Wednesday☕️

Trending:
- On February 16, 2026, late in the day, Joint Task Force Southern Spear—under the direction of U.S. Southern Command (SOUTHCOM) commander Marine Gen. Francis L. Donovan—conducted three airstrikes on vessels operated by Designated Terrorist Organizations. Intelligence indicated the vessels were transiting known narco-trafficking routes and engaged in narco-trafficking activities. The strikes resulted in the deaths of 11 individuals described as male narco-terrorists: four on the first vessel and four on the second in the Eastern Pacific, and three on the third in the Caribbean. No U.S. military personnel were harmed.
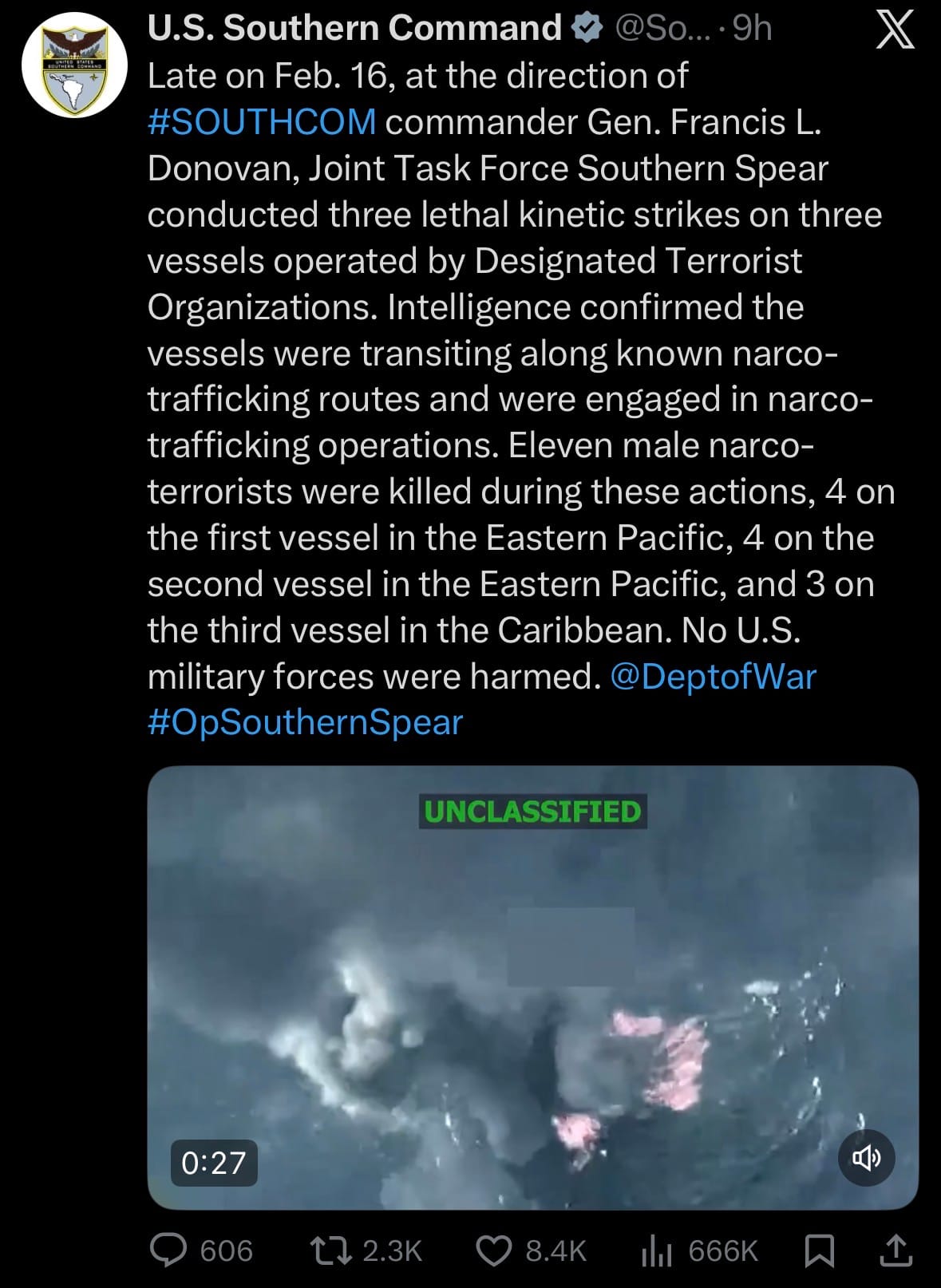
- The actions were part of ongoing Operation Southern Spear, aimed at disrupting illicit narcotics trafficking linked to designated terrorist groups. U.S. Southern Command released details via official channels, including a press release and social media, emphasizing the strikes occurred in international waters with confirmed intelligence support.
