Wednesday☕️

Trending:
- On February 10, 2026, Tavus launched Raven-1, a new AI model built to make conversational AI understand people more like humans do—by paying attention to both words and how someone actually looks and sounds. Unlike most AI that mainly reads text or just hears spoken words, Raven-1 watches video and listens to audio at the same time in real time. It picks up on tone of voice, speed of talking, laughs, pauses, facial expressions, gestures, body language, and even the surroundings.
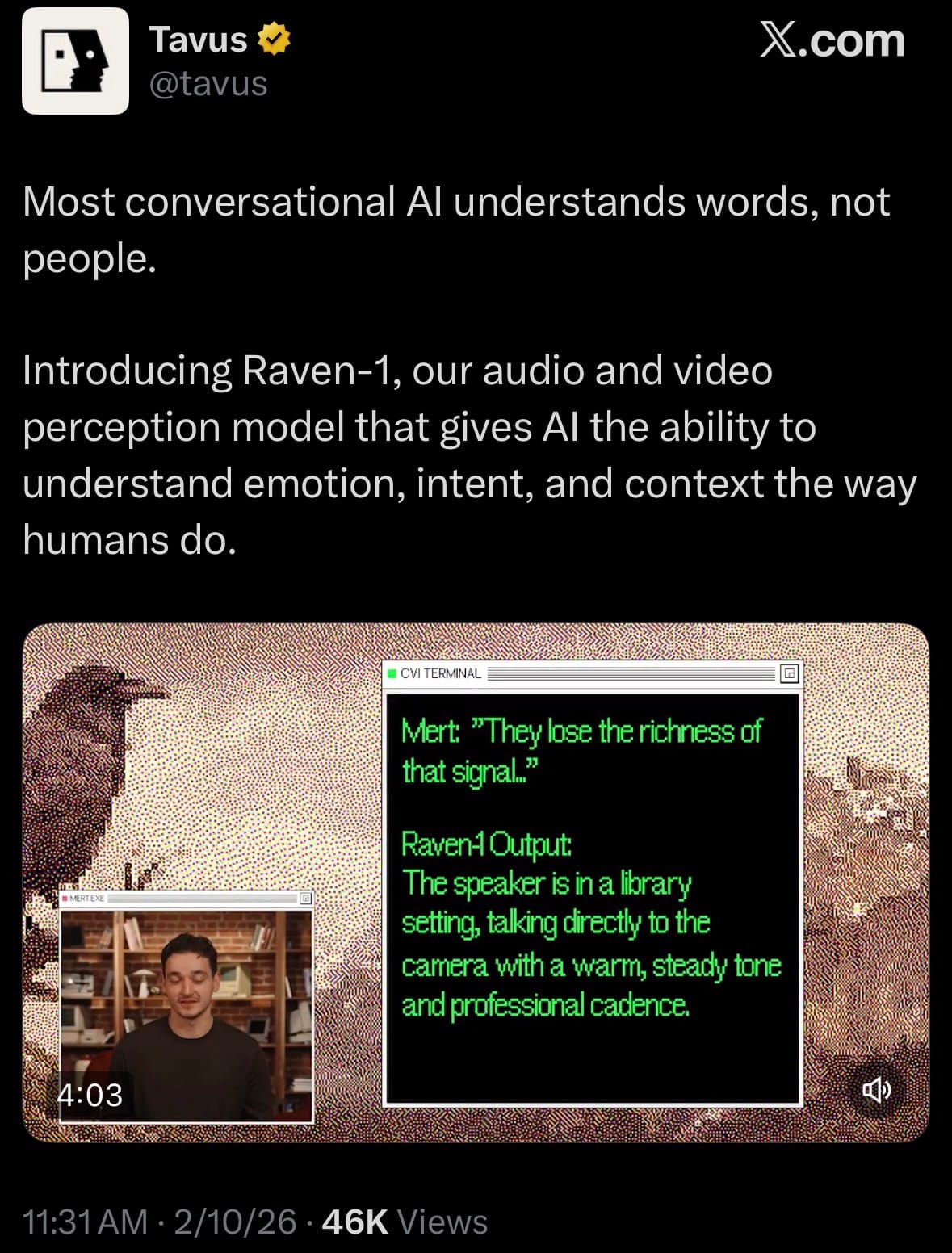
- It uses all these clues to figure out emotions, sarcasm, hidden frustration, hesitation, or true intent, then describes everything in clear, natural sentences instead of simple labels like “angry” or “happy.” This helps AI respond in a much more natural and understanding way. Raven-1 processes quickly (around 15 video frames per second plus audio), works with live conversations, and is already powering Tavus’s AI avatars and voice features. A public demo is available now for anyone to test.
