) from a major brokerage. In 2019, Schwab catalyzed an industry-wide transformation by cutting online trading commissions to zero, forcing virtually every major competitor—E*TRADE, TD Ameritrade, and even full-service firms—to match the move. In 2020, Schwab completed a landmark $26 billion acquisition of TD Ameritrade, integrating one of the largest active-trading platforms into the Schwab ecosystem. By the mid-2020s, Schwab oversaw trillions in client assets across brokerage, retirement, ETFs, advisory, and bank deposits, and its market capitalization rose to roughly $170 billion, placing it among the largest financial services firms in U.S. history. Today, Schwab remains a central pillar of American retail investing—not because it sought to replace Wall Street’s traditional brokers, but because it systematically widened access to investing, embraced new technologies early, and built an infrastructure capable of serving both everyday investors and large advisory institutions. Its rise reflects a broader transformation in U.S. finance: from high-cost, relationship-based brokerage models to low-cost, high-volume digital platforms that define the modern investment landscape.
Image of the day:
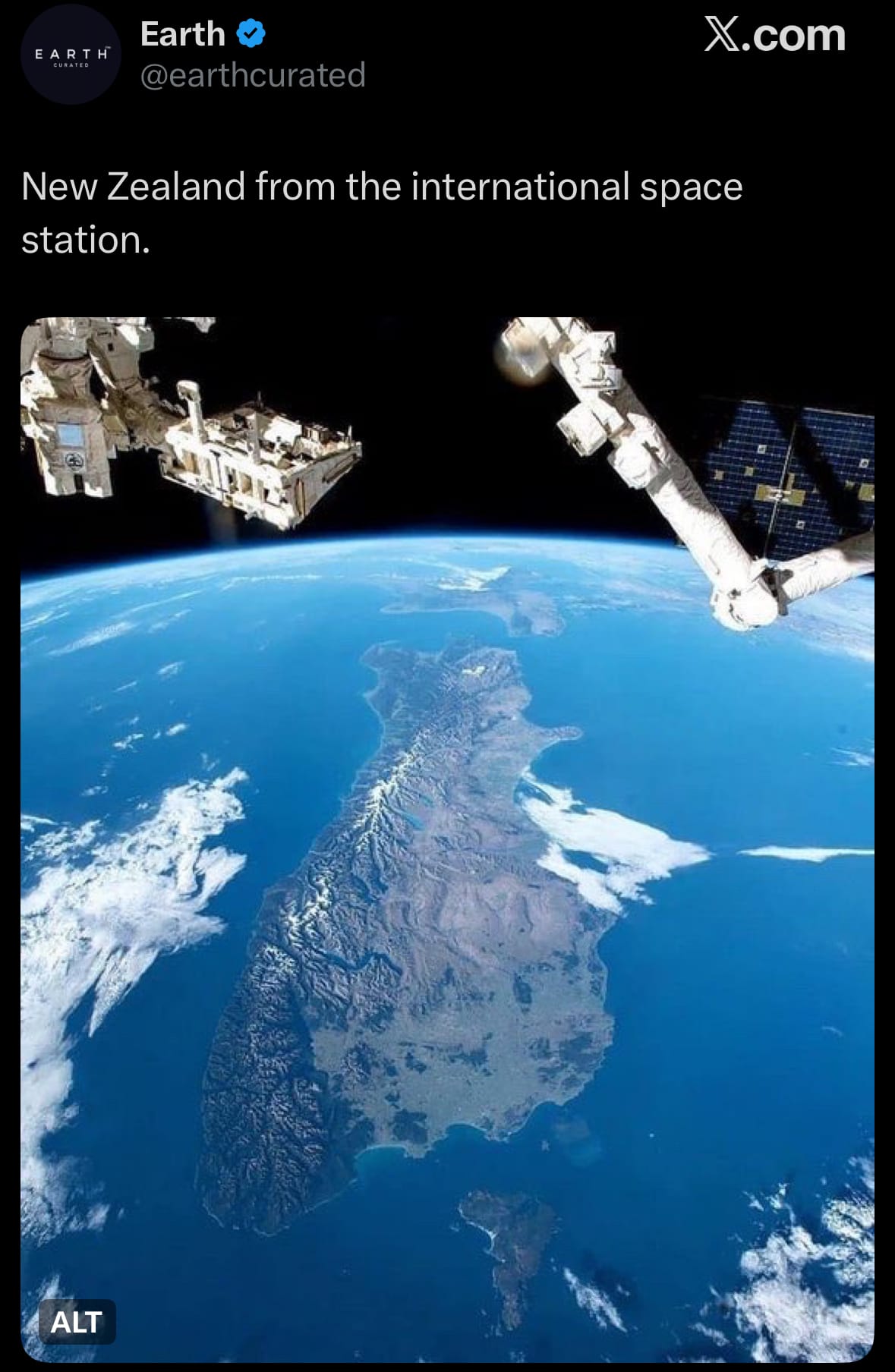
Thanks for reading! Earth is complicated, we make it simple.