Economics & Markets:
- Yesterday’s U.S. stock market:

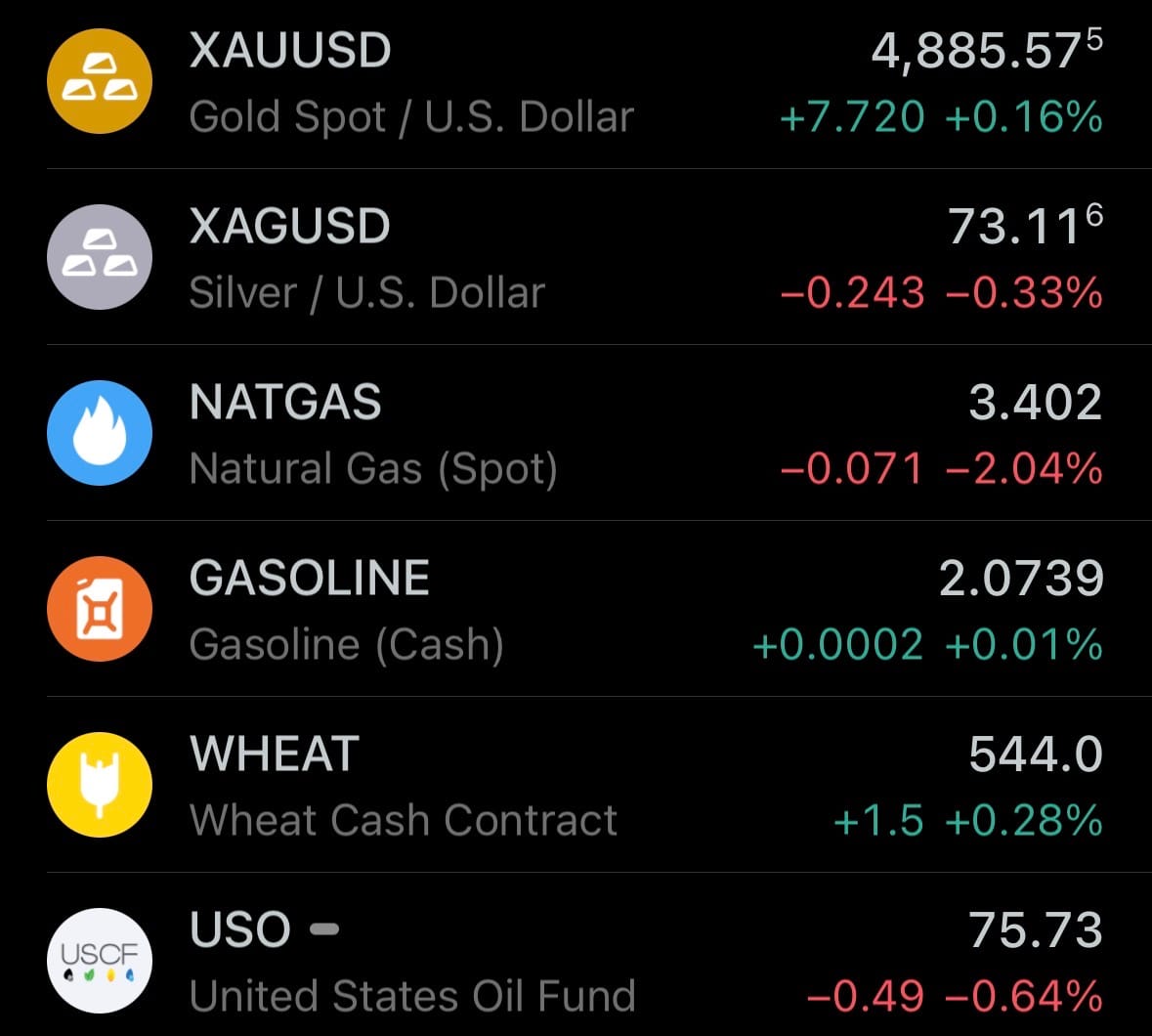
- Yesterday’s commodity markets:
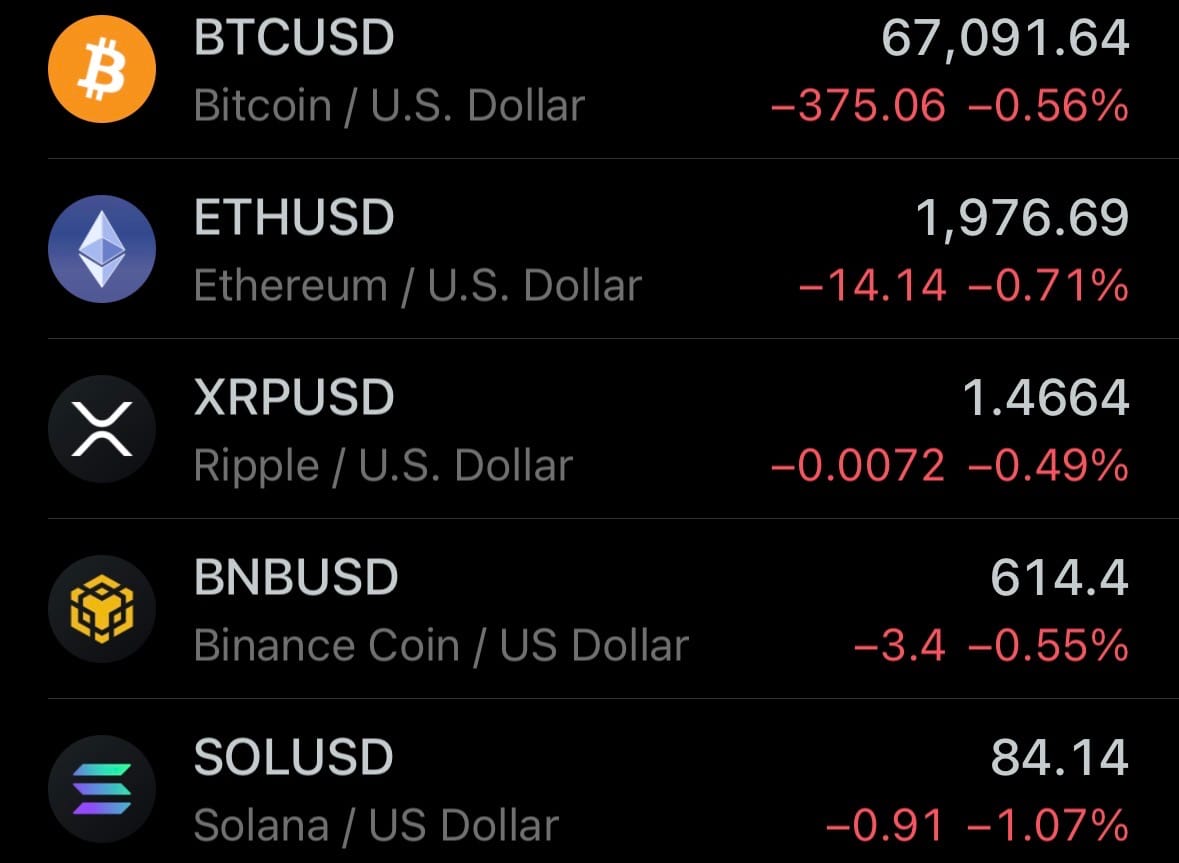
- Yesterday’s crypto market:
Cyber:
- On February 17, 2026, YouTube experienced a widespread outage beginning around 7:45 p.m. EST (4:45 p.m. PT), with user reports surging sharply by approximately 8 p.m. EST. Outage tracking site Downdetector recorded over 300,000 complaints in the U.S., peaking higher in some updates, primarily related to the app (about 56% of reports), website loading issues (around 20%), and login problems. Many users encountered a "something went wrong" error, with difficulties accessing the homepage, subscriptions feed, and video playback, though some individual videos remained viewable in limited cases. The disruption also affected YouTube TV to a lesser extent.