Economics & Markets:
- Yesterday’s U.S. stock market:

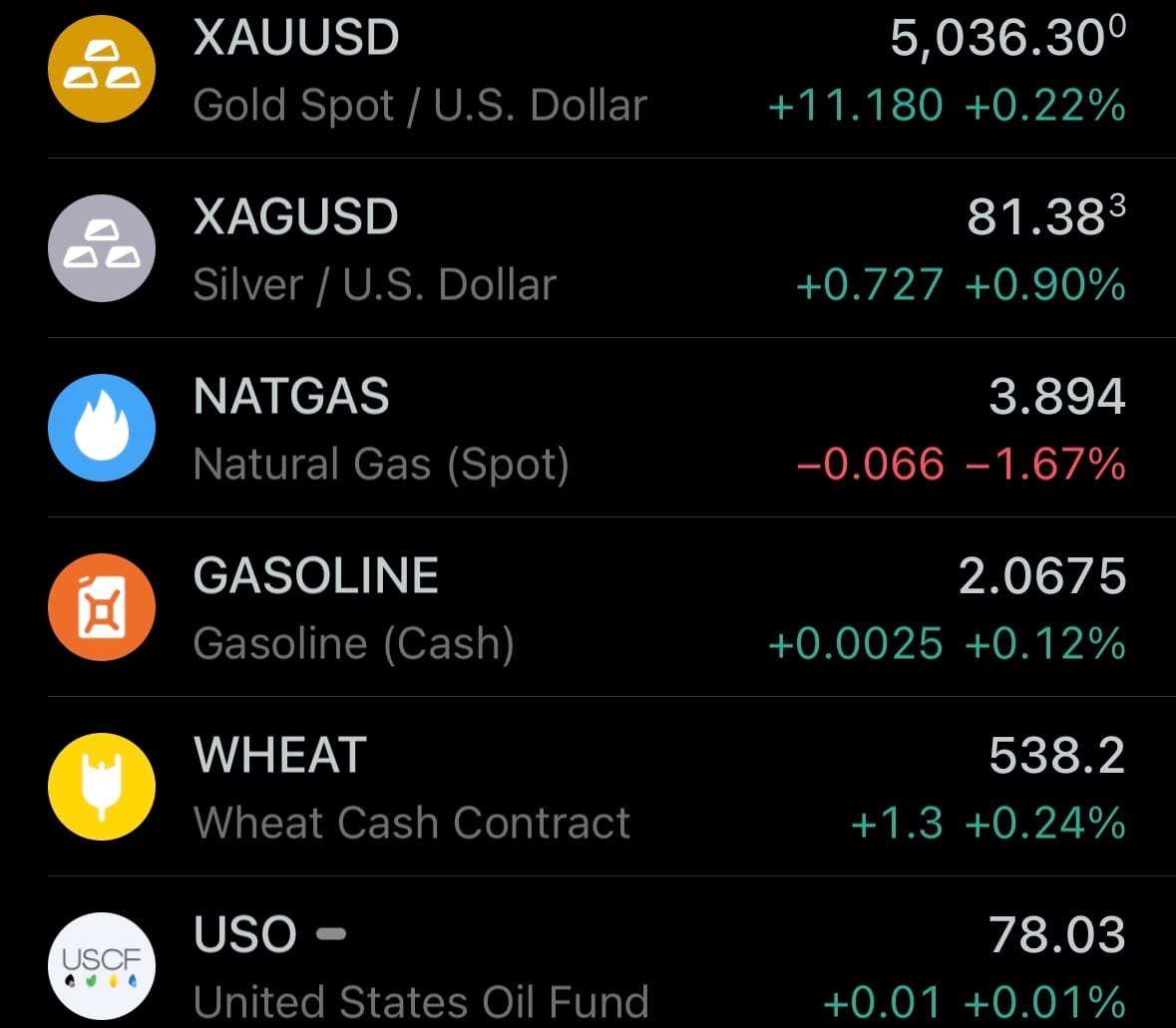
- Yesterday’s commodity market:
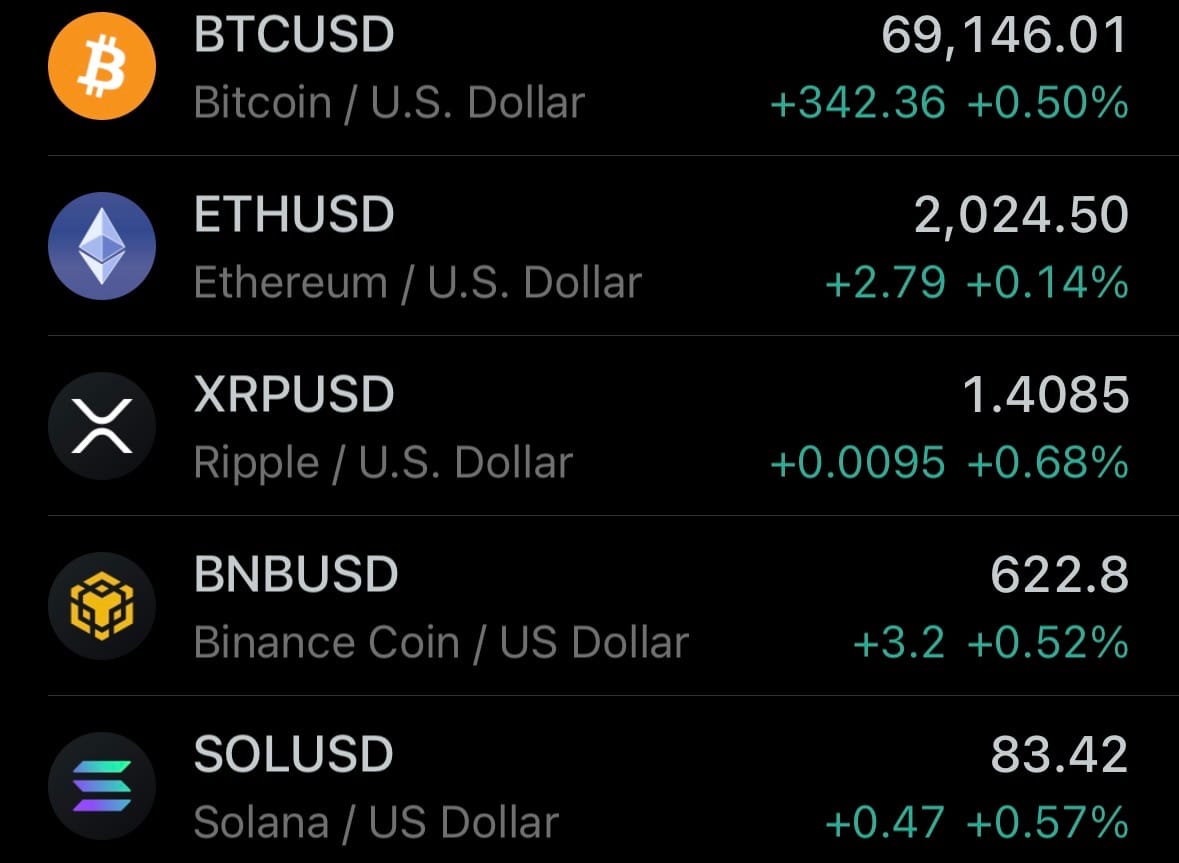
- Yesterday’s crypto market:
Geopolitics & Military Activity:

Business:
- February 10, 2026 – Palantir Technologies announced a multi-year extension of its strategic partnership with Airbus, originally established in 2015. The collaboration focuses on Palantir’s ongoing role in supporting Skywise, Airbus’s open data platform for the civil aviation industry. Skywise supports data-driven decision-making in planning, supply chain management, airline operations, aircraft production, and aircraft maintenance, and is currently used by over 50,000 daily active users.

- The extended agreement ensures continued provision of Palantir’s scalable and secure software infrastructure to Airbus and its airline customers. It specifically includes access to AI-enabled tools that integrate multiple large language models to improve efficiency in manufacturing processes, supply chain operations, aircraft maintenance, and flight operations. The contract also covers support for migrating relevant workloads to sovereign cloud environments to meet data residency and regulatory requirements in different regions.