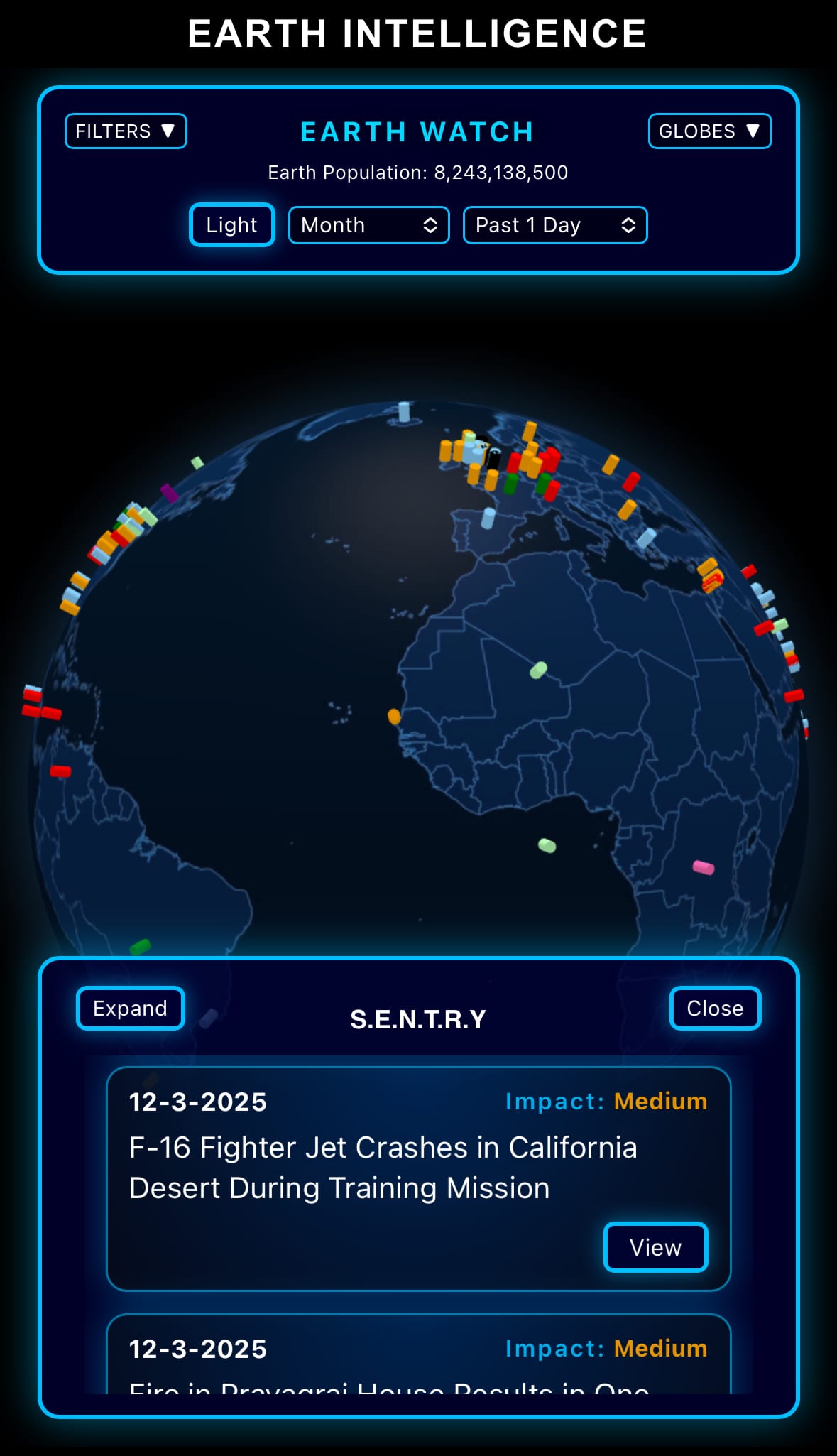
- Click below if you’d like to view our free EARTH WATCH globe:
- Download our mobile app on the Apple App Store (Android coming soon):

Click below to view our previous newsletters:

Support/Suggestions Email:
earthintelligence@earthintel.news