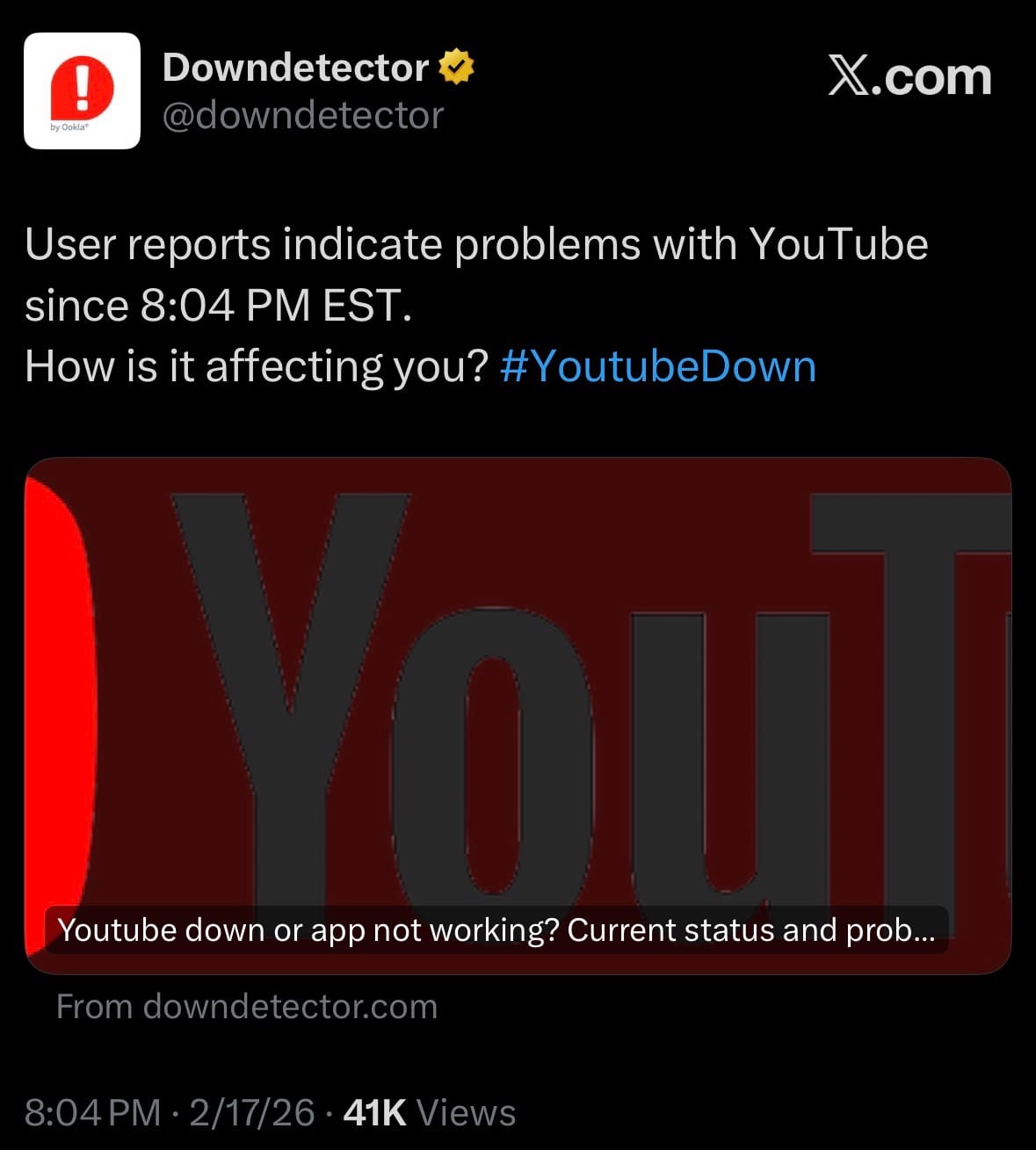
- The outage appeared widespread across the U.S. and potentially global, though YouTube (owned by Alphabet) had not issued an official statement or confirmed the cause as of late evening reports. No resolution timeline was provided in initial coverage, and the issue was ongoing for many users into the night. This marks a notable service interruption for the platform, which relies on stable access for streaming and content delivery.
Science & Technology:
- On February 17, 2026, Tesla announced that the first production Cybercab—a purpose-built, two-door robotaxi without a steering wheel or pedals—rolled off the assembly line at Gigafactory Texas (Giga Texas) in Austin.

- This marks the start of initial production for the autonomous vehicle, ahead of the previously stated volume production target in April 2026. The Cybercab is designed for Tesla's robotaxi service, with officials noting it represents progress toward scaling autonomous transportation, though full regulatory approval and operational deployment timelines remain pending.