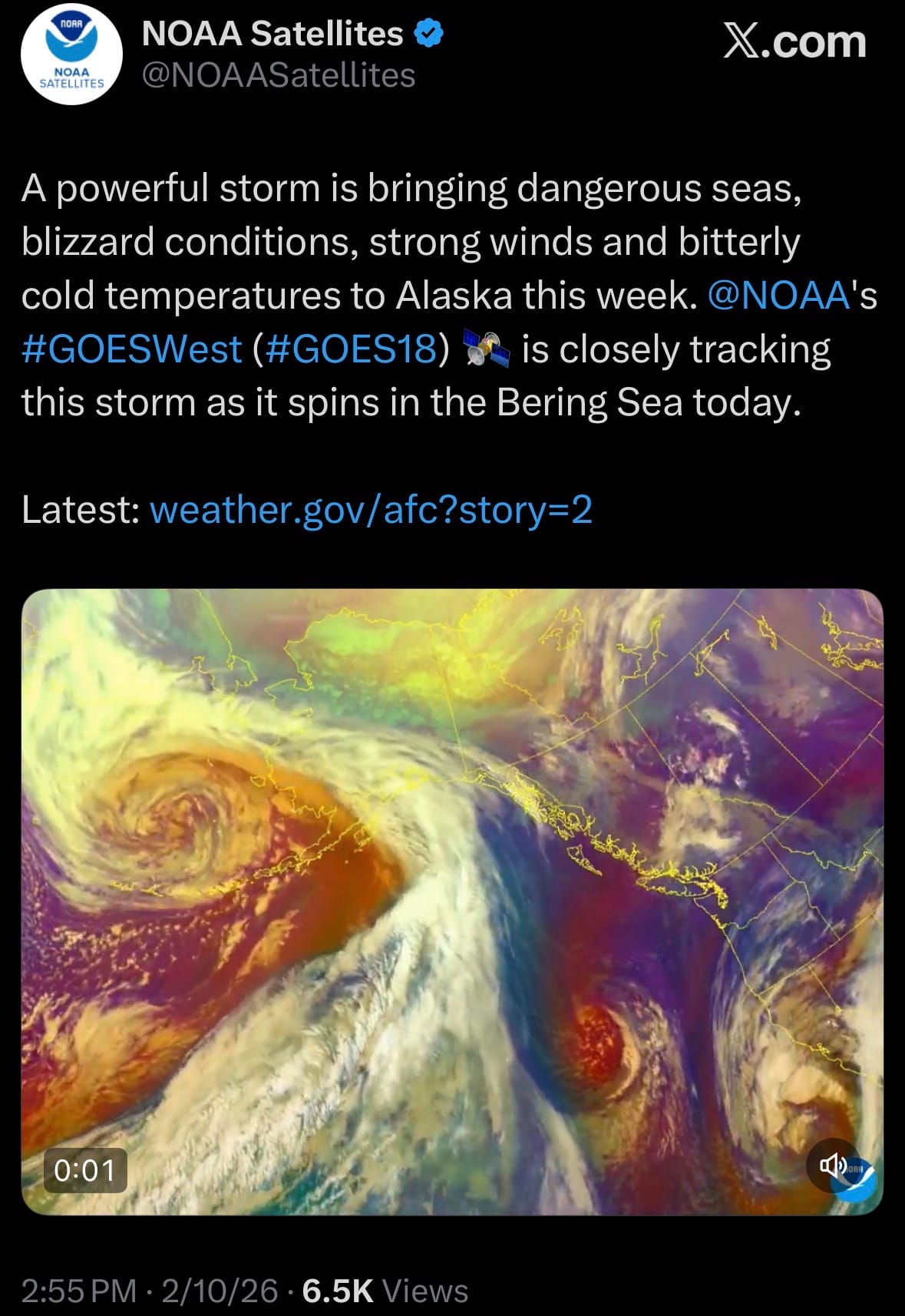
Environment & Weather:
Science & Technology:
- February 10, 2026 – OpenAI has released an update to the Deep Research feature in ChatGPT, introducing several enhancements aimed at improving accuracy, control, and usability for in-depth queries. The update enables users to connect Deep Research to external apps (including those via MCP) and restrict searches to specific trusted websites or sources.
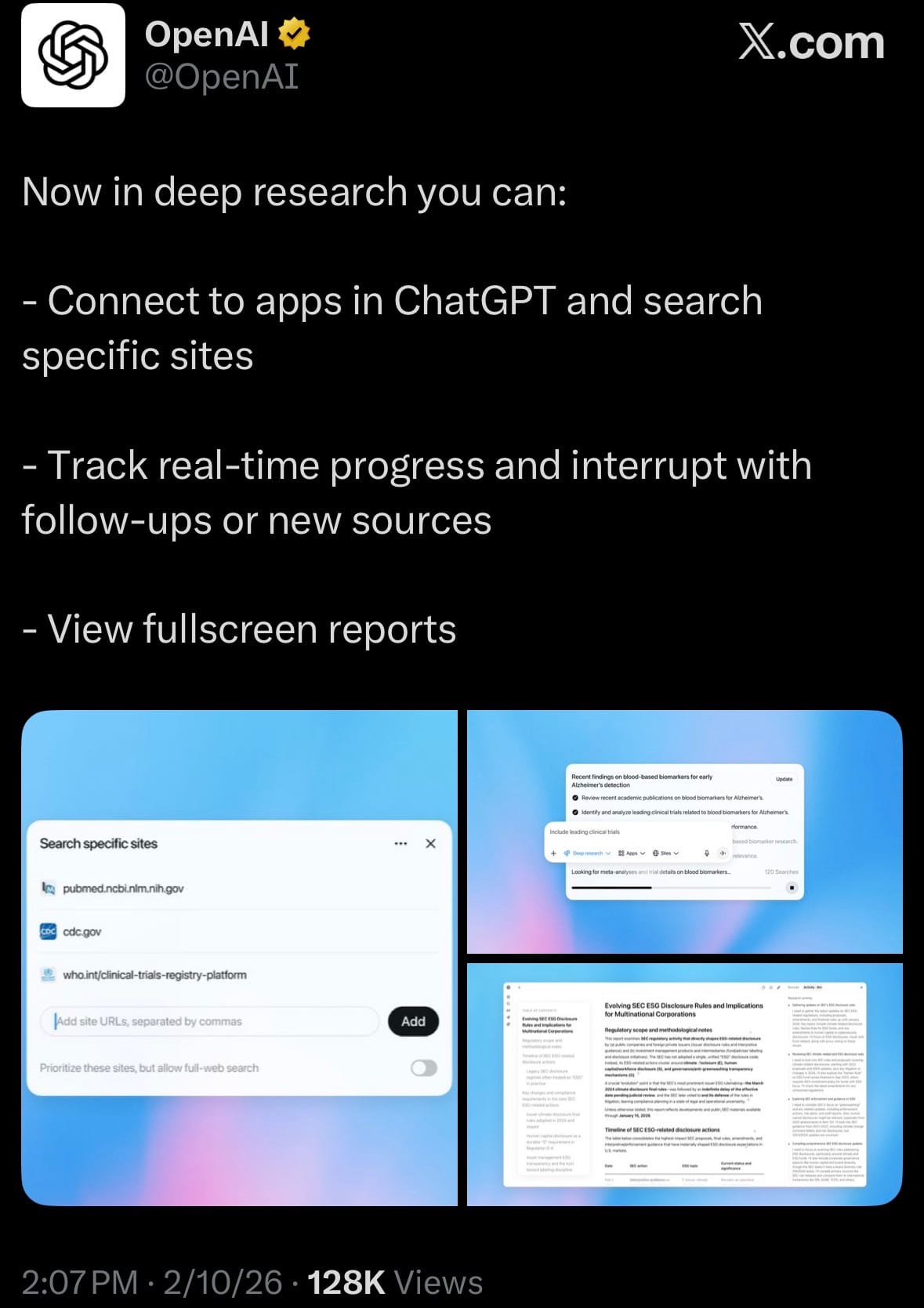
- This allows for more targeted and credible information retrieval from authenticated or industry-standard references. Real-time progress tracking is now supported, so users can follow ongoing research in progress and interrupt it to add follow-up questions, incorporate new sources, or redirect the inquiry as needed. Completed reports can be viewed in a dedicated fullscreen mode with features such as a table of contents, source lists, and improved navigation for easier review of summaries, citations, and any generated visuals.