Statistic:
- Largest public companies on Earth by market capitalization:
- 🇺🇸 NVIDIA: $4.503T
- 🇺🇸 Apple: $3.878T
- 🇺🇸 Alphabet (Google): $3.663T
- 🇺🇸 Microsoft: $2.949T
- 🇺🇸 Amazon: $2.159T
- 🇹🇼 TSMC: $1.888T
- 🇸🇦 Saudi Aramco: $1.640T
- 🇺🇸 Meta Platforms: $1.617T
- 🇺🇸 Broadcom: $1.576T
- 🇺🇸 Tesla: $1.540T
- 🇺🇸 Berkshire Hathaway: $1.086T
- 🇺🇸 Walmart: $1.027T
- 🇺🇸 Eli Lilly: $977.36B
- 🇰🇷 Samsung: $840.88B
- 🇺🇸 JPMorgan Chase: $836.08B
- 🇺🇸 Exxon Mobil: $616.50B
- 🇺🇸 Visa: $616.00B
- 🇨🇳 Tencent: $612.26B
- 🇺🇸 Johnson & Johnson: $586.40B
- 🇳🇱 ASML: $551.08B
- 🇺🇸 Mastercard: $465.79B
- 🇺🇸 Micron Technology: $449.95B
- 🇺🇸 Costco: $449.30B
- 🇺🇸 Oracle: $442.52B
- 🇰🇷 SK Hynix: $421.72B
History:
- Tesla’s history is the story of electric mobility evolving from a marginal curiosity into one of the central industrial revolutions of the 21st century. The company was founded in 2003, emerging from the realization that lithium-ion batteries—already powering laptops—could be scaled into high-performance vehicle packs. Elon Musk joined early as a major investor and became the company’s defining leader, pushing Tesla toward an aggressive mission: make electric vehicles not just viable, but superior. The first breakthrough was the Tesla Roadster (2008), which proved an EV could deliver real range and sports-car acceleration, destroying the stereotype of electric cars as slow compliance machines. Tesla then went public in 2010, gaining capital to scale, and delivered its true industry shockwave with the Model S (2012)—a long-range, software-defined luxury sedan that won major awards and introduced the modern EV template: instant torque, massive battery capacity, and continuous over-the-air updates. The Model S wasn’t just a car, it was a computing platform with wheels, signaling that the future of vehicles would be as much software as steel.
- The 2010s became Tesla’s industrial crucible. The company built the Supercharger network, solving the infrastructure problem that had crippled EV adoption for decades. It expanded with the Model X (2015) and then launched its most important scaling weapon: the Model 3 (2017), designed for mass production and global volume. This era was defined by “production hell,” where Tesla nearly collapsed under manufacturing complexity before emerging as a serious high-output automaker. Gigafactories became central to Tesla’s strategy: vertical integration of batteries, drivetrains, and assembly at unprecedented scale. Tesla also pushed autonomy early, introducing Autopilot (2014 onward) and later the more ambitious Full Self-Driving program, framing the car as an AI system in training. Even as FSD remained incomplete and controversial, it reinforced Tesla’s core thesis: transportation is converging with machine intelligence. By the end of the decade, Tesla was no longer a startup—it was the company that forced every major automaker on Earth to electrify or fall behind.
- Today, Tesla’s roadmap extends far beyond the original EV revolution into a broader vision of autonomous fleets, robotics, and energy infrastructure. The Model Y became one of the world’s best-selling vehicles, while Tesla expanded into grid-scale power through Megapack battery systems and home energy products like Powerwall. Its next-generation platform is aimed at radical cost reduction and autonomous deployment: the long-discussed Cybercab/Robotaxi concept represents Tesla’s push toward a future where vehicles are not personally owned machines but networked autonomous assets—cars as services operating continuously like AI-driven logistics nodes. Alongside this, Tesla has developed the Cybertruck, a high-profile rethinking of utility vehicles, and is building the Optimus humanoid robot program as a longer-term bet that Tesla’s real advantage is manufacturing intelligence, not just automotive design. Tesla’s dominance comes from stacking batteries, software, charging, AI, and industrial scale into one unified system. Its history is not simply the rise of an automaker—it is the emergence of a new technological-industrial empire trying to redefine transportation, energy, and autonomy as one integrated platform for the future.
Image of the day:

Thanks for reading! Earth is complicated, we make it simple.
- Click below if you’d like to view our free EARTH WATCH globe:
- Download our mobile app:



Click below to view our previous newsletters:

Support/Suggestions Email:
earthintelligence@earthintel.news