Statistic:
- Largest public companies on Earth by market capitalization:
- 🇺🇸 NVIDIA: $4.590T
- 🇺🇸 Apple: $4.022T
- 🇺🇸 Alphabet (Google): $3.854T
- 🇺🇸 Microsoft: $3.071T
- 🇺🇸 Amazon: $2.221T
- 🇹🇼 TSMC: $1.877T
- 🇺🇸 Meta Platforms: $1.696T
- 🇸🇦 Saudi Aramco: $1.667T
- 🇺🇸 Broadcom: $1.614T
- 🇺🇸 Tesla: $1.595T
- 🇺🇸 Berkshire Hathaway: $1.079T
- 🇺🇸 Walmart: $1.010T
- 🇺🇸 Eli Lilly: $918.86B
- 🇺🇸 JPMorgan Chase: $866.44B
- 🇰🇷 Samsung: $752.53B
- 🇺🇸 Exxon Mobil: $639.28B
- 🇨🇳 Tencent: $637.52B
- 🇺🇸 Visa: $632.72B
- 🇺🇸 Johnson & Johnson: $574.25B
- 🇳🇱 ASML: $548.69B
- 🇺🇸 Mastercard: $482.80B
- 🇺🇸 Oracle: $459.53B
- 🇺🇸 Costco: $431.18B
- 🇺🇸 Micron Technology: $420.09B
- 🇰🇷 SK Hynix: $406.34B
History:
- The history of trains begins with the search for reliable land transport that could move heavy loads faster than animals and carts. Early rail concepts appeared in 16th-century Europe, where wooden rails guided wagons in mines, reducing friction and increasing haul capacity. The true revolution arrived with steam power. In 1804, Richard Trevithick demonstrated the first steam locomotive, and by 1825, the Stockton and Darlington Railway in England became the world’s first public railway to use steam locomotives for both freight and passengers. The breakthrough moment came in 1830 with the Liverpool and Manchester Railway, proving rail could outperform canals and horse transport in speed, cost, and reliability. Railways rapidly reshaped nations in the 19th century, enabling industrialization, urbanization, and empire-scale logistics. The United States used rail to bind a continent together, culminating in the Transcontinental Railroad (1869); Europe built dense national networks; and Russia began what would become the world’s longest rail system. Trains became strategic infrastructure—moving coal, steel, troops, food, and information—while standard time zones themselves were created to keep rail schedules synchronized.
- The 20th century pushed trains through multiple technological phases. Steam gave way to diesel-electric and electric locomotion, dramatically improving efficiency, reliability, and power. Railways played decisive roles in both World Wars, enabling mass mobilization and industrial-scale logistics. After World War II, many countries faced competition from automobiles and aviation, forcing rail to evolve. Europe and Japan focused on electrification and speed, while freight rail remained dominant in countries like the U.S. The defining leap came with high-speed rail. In 1964, Japan launched the Shinkansen, the world’s first true bullet train, built for dedicated high-speed lines, safety, and punctuality. This set the template for modern high-speed rail: streamlined electric trains, advanced signaling, grade-separated tracks, and precision scheduling. France followed with the TGV in the 1980s, proving high-speed rail could compete directly with air travel on medium-distance routes. Germany, Spain, Italy, and others developed their own high-speed systems, turning rail into a backbone of regional mobility across Europe.
- Today, high-speed rail is dominated by China, which has built the largest and fastest-expanding network in history since the late 2000s, spanning tens of thousands of kilometers and connecting nearly every major city. China operates multiple train families routinely running at 300–350 km/h, supported by massive state investment, domestic manufacturing, and integrated planning. Japan remains the global benchmark for safety and reliability, with decades of accident-free high-speed operation, while European systems lead in cross-border integration and signaling sophistication. Meanwhile, freight rail continues to dominate heavy logistics in the U.S., Russia, and parts of Asia. The future of trains is moving toward ultra-high-speed rail, automation, AI-driven traffic control, and experimental concepts like maglev, which eliminates wheel-rail contact entirely. From wooden mine rails to continent-spanning bullet train networks, railways have evolved into one of humanity’s most efficient and strategic transportation systems—quietly shaping economies, military logistics, energy use, and national power.
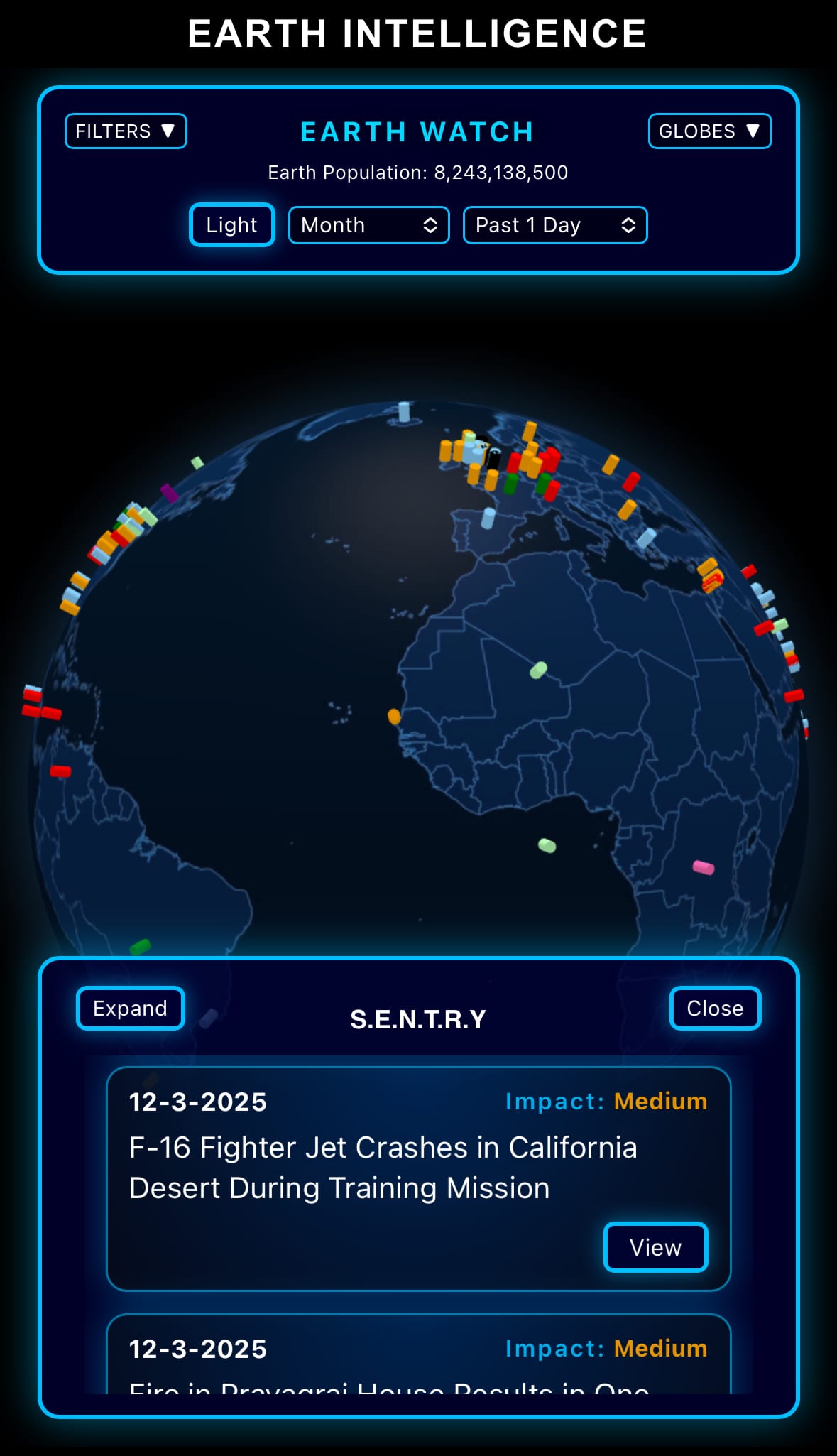
Image of the day:

Thanks for reading! Earth is complicated, we make it simple.
- Click below if you’d like to view our free EARTH WATCH globe:
- Download our mobile app:



Click below to view our previous newsletters:

Support/Suggestions Email:
earthintelligence@earthintel.news




